Blogs
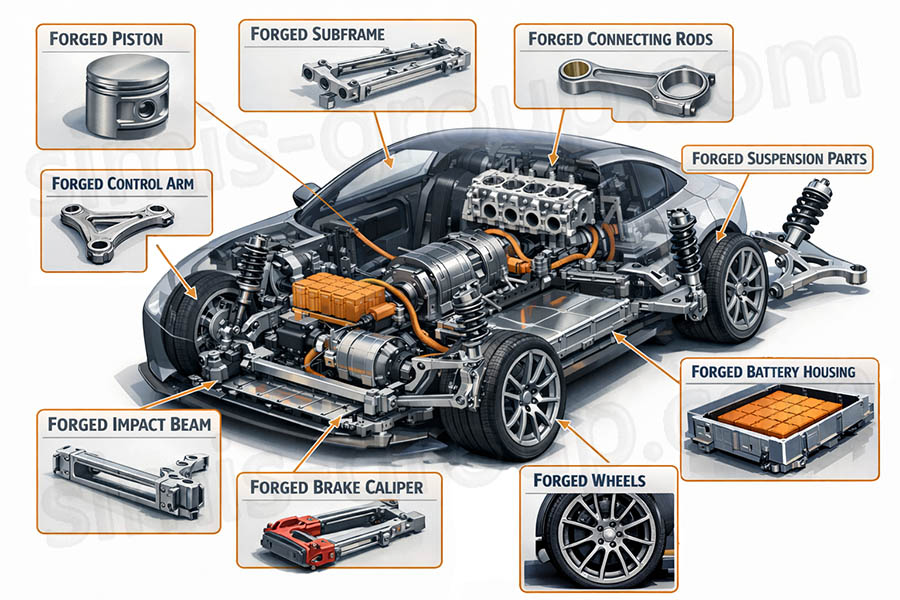
Forged aluminum has established itself as a core technology for EVs / hybrid vehicle and auto modification by addressing the most critical challenges in these fields: lightweighting for extended EV range, high strength for safety and performance, and durability for harsh operating conditions. Unlike forged steel, cast steel, and cast aluminum, it strikes a balanced chord between performance and practicality, making it irreplaceable for key components.

Hot forging utilizes high temperatures to improve the ductility of metals, reduce deformation forces, and allow materials to be smoothly formed into complex geometries. Simultaneously, the recrystallization process eliminates strain hardening and refines the grain structure, resulting in uniform mechanical properties and higher toughness. Compared to cold forging and warm forging, hot forging offers significant advantages in machining large/complex parts and achieving high toughness, while requiring less deformation force.
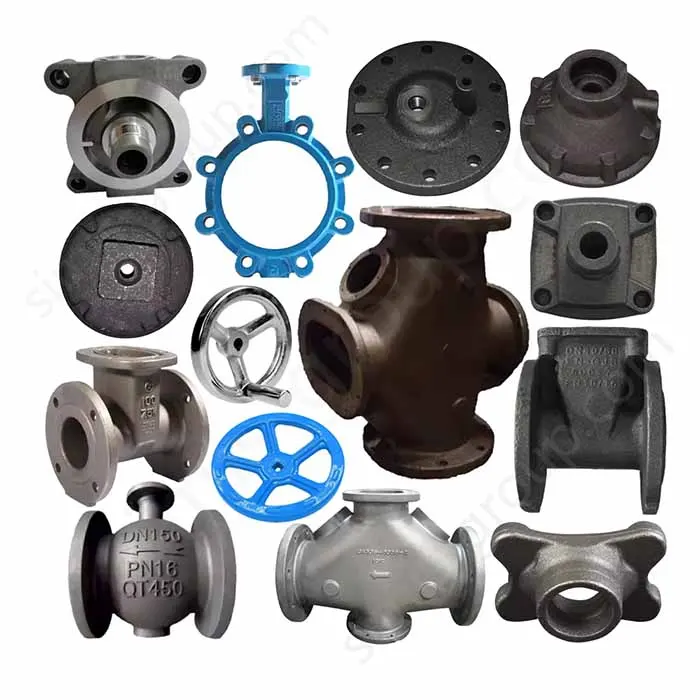

For buyers, choosing a reliable OEM custom valve and valve parts manufacturer is far more than a routine purchasing task. OEM cooperation involves complex challenges including design customization, mold development, precision manufacturing, quality consistency, certification compliance, and intellectual property protection.
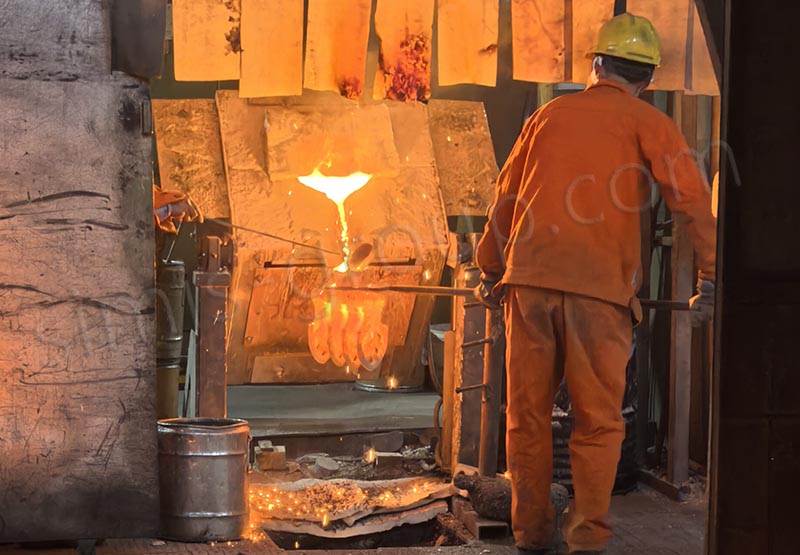

The superior surface finish of investment castings is due to precision in every step, from the wax pattern to the ceramic shell, to pouring and cooling. The absence of parting lines, the absence of sand particles, and the smooth flow of molten metal all contribute to a superior surface finish. While investment casting is costly and suitable for high-value-added parts.

Most commonly used cast iron and cast steel are strongly magnetic, but by adjusting the alloy composition and performing specific heat treatment processes, the microstructure of steel and iron can be changed, making them lose their magnetism (weak magnetism). For example, austenitic cast iron and austenitic stainless steel castings respond very weakly to magnetic fields and cannot be attracted by ordinary magnets.
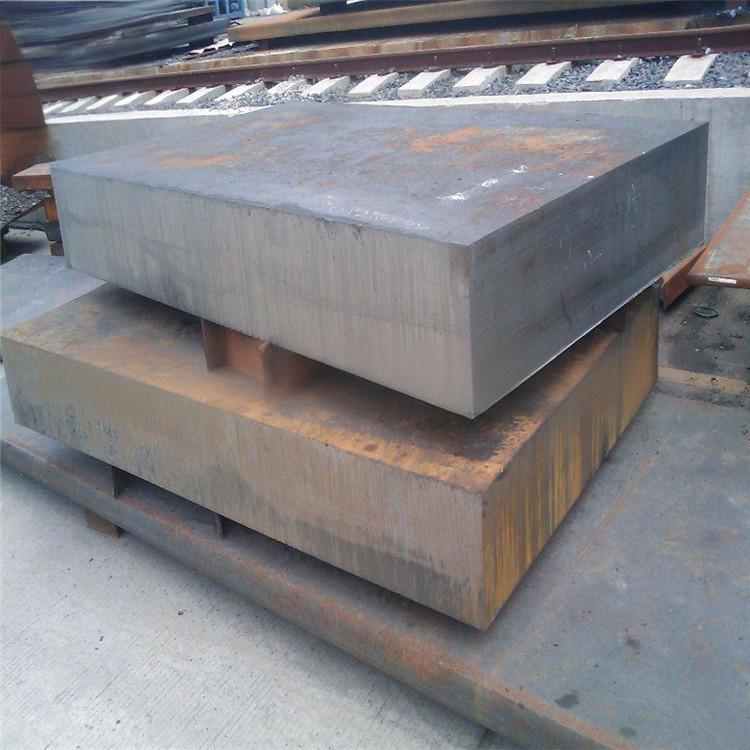

4130 Chromoly steel is unsuitable for casting due to its narrow solidification range, high hot crack sensitivity, and poor as-cast microstructure. However, forging can help optimize its microstructure and properties, improve economic efficiency, and enhance quality and reliability. Using various forging processes, 4130 Chromoly steel plays an important role in the manufacture of key components such as aerospace landing gear, high-performance racing connecting rods, oil drilling tools, and heavy machinery shafts.
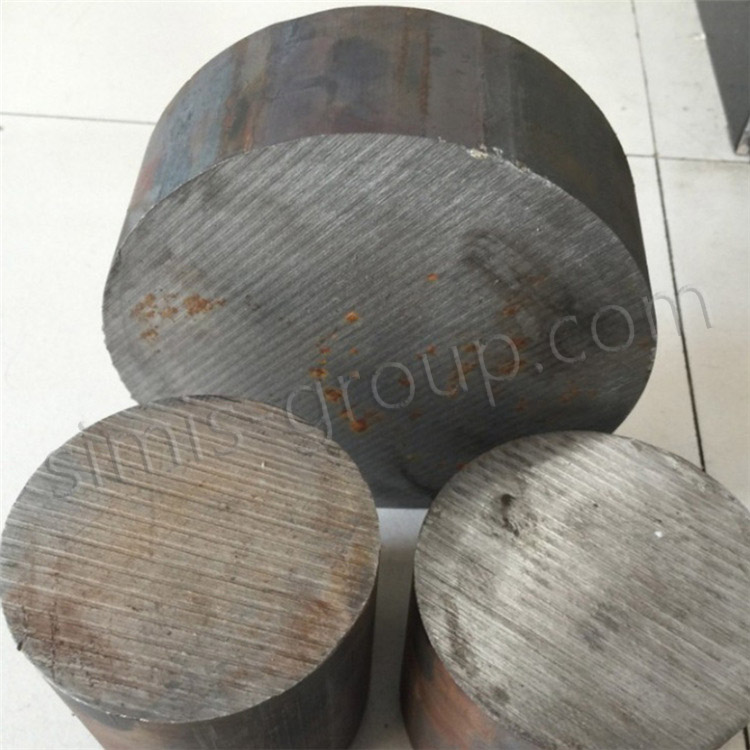

FCD400 is a ductile iron material with excellent comprehensive properties. It has good casting properties, mechanical properties and processing properties. It is particularly suitable for the production of castings with complex shapes and high strength and toughness requirements, such as automotive parts, piping systems, mechanical structural parts, etc.

Shafts, as core components of mechanical transmission systems, have a direct impact on their reliability and service life. Approximately 38% of global industrial shafts are forged, while 45% are cast. An analysis of the technical characteristics, microstructural evolution, and mechanical properties of the two processes reveals that forged shafts maintain their performance advantages in critical power transmission applications, while cast shafts offer significant economic advantages in the production of large, complex structural parts.
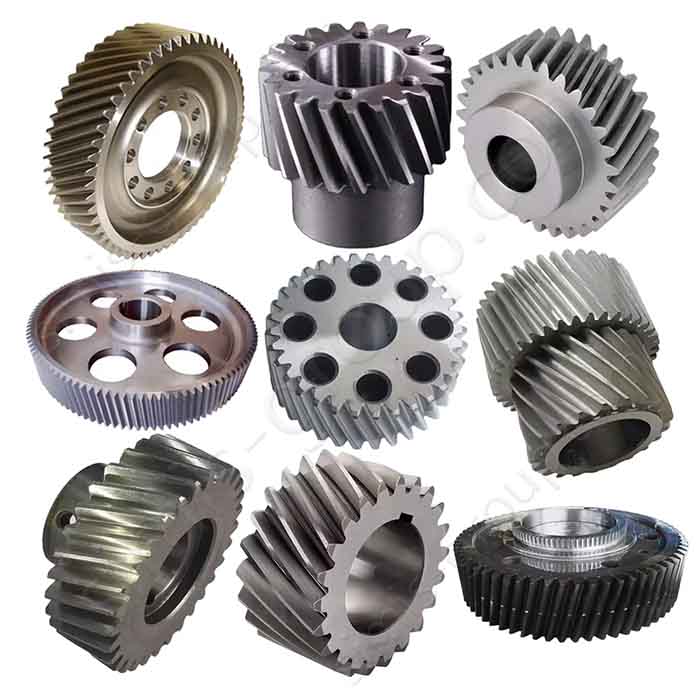

In the field of industrial manufacturing, casting and forging are the two most important gear forming processes. Casting gears have obvious advantages in the production of large-size and complex structural parts, while forged gears perform better in high-load and high-precision applications.
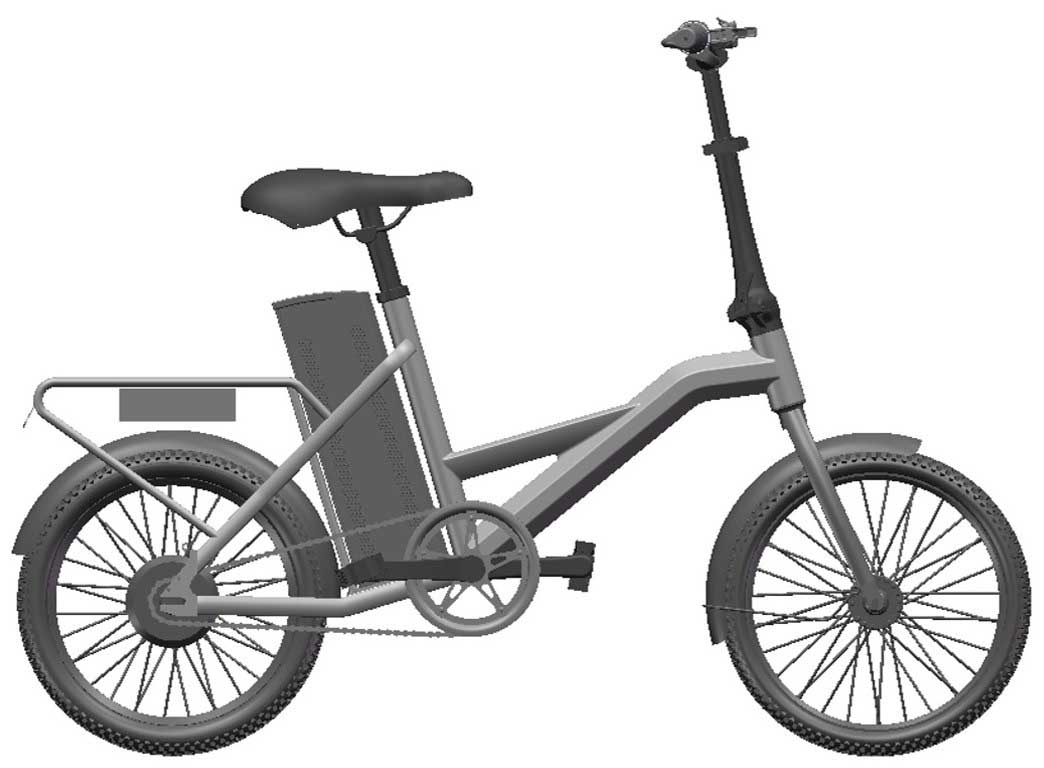

Forged aluminum is an aluminum alloy material strengthened through plastic deformation. Its core advantage lies in the significant improvement of the metal's microstructure through machining, resulting in mechanical properties superior to those of cast aluminum. Forged aluminum has gradually become the "skeleton" and "joint" of mid-range and high-end electric bicycles.
