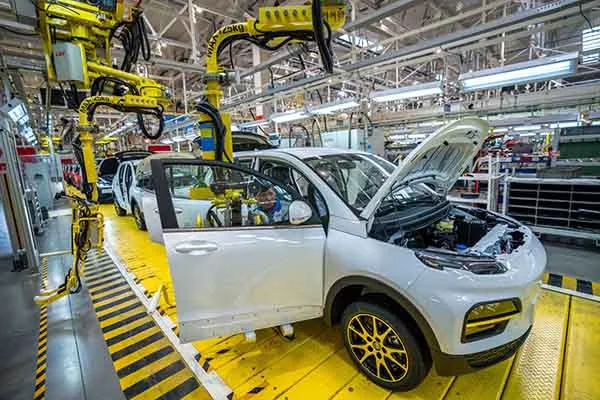
Die Casting Foundry for OEM Custom Manufacturing
Die Casting Factory Introduction
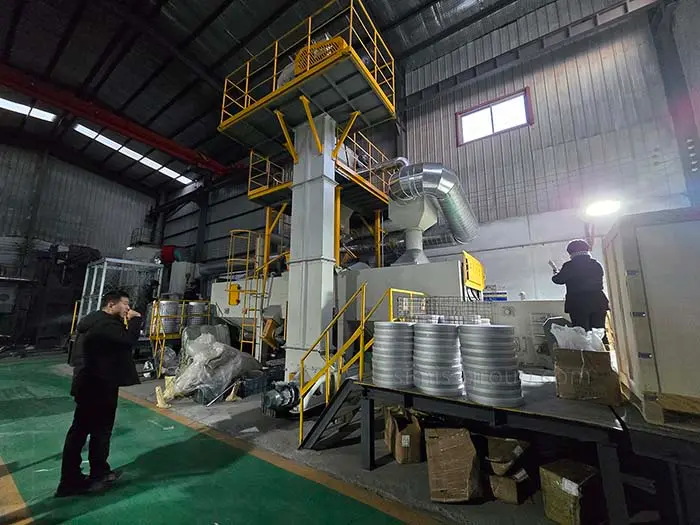
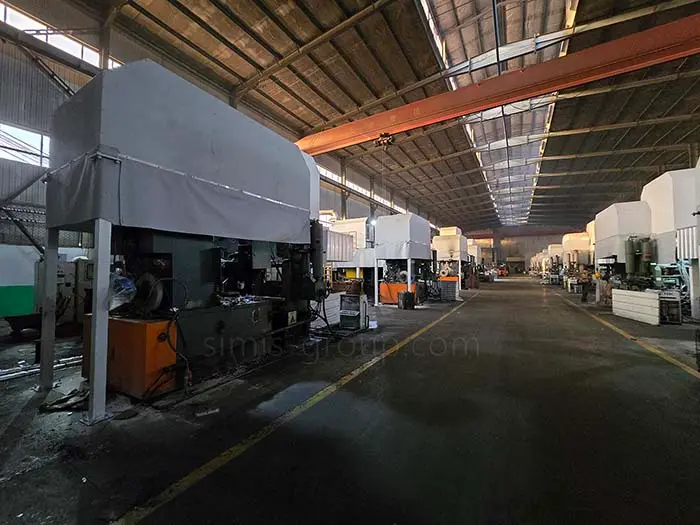
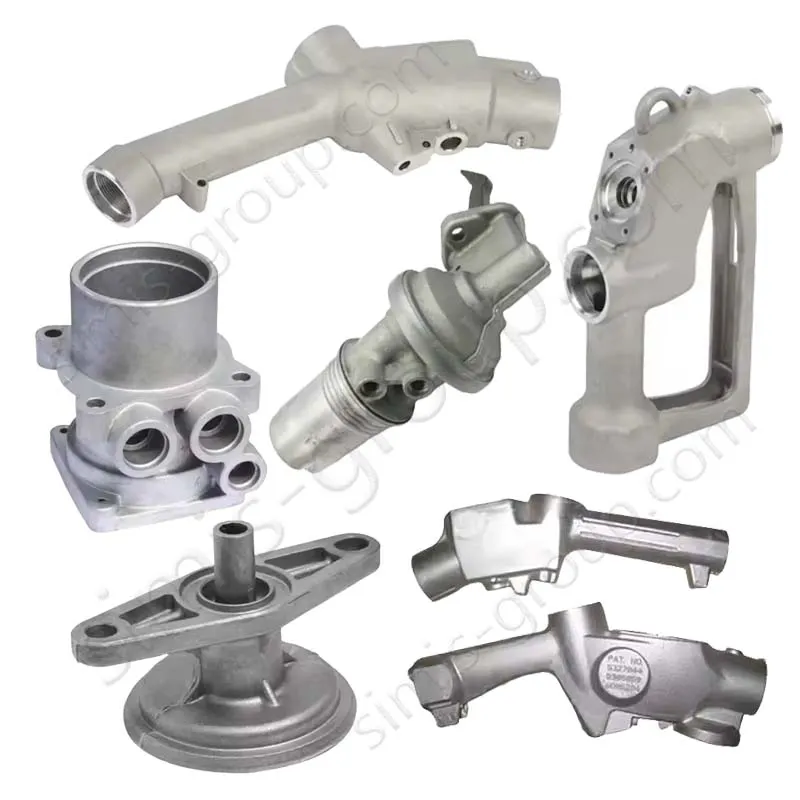
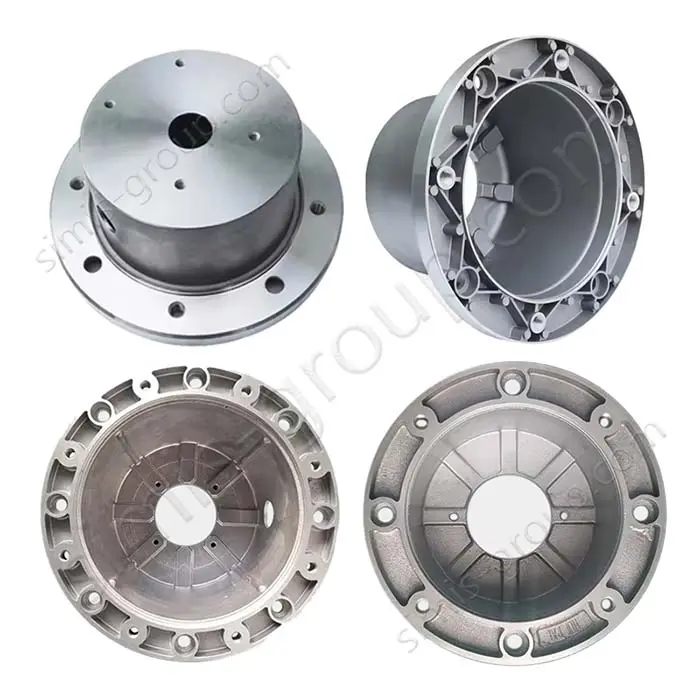
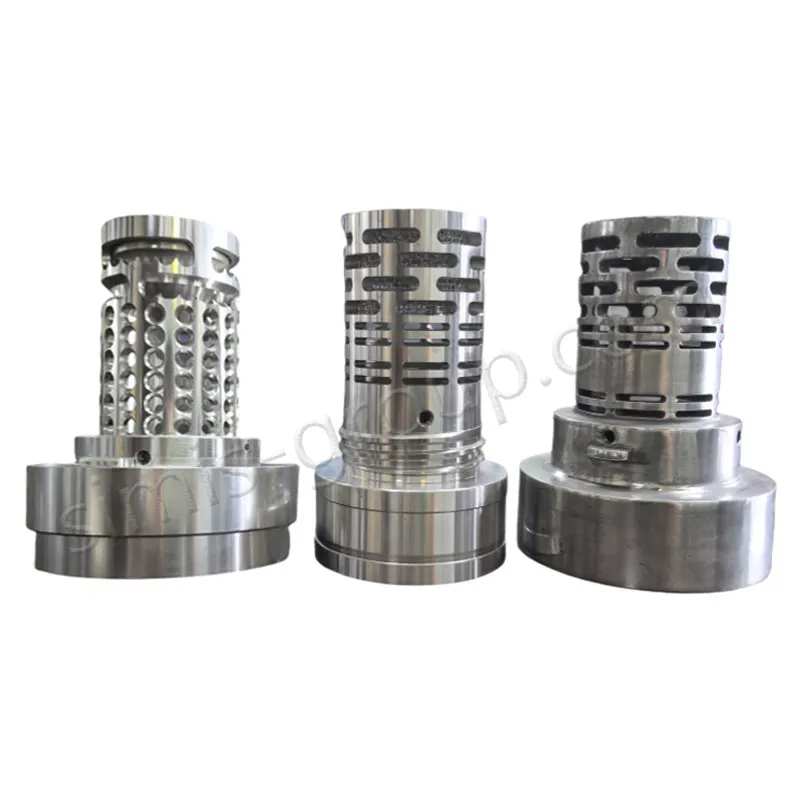
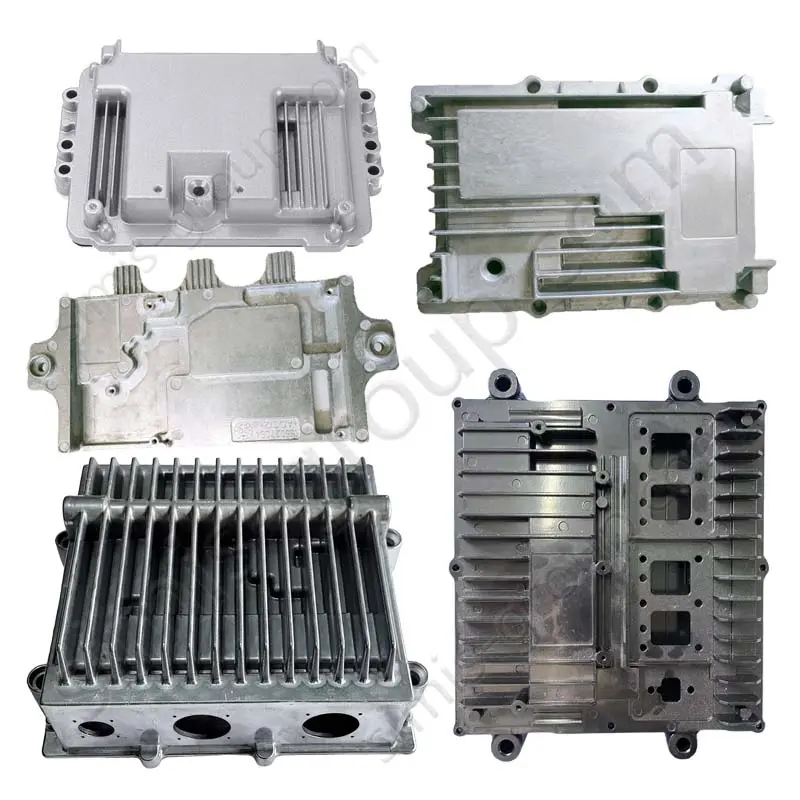
SIMIS Die Casting Foundry specializing in aluminum and zinc alloy die castings. The foundry integrates mold design and manufacturing, alloy melting, die casting production, finishing, surface treatment, and precision machining, offering complete solutions for complex and high-performance components.
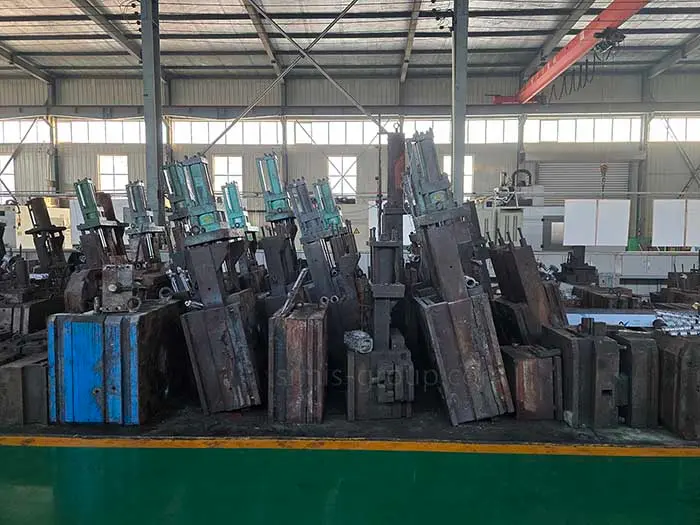
Cold-Chamber Die Casting Machines: 280T, 500T, 800T, 1250T, 1600T
Hot-Chamber Die Casting Machines: 88T, 160T, 280T
Automatic Pouring and Extraction Robots
Central Alloy Melting and Holding Furnaces
Mold Temperature Control Units (Oil and water systems)
Shot Blasting, Vibratory Deburring, and Polishing Lines
Clamping Force: 88T – 1600T
Casting Weight: 0.01 kg – 25 kg
Maximum Dimensions: 800 mm × 600 mm × 300 mm
Minimum Wall Thickness: 0.8 - 1.2 mm
Surface Roughness: Ra 0.8 - 1.6 μm
Dimensional Accuracy: CT3 – CT6
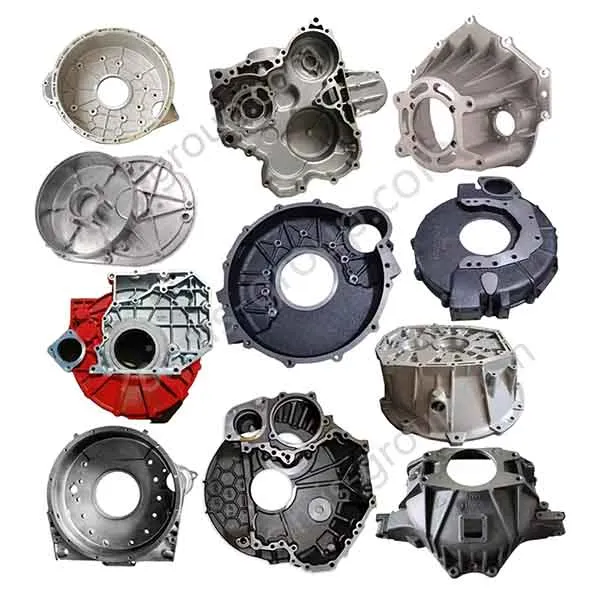
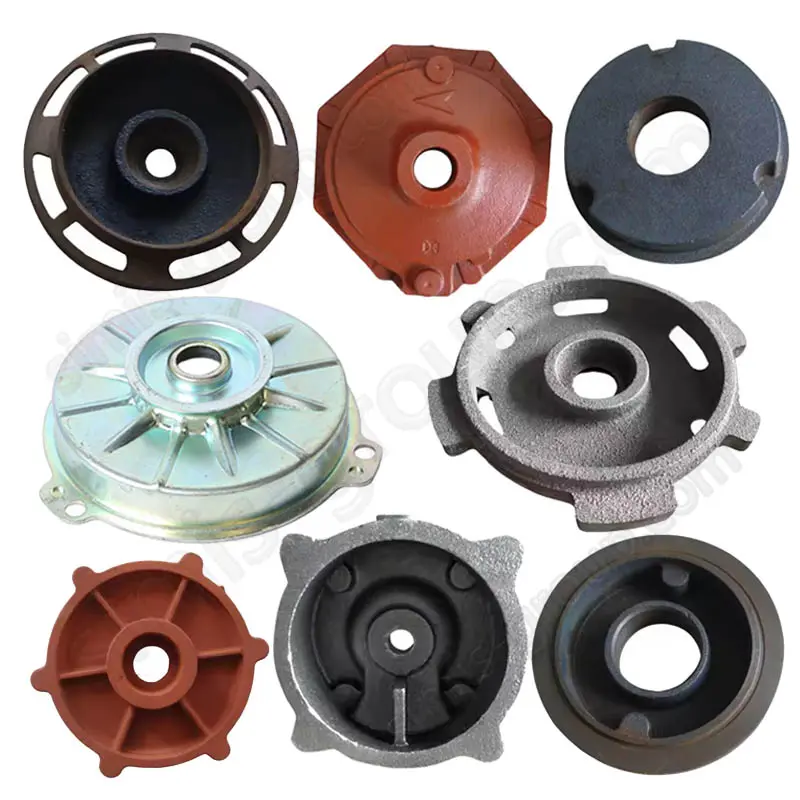
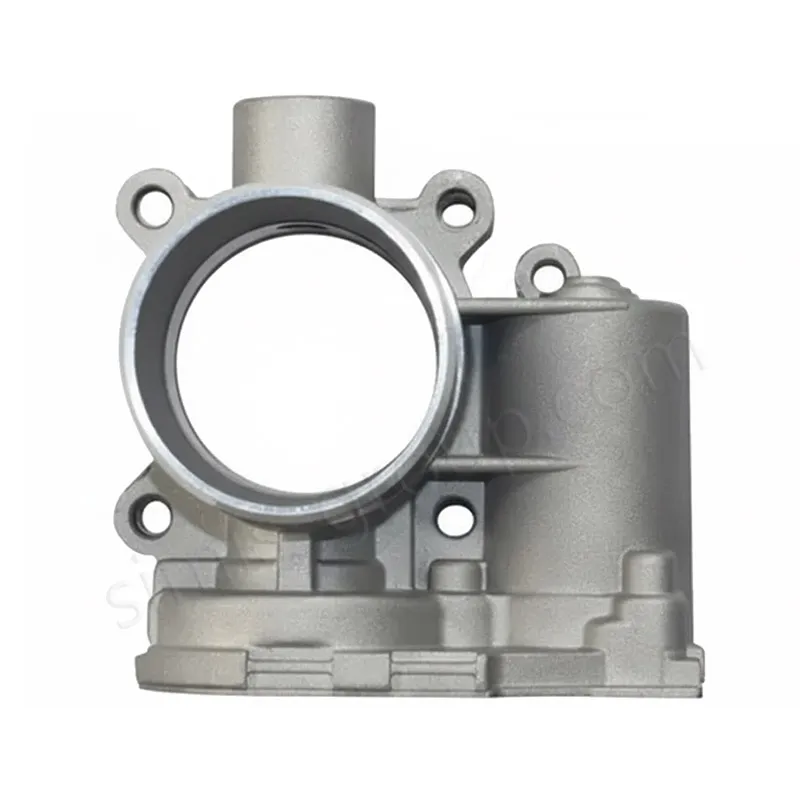
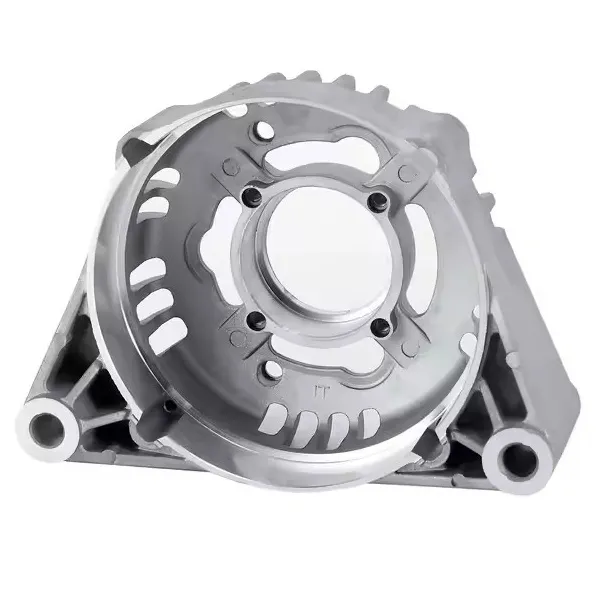
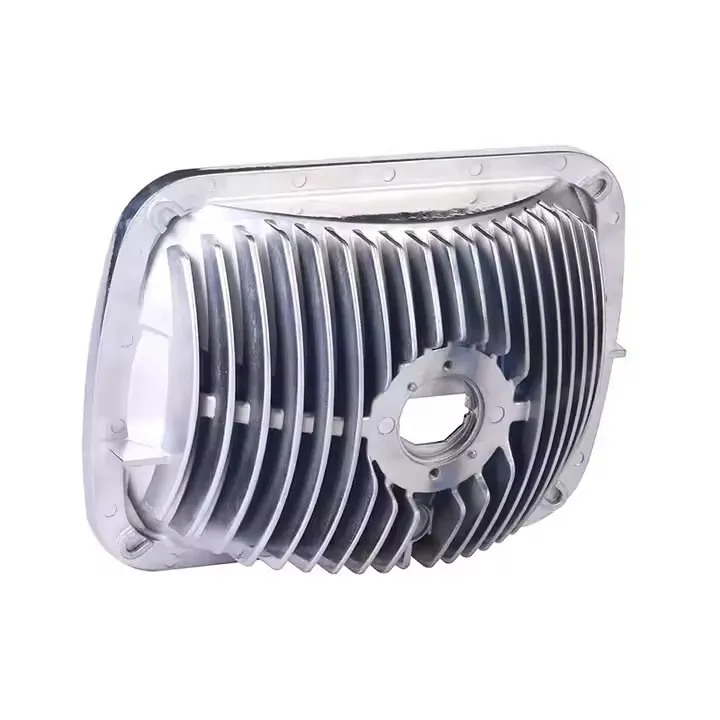
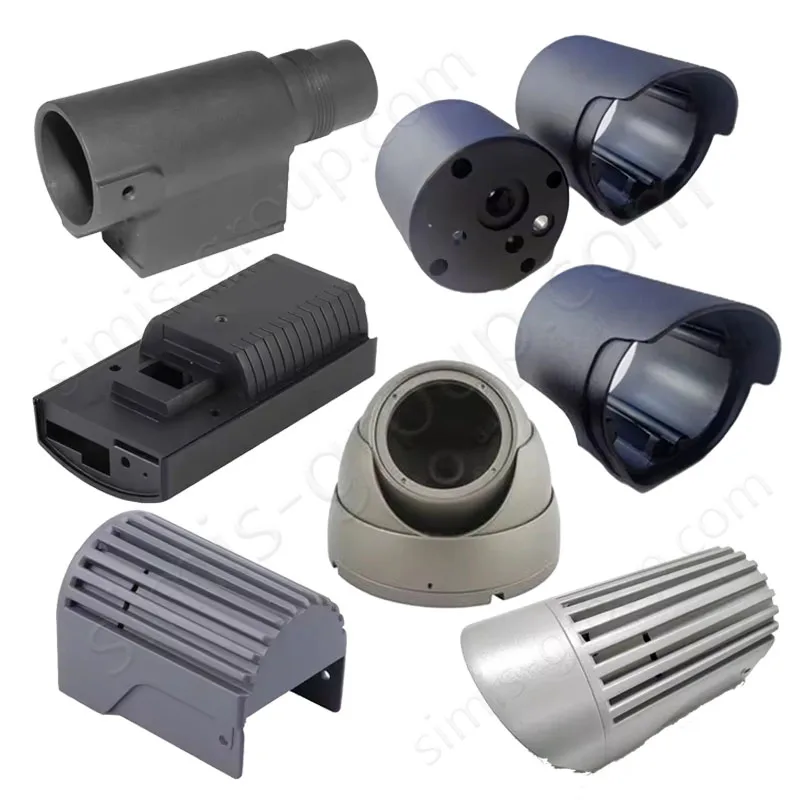
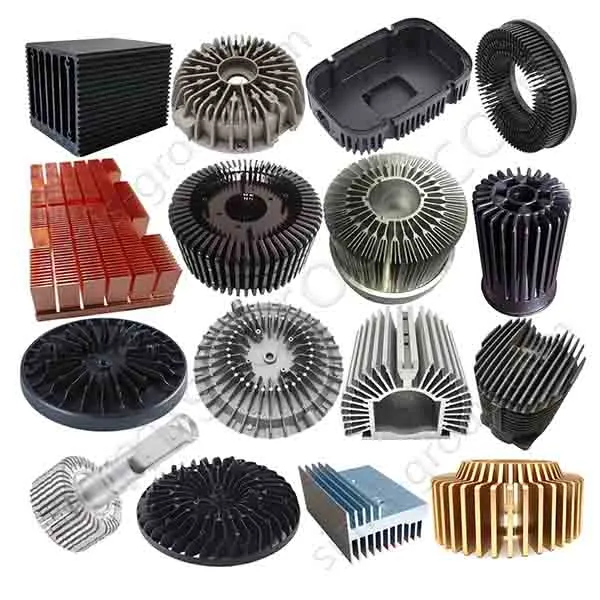
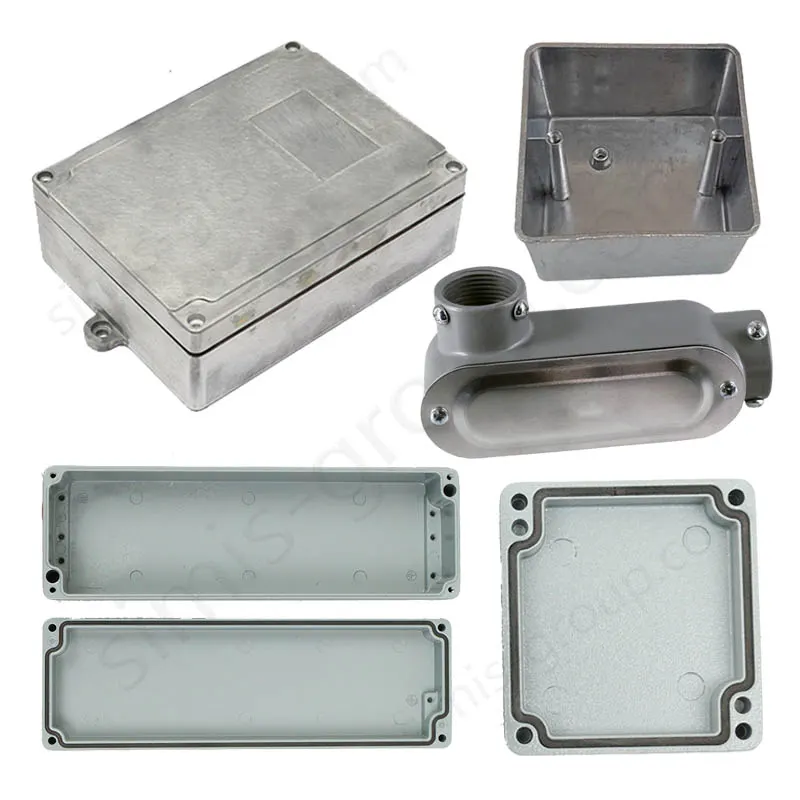
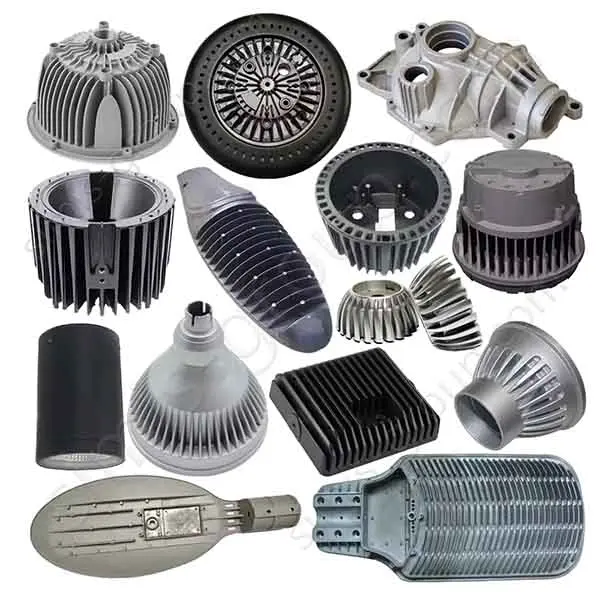
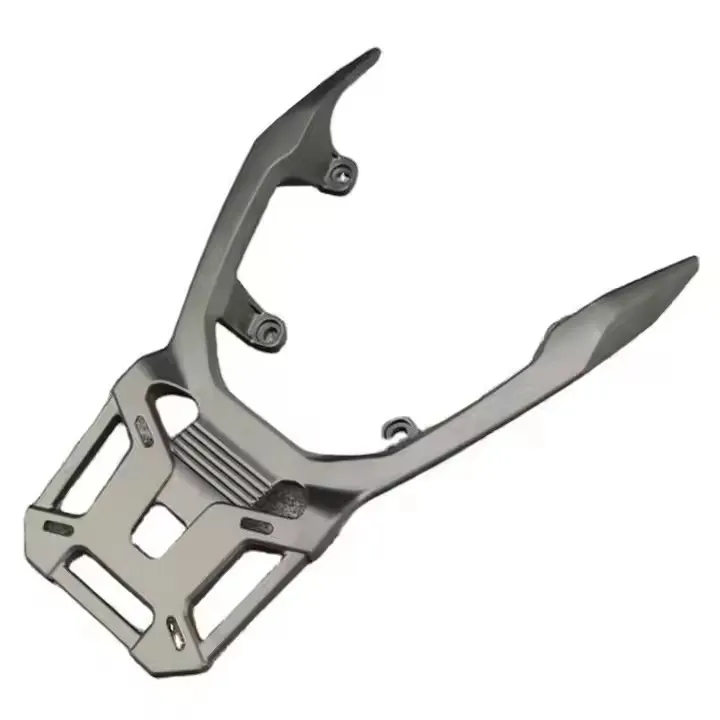
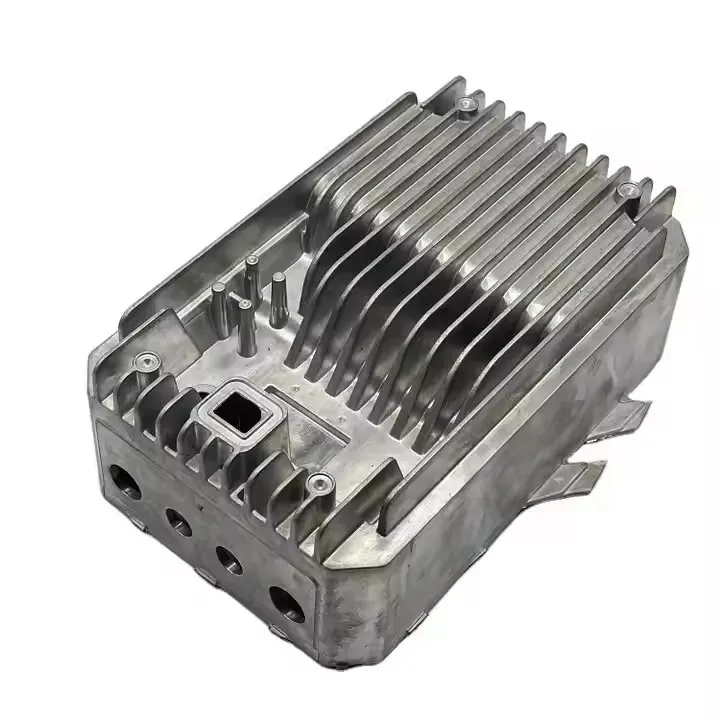
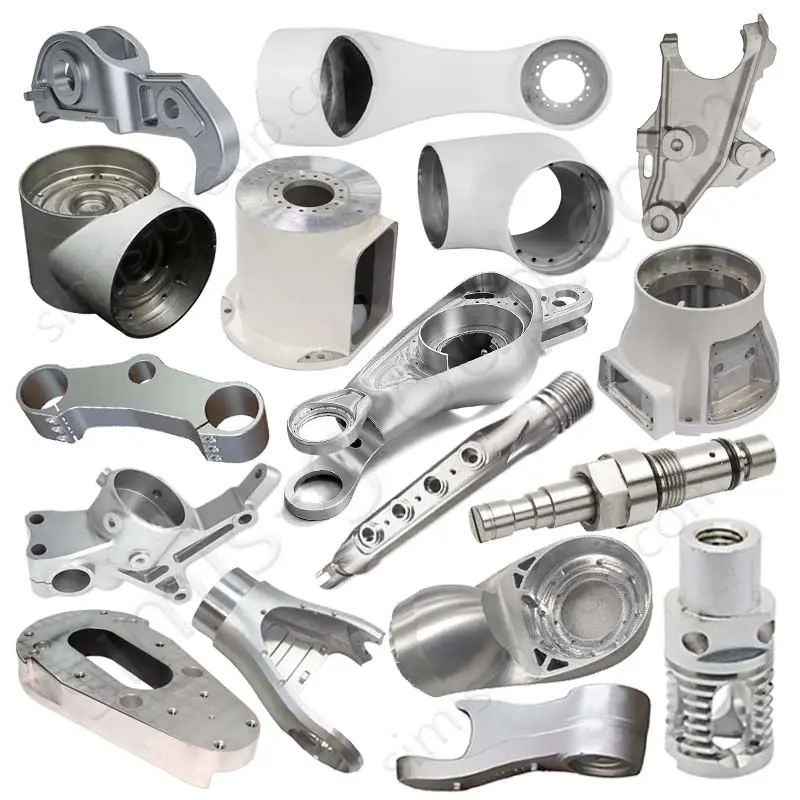
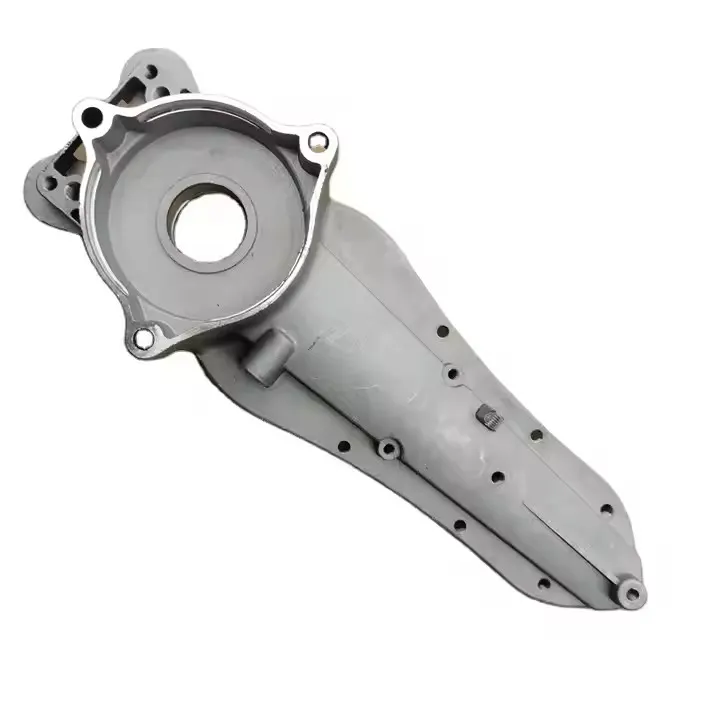
OEM Custom Die Casting Parts
Pressure Die Casting Process for Custom Metal Parts
Die Casting process overview
The die-casting process is to quickly inject molten metal into a precision mold under high pressure to cool and solidify it, so that the die-casting parts have clear details and stable precision. It is suitable for mass production of aluminum alloy, zinc alloy and other parts with complex shapes, precise dimensions and smooth surfaces.
1. Die-casting mold design
Die-casting molds are designed according to the product's size, structure, precision requirements and material properties to ensure the quality and production efficiency of castings.
2. Mold manufacturing
Die-casting molds are made of high-strength steel (such as H13, P20, etc.). Through precision machining, heat treatment and surface polishing, the durability, precision and surface quality of the mold are guaranteed.
3. Metal smelting and alloy preparation
Smelting: Select a metal material smelting furnace to heat to the melting temperature of the alloy so that the metal is completely melted into a liquid state.
Alloy preparation: According to the required alloy formula, necessary alloy elements are added to the molten metal to ensure that the metal composition meets the design requirements.
4. Die casting
The molten metal is injected into the preheated die-casting mold cavity through the die-casting machine injection system. Under extremely high pressure, the metal is quickly injected into the mold, so that the molten metal fills every detail of the mold, ensuring that the details of the casting are clear and there are no holes.
5. Cooling and solidification
The metal injected into the mold is rapidly cooled and solidified with the help of the mold cooling system to form the final shape, which depends on the size and complexity of the die casting.
6. Demolding and cleaning
After the metal cools and solidifies, open the mold and remove the casting from the mold.
After the die casting is demolded, there will be some burrs, overflows and residual metal, which can be cleaned by vibration cleaning machine, air sand cleaning, cutting, deburring and other methods to improve the surface quality and dimensional accuracy of the die casting.
7. Post-processing
Surface treatment: polishing, spraying, sandblasting, anodizing and other casting surface treatments to improve the beauty, corrosion resistance and wear resistance of the casting.
Heat treatment: high-strength aluminum alloy or other alloy castings may require heat treatment (such as aging treatment, annealing treatment, etc.) to improve the mechanical properties and hardness of the die casting.
8. Quality inspection
The die casting is comprehensively measured by quality inspection methods such as surface quality inspection, dimensional inspection, and mechanical property test to ensure that the die casting meets the requirements of the design drawings.




Available Materials for Die Casting Applications
What metal parts can be cast in Simis die casting factory?
Die casting is a high-pressure permanent mold casting process, particularly suited for metals with low melting points and good fluidity, enabling the production of thin-walled, complex, and high-volume components with minimal machining. Simis Die casting is primarily applied to aluminum alloys, magnesium alloys, zinc alloys, and selected copper alloys, where high repeatability and surface finish are critical.
| Material Category | Why It Is Suitable for Die Casting | Simis Die Casting Foundry Typical Applications | Simis Die Casting Foundry Common Grades |
| Aluminum Alloys | Excellent fluidity and low melting temperature allow high-speed mold filling and replication of fine details. Die casting produces thin-walled components with superior dimensional accuracy and surface finish, suitable for high-volume production | Automotive engine and gearbox components, housings, brackets, structural parts | ASTM A380 series, A383, EN AC-43000 (AlSi9Cu3), EN AC-46000 (AlSi12Cu) |
| Magnesium Alloys | Extremely low melting temperature and good flowability enable safe, precise, high-speed injection into steel molds. Die casting supports lightweight, thin-walled components with high repeatability | Aerospace and automotive structural brackets, housings, electronic components | AZ91D, AM60, AZ31 |
| Zinc Alloys | Very low melting point and excellent fluidity allow complex geometries with fine detail and very thin walls. High-volume production with tight tolerances is economically feasible | Small mechanical components, fasteners, decorative hardware, precision housings | Zamak 3, Zamak 5, ZA-8 |
| Copper Alloys (selected) | Certain low-melting copper-based alloys with good fluidity can be die-cast for small, precision components. Mold and process control is critical to avoid porosity | Bushings, connectors, small pump or valve components | C83600, C84500 |