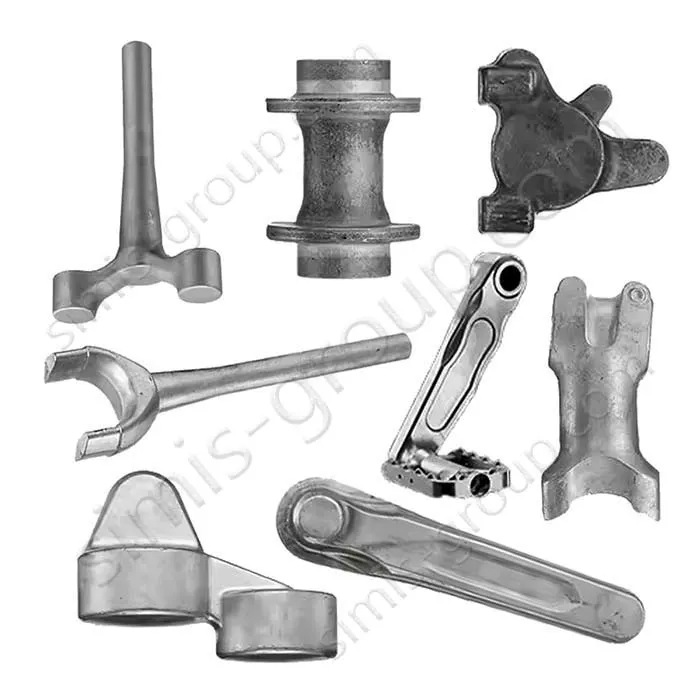
Closed Die Forging Factory for Custom Manufacturing
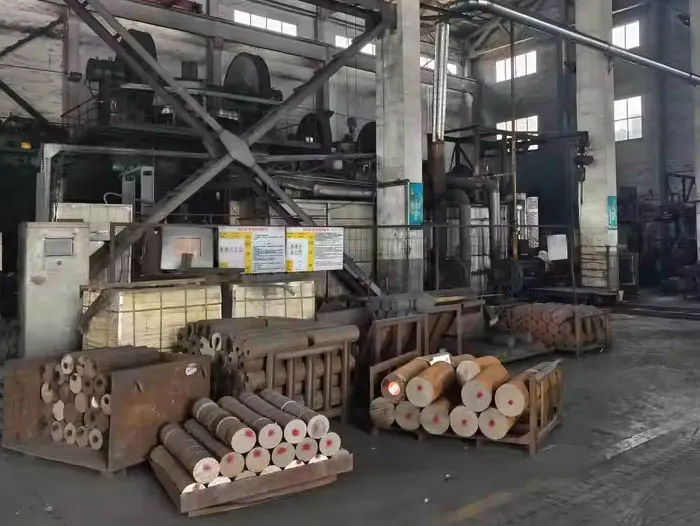
SIMIS Closed Die Drop Forging Factory Introduction
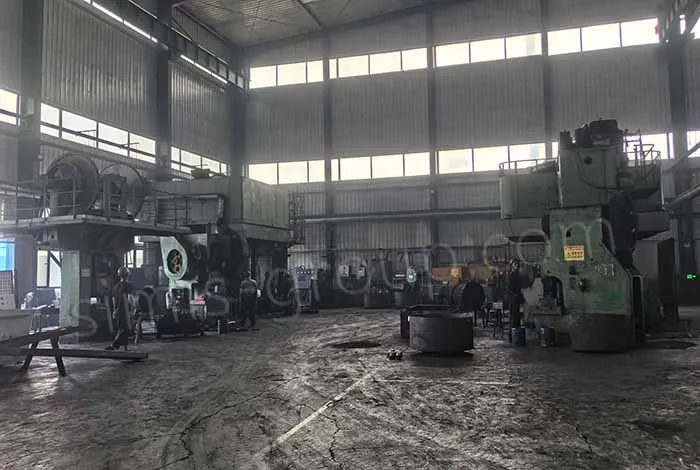
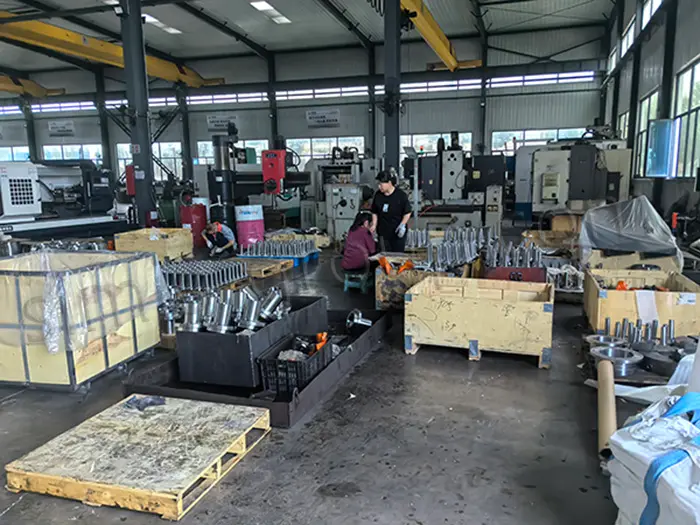
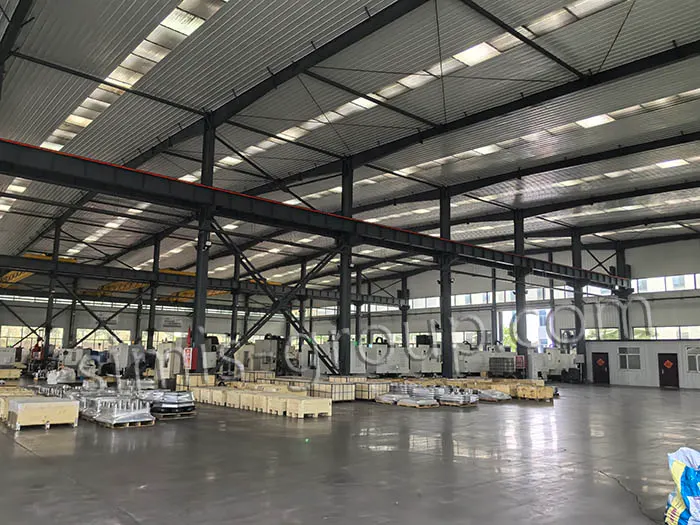
SIMIS Closed Die Forging Factory specialized in the production of high-precision closed die forgings. The plant integrates mold design and manufacturing, billet heating, closed die forging, heat treatment, machining, and inspection, and is capable of producing various carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, and aluminum alloy forgings.
With advanced forging lines, an in-house die manufacturing center, and strict quality management, SIMIS provides high-performance forged components for industries such as automotive, construction machinery, railway, energy, hydraulics, aerospace.
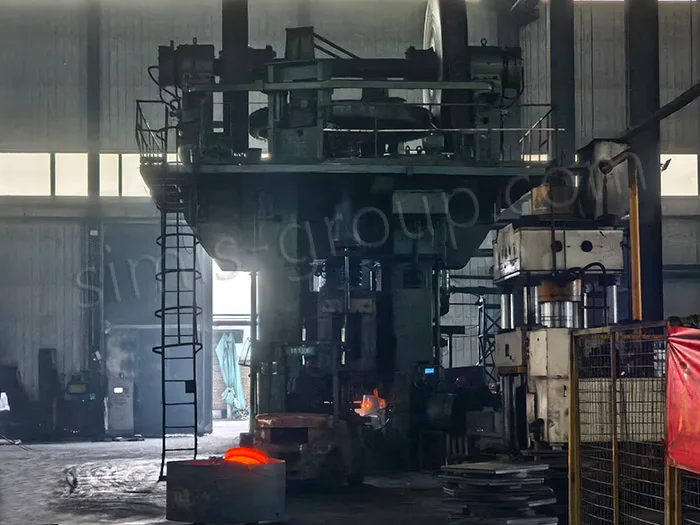
Main Forging Equipment: 1,600T, 2,500T, and 4,000T closed die forging presses
Auxiliary Presses: 400T & 630T friction presses; 630T hot die forging hydraulic press
Heating Equipment: Medium-frequency induction furnace (±10°C temperature control)
Die Manufacturing Equipment: CNC machining centers, wire cutting, slow-feeding EDM machines
Forging Weight Range: 0.2 kg – 25 kg
Max Forged Dimensions: 0.6 m x 0.4 m x 0.2 m
Dimensional Tolerance Grade: IT12 - IT14 Grade
High dimensional accuracy: tolerance up to ±0.3 mm
High material utilization: 80%–90%
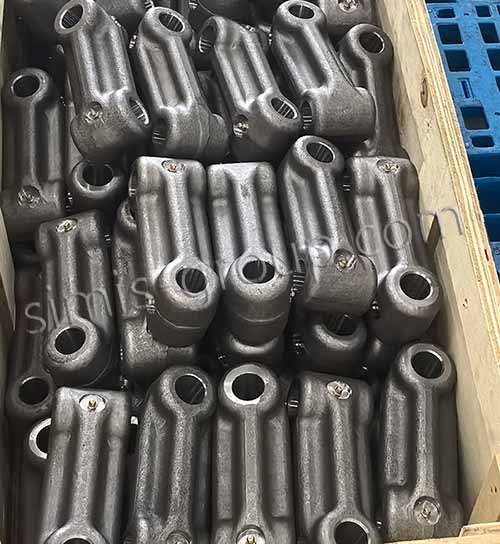
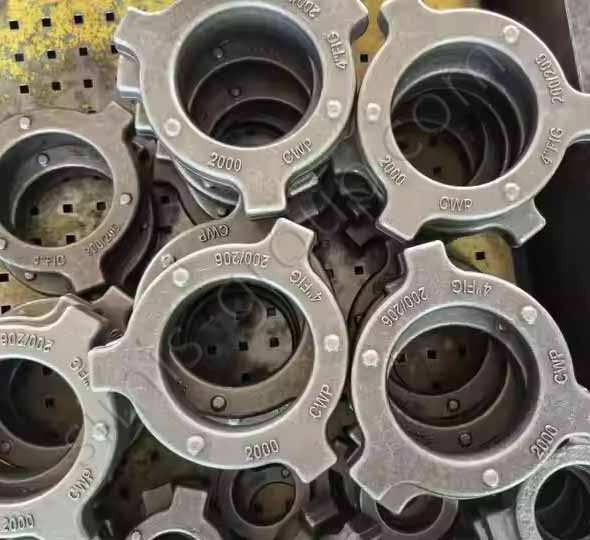
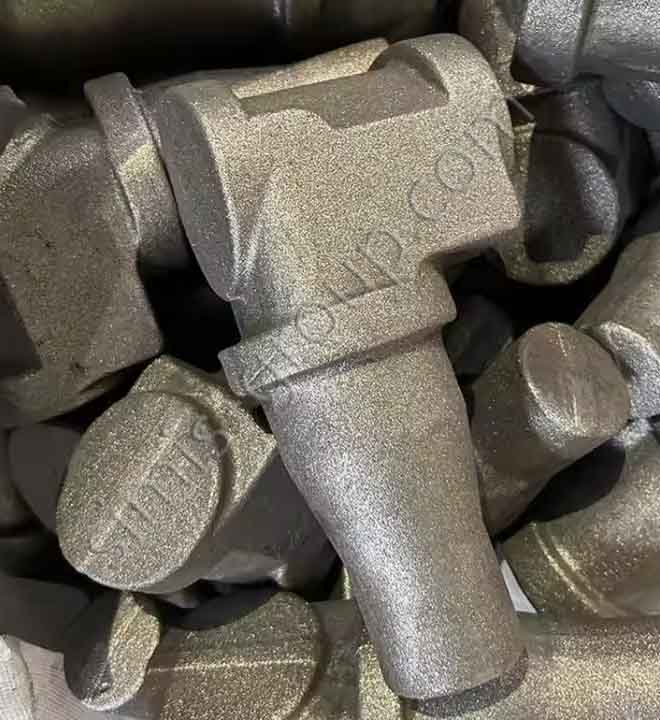
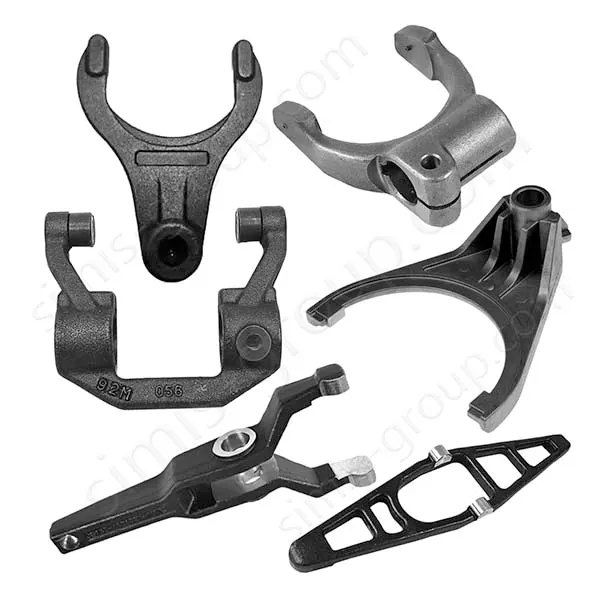
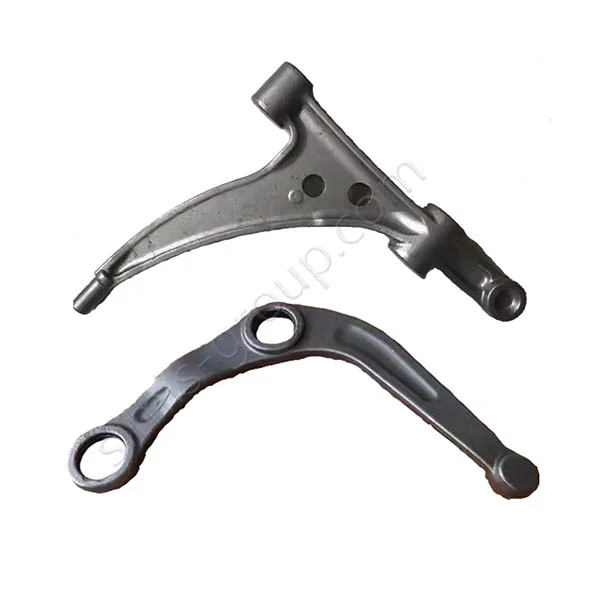
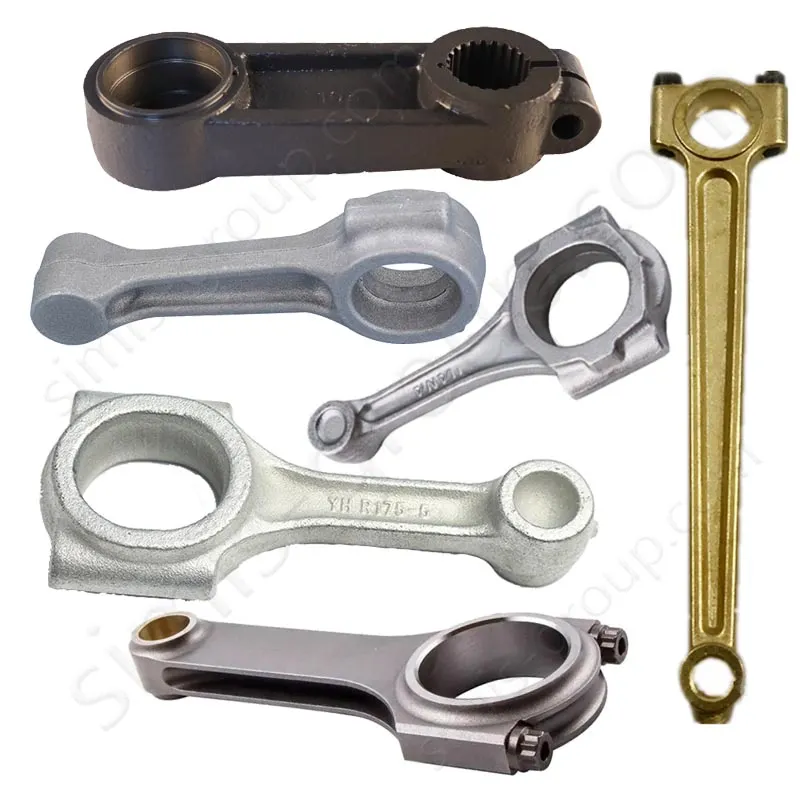
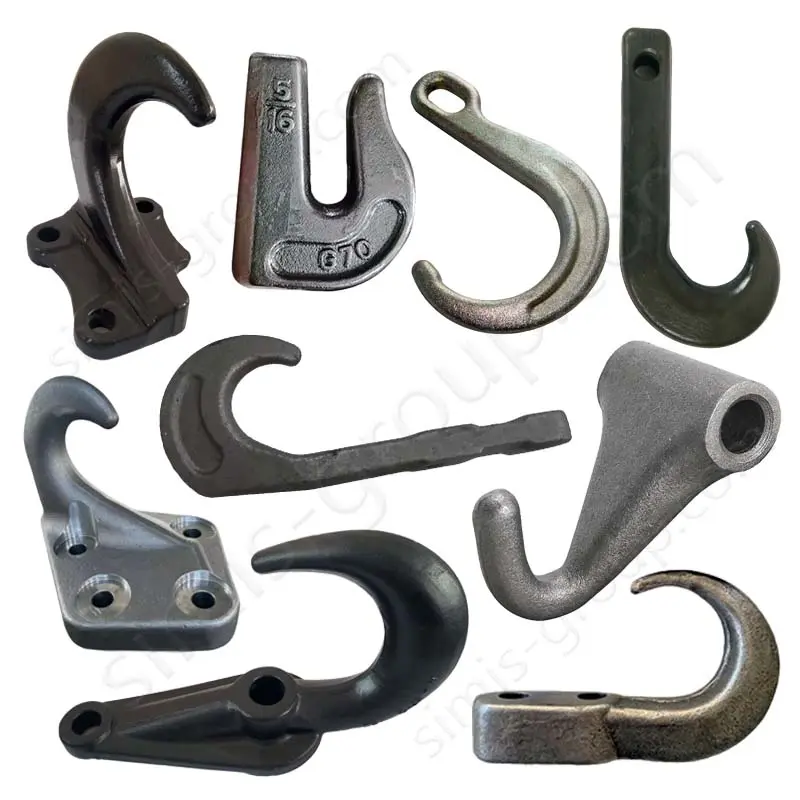
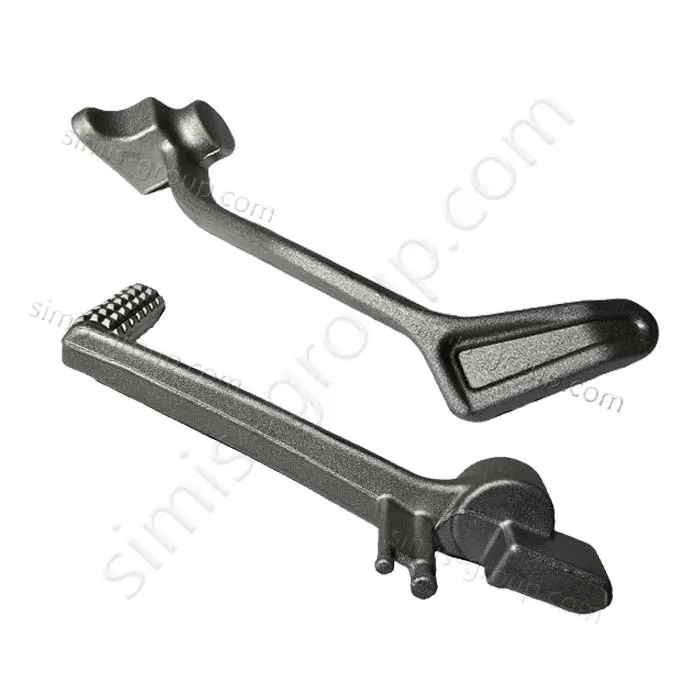
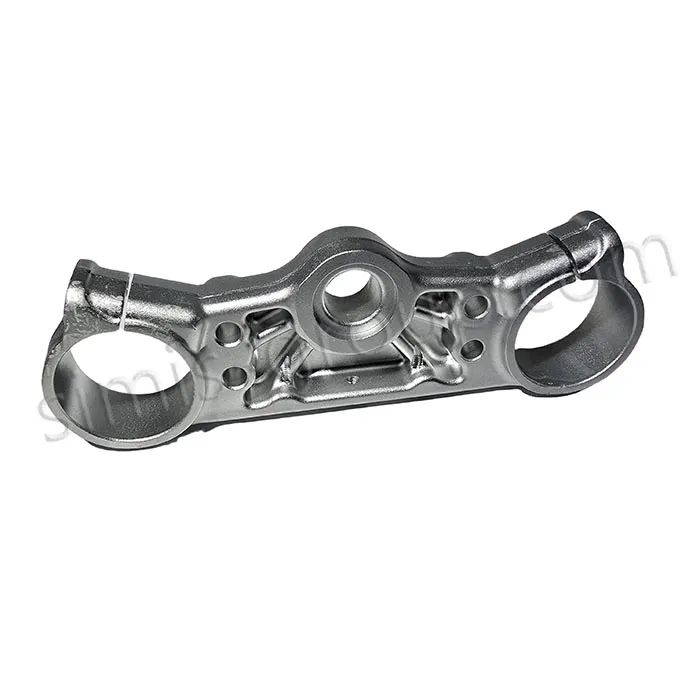
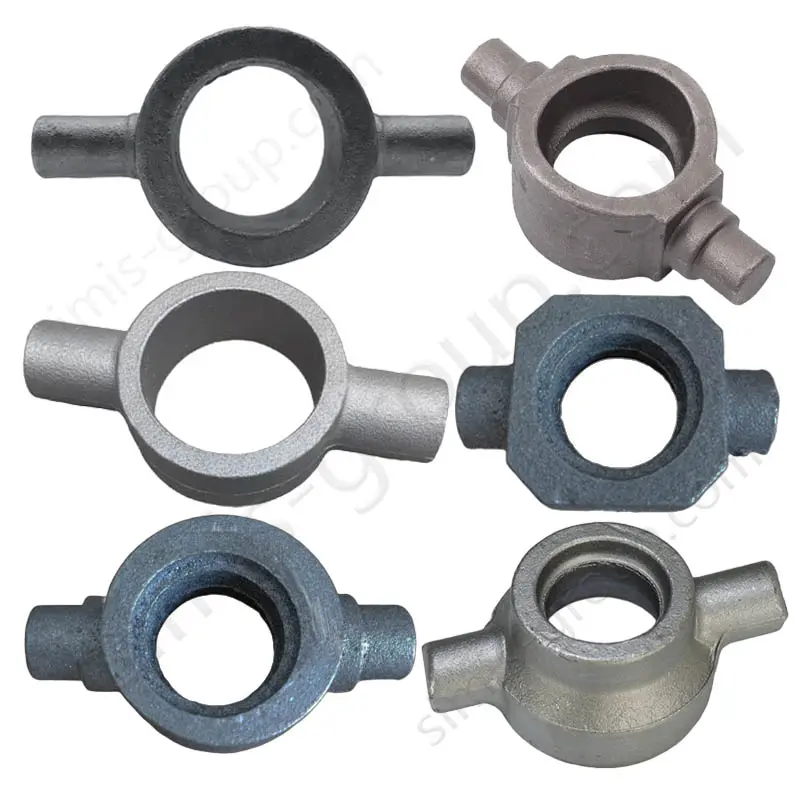
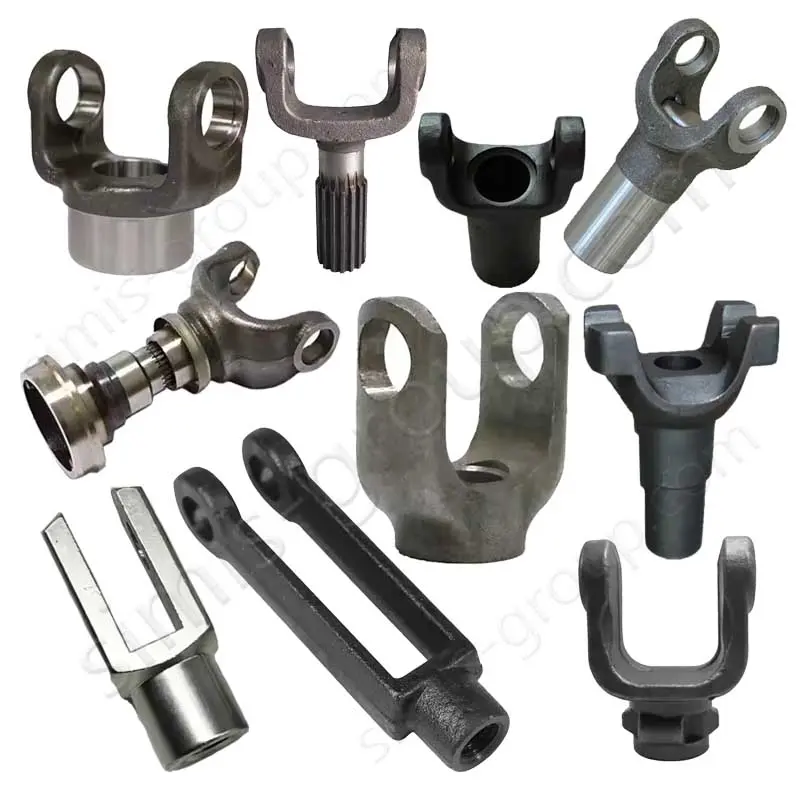
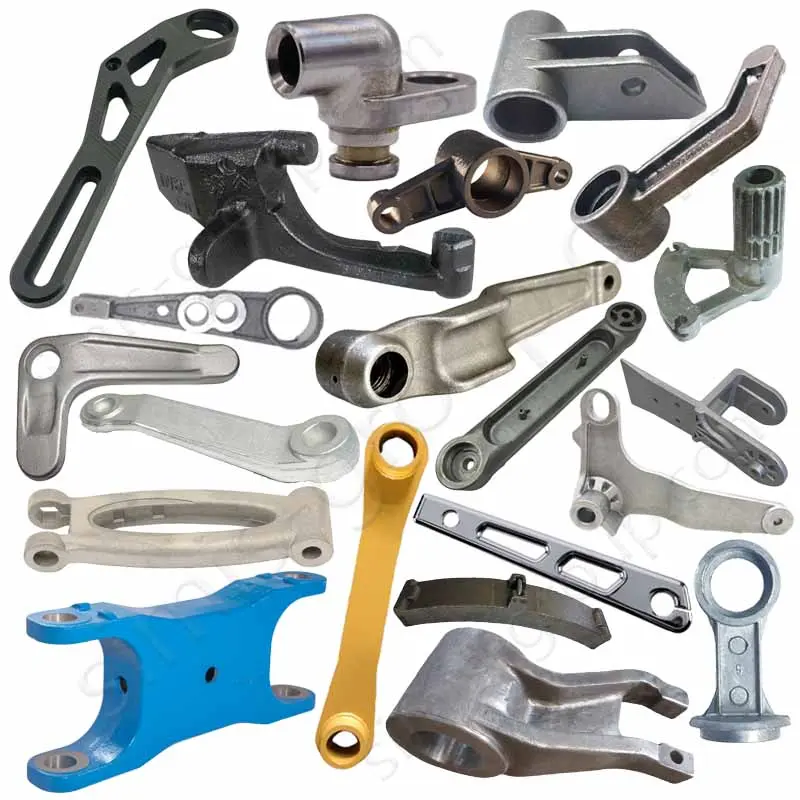
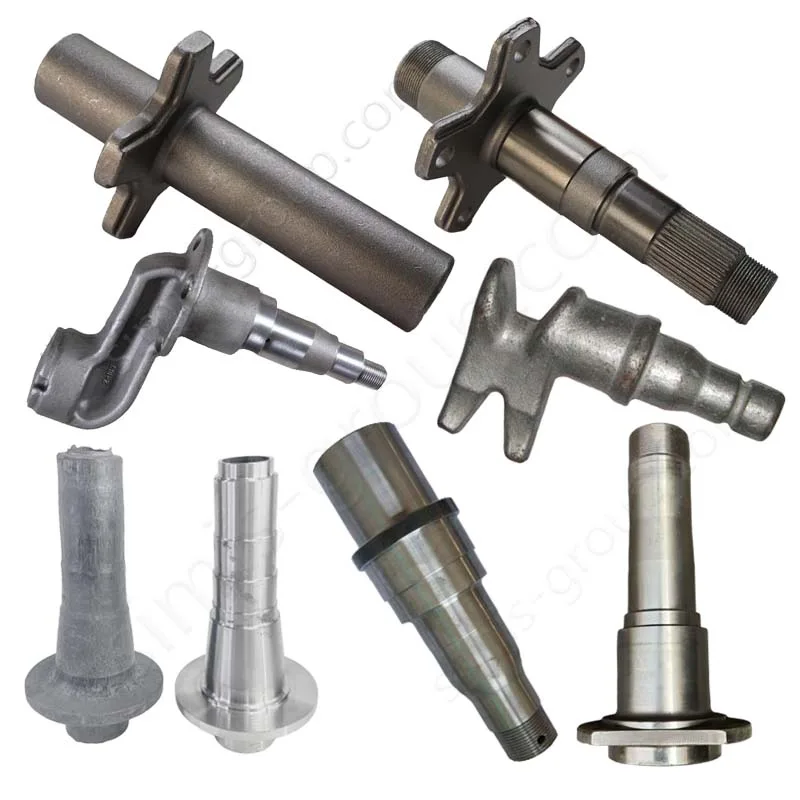
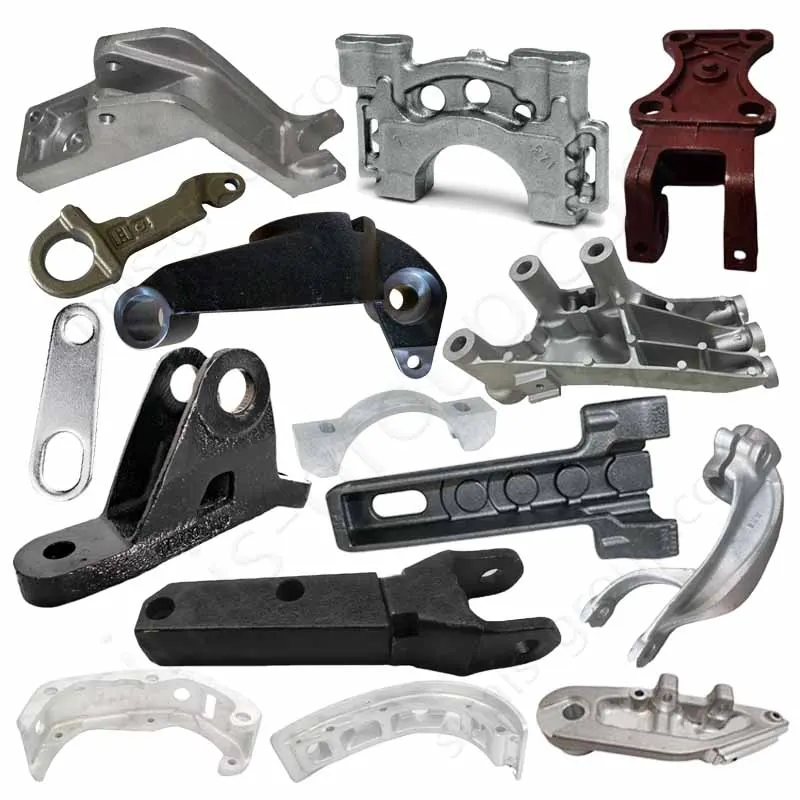
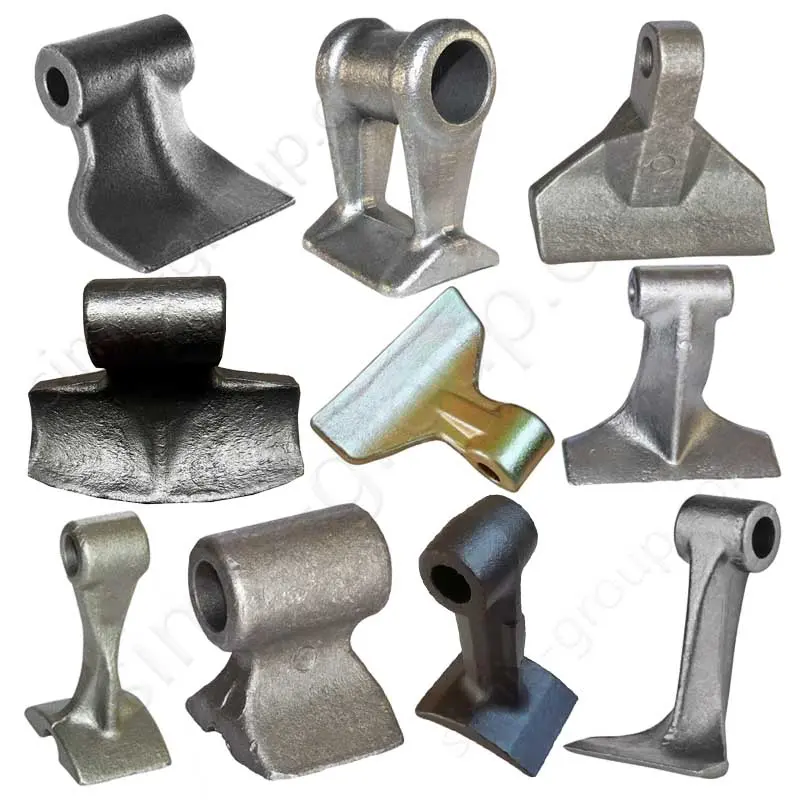
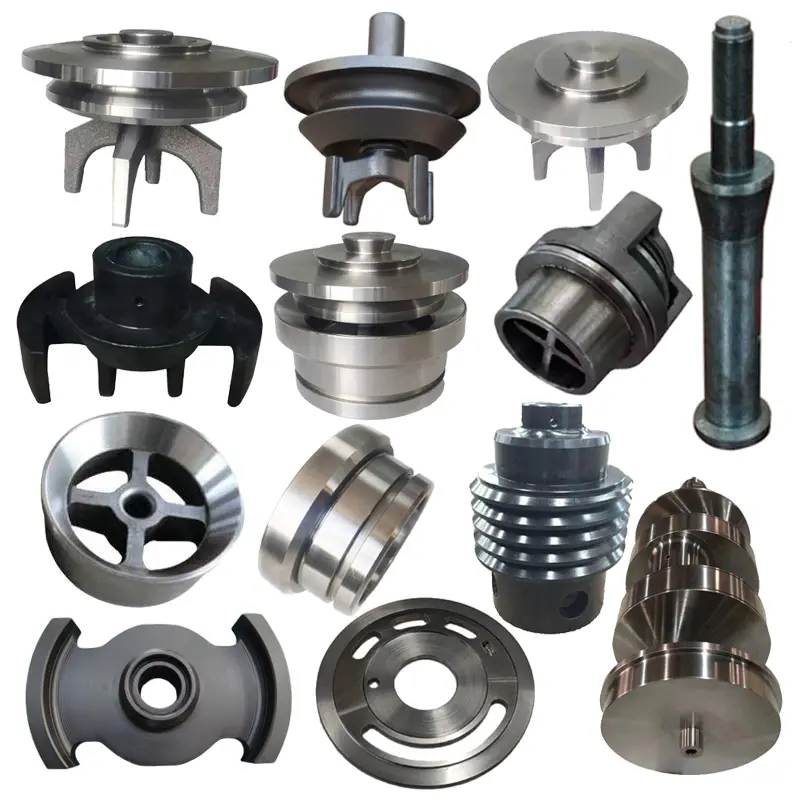
OEM Custom Closed Die Forging Parts
Closed Die Forging Process for Custom Metal Parts
Closed Die Drop Forging process overview
Closed Die Forging (Die Drop Forging) is a process that places heated metal billets into a die with a fixed shape and then applies high pressure or forging to shape them. It can accurately produce metal parts with complex shapes and high precision. Die Forging parts are widely used in the automotive, aerospace, energy and other industries to produce important parts such as gears, shafts, flanges, gears, etc.
1. Prepare the raw materials
Select the appropriate metal blank (such as carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloy, titanium alloy, etc.) according to the use requirements of the parts, and cut the blank to the appropriate size according to the design of the parts.
2. Heat the metal blank
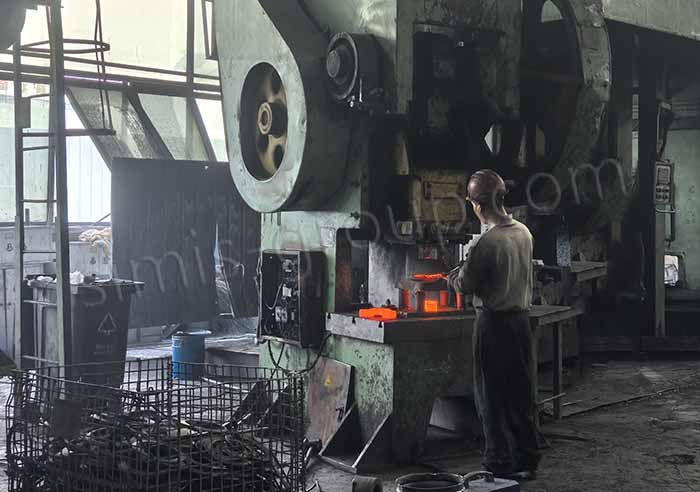
Heat the metal blank to the appropriate forging temperature through a high-temperature furnace.
3. Put it into the mold and apply pressure
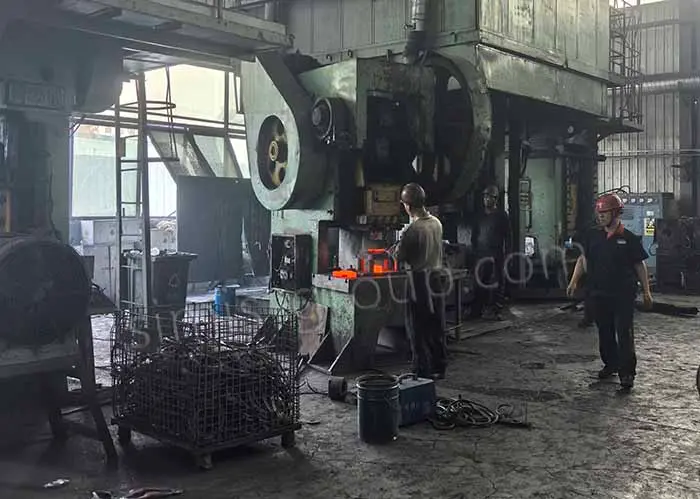
The heated metal blank is sent into the closed die equipment (hydraulic forging machine or mechanical forging hammer),
The forging press applies strong pressure or impact force to the die to press the metal blank into the desired shape.
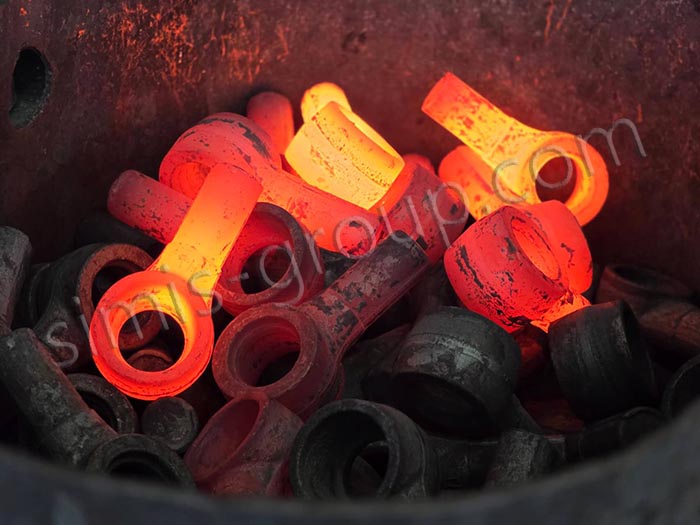
4. Metal flow and forming
When pressure is applied, the metal will flow into every corner of the die and be plastically deformed to the shape of the die. The whole process may require multiple pressures or forgings until the metal completely fills the die and has the desired shape and size.
5. Cooling and solidification
After forging, the forging is removed from the die and begins to cool.
During the cooling process, the grain structure of the metal gradually solidifies, and finally forms the desired mechanical properties.
6. Heat Treatment
Depending on the material and part requirements, forgings may need to be heat treated (Annealing, Quenching, Tempering...) to improve their mechanical properties and eliminate internal stress.
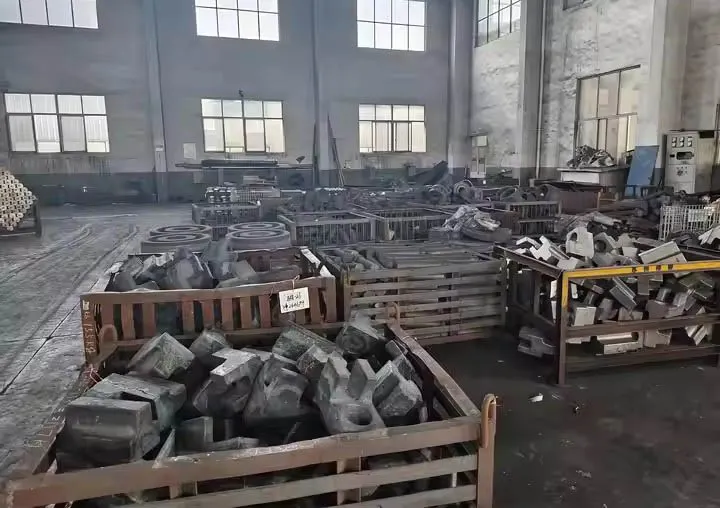
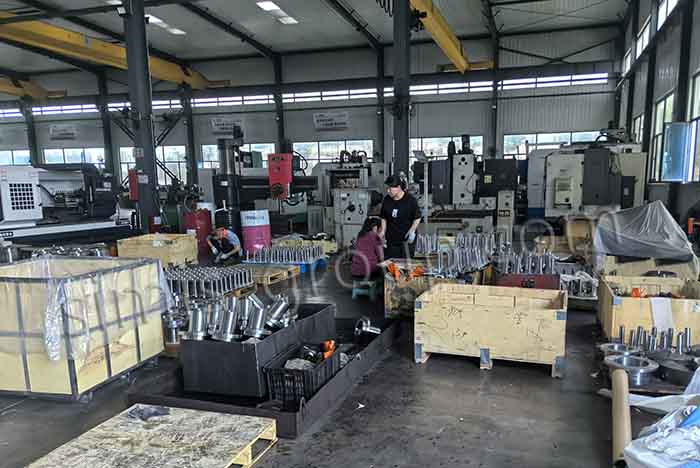
7. Deburring and Post-processing
After the forgings are cooled, they may need to be machined, deburred, polished and other processes to further improve the accuracy and surface quality of the forgings.
8. Quality Inspection
Comprehensive measurement is carried out through surface quality inspection, dimension inspection, mechanical property test and other quality inspection methods to ensure that the die forgings meet the requirements of the design drawings.




Available Materials for Closed Die Forging Applications
What metal parts can be forged in Simis Closed Die Forging Factory?
Closed-die forging method allows high-precision, near-net-shape production of complex geometries with superior mechanical properties, including enhanced strength, fatigue resistance, and controlled grain flow. Simis Precision Closed Forging Factory can forge parts made of carbon steel, low alloy steel, stainless steel, high alloy steel, and aluminum alloys, particularly suitable for medium to high-volume production of structural, load-bearing, or high-stress components.
| Material Category | Why It Is Suitable for Closed-Die Forging | Simis Precision Closed-Die Forging Factory Typical Applications | Simis Precision Closed-Die Forging Factory Common Grades |
| Carbon Steel | Good hot deformability and cost-effective. Closed-die forging refines grain structure, enhances strength, and produces near-net-shape components, reducing machining | Shafts, gears, crankshafts, connecting rods, large structural parts | AISI 1045, 1050, 1060; EN C45, C50 |
| Stainless Steel | Austenitic and precipitation-hardening stainless steels can be closed-die forged to achieve high strength, corrosion resistance, and toughness. Temperature and strain rate control is critical to avoid cracking | Pump and valve components, chemical and food processing equipment, structural shafts | AISI 304, 316, 17-4PH; EN 1.4301, 1.4404, 1.4542 |
| Low-Alloy Steel | Alloying elements increase hardenability, wear resistance, and toughness. Closed-die forging enables high-volume production of load-bearing parts with controlled mechanical properties | Automotive components, flanges, heavy machinery parts, pressure vessel components | AISI 4140, 4340; EN 19, 42CrMo4 |
| High-Alloy Steel | High-strength or heat-resistant steels can be forged to near-net-shape for critical components exposed to high stress or temperature | Turbine disks, aerospace shafts, high-performance mechanical parts | AISI 4145, 4340 modified, Inconel 718 |
| Aluminum Alloys | Aluminum alloys have low melting temperature and excellent hot formability, making them suitable for closed-die forging. The process improves grain structure, strength, and surface finish for lightweight, high-performance components | Aerospace structural parts, automotive lightweight components, housings, brackets | AL 7075, 2024, 6061, 6082 |