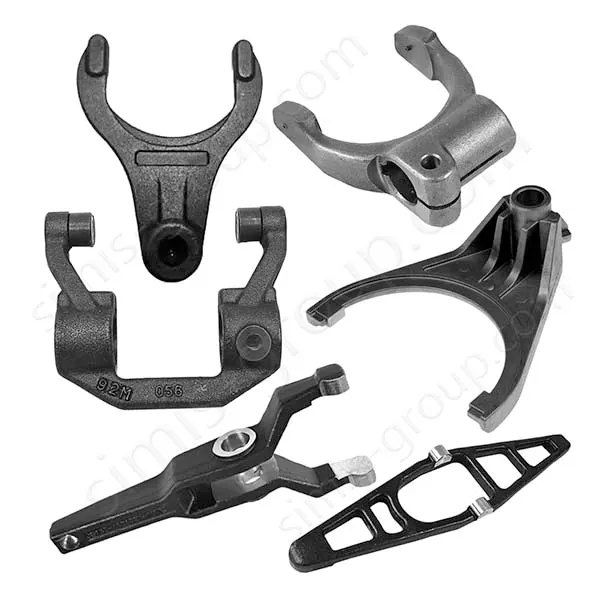
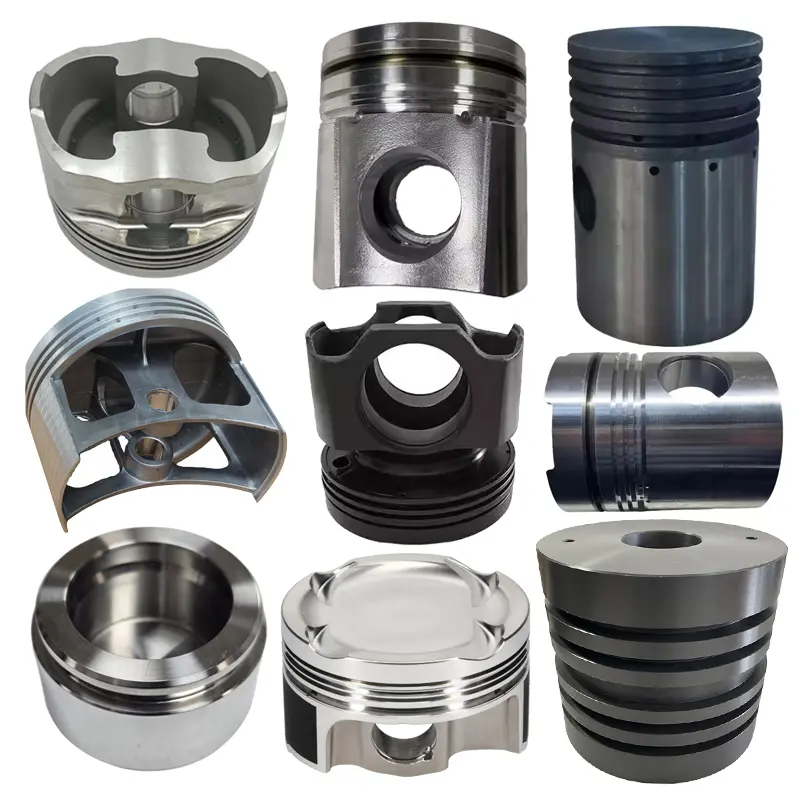
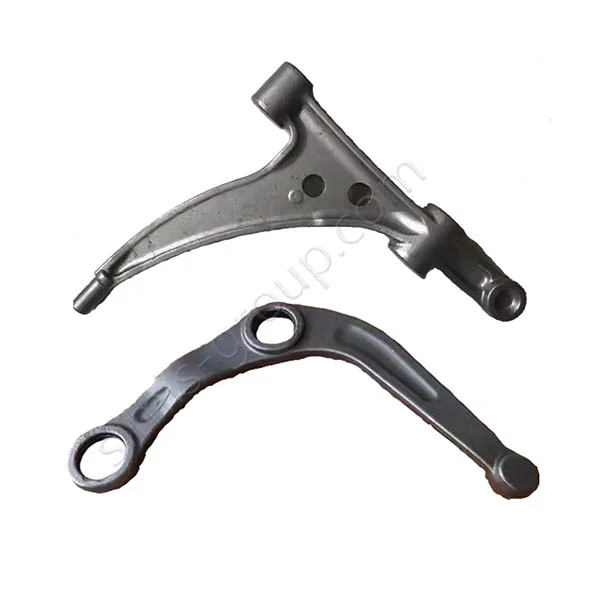
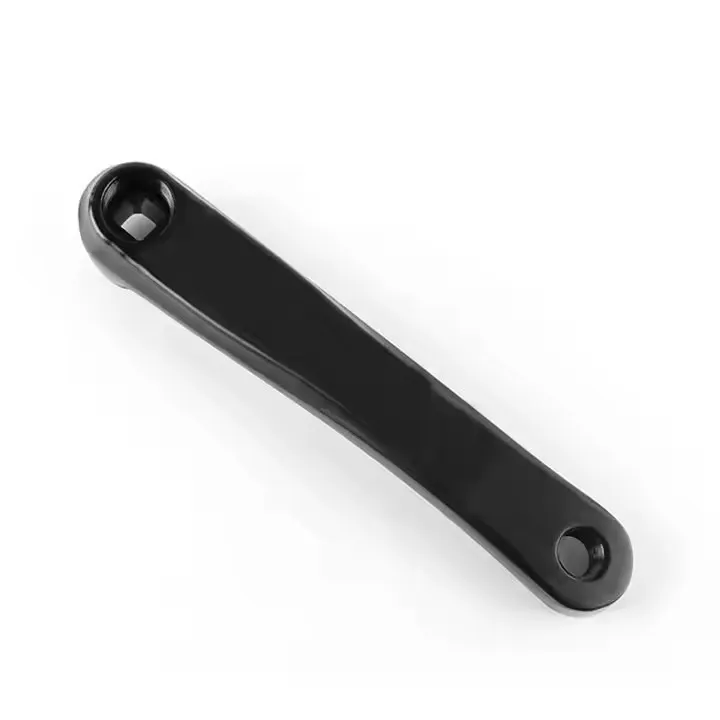
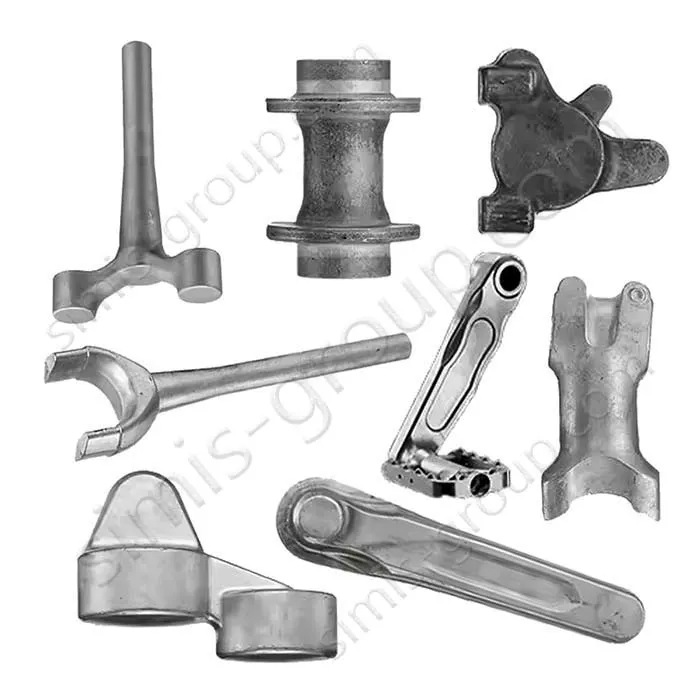
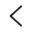Manufacturing Capabilities of Aluminum Forging Factory
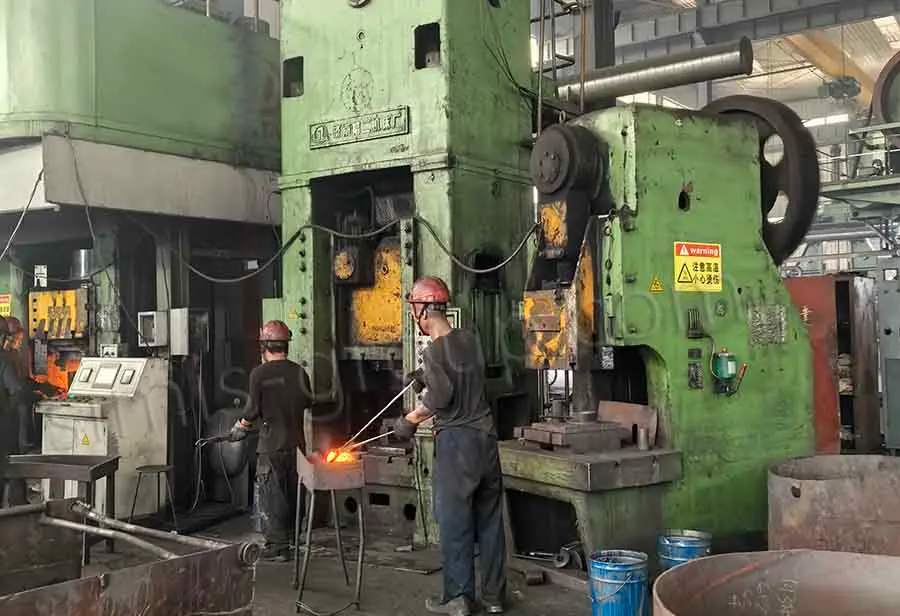

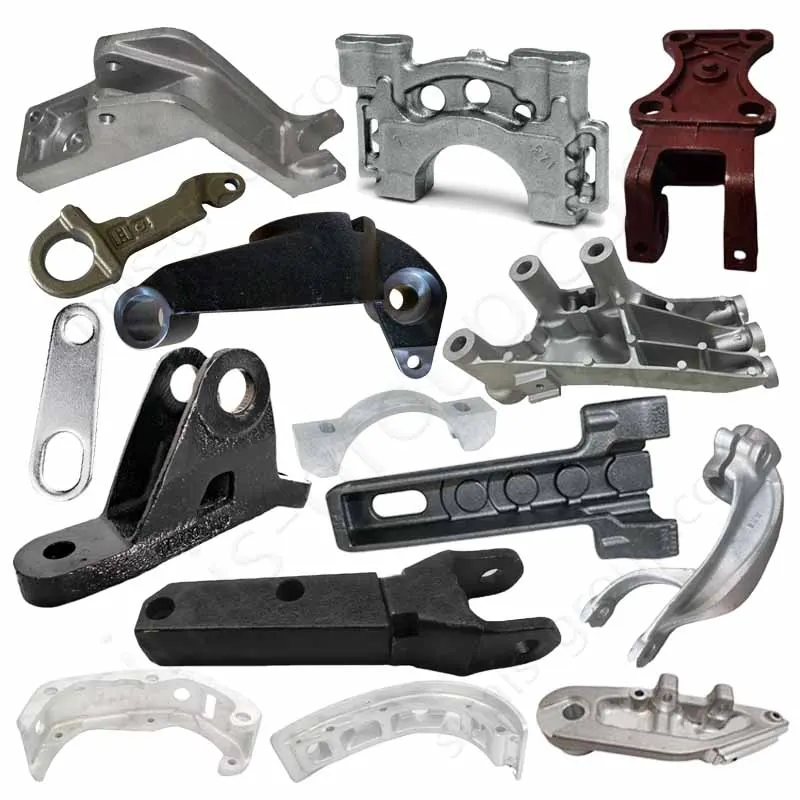
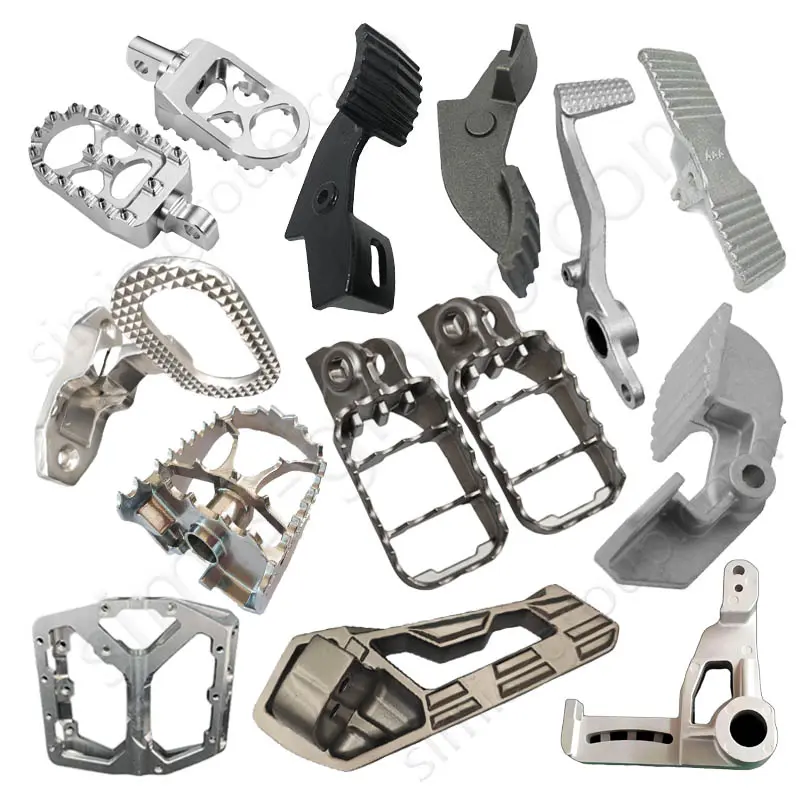
Aluminum Closed Die Forging
Aluminum closed-die forging involves placing heated aluminum alloy billets in a forging die with a precision cavity. The metal is forced to flow and take shape within the closed space by strong pressure. This results in aluminum forgings having fatigue strength, impact toughness, and strength-to-weight ratio far exceeding those of any aluminum alloy castings. It is suitable for mass production of lightweight aluminum alloy forgings with extremely high requirements for structural reliability.
Forging Weight Range: 0.1 kg – 15 kg
Max Forged Dimensions: 1 m x 0.4 m x 0.2 m
Dimensional Tolerance Grade: IT12 - IT14 Grade
Machining Allowance: 1 mm - 3 mm

Aluminum Ring Forging
Aluminum alloy ring rolling first processes heated aluminum alloy billets into preforms (discs) with a central hole. Then, through precise control of radial and axial rolls, plastic deformation is carried out under high-temperature conditions, giving aluminum forged rings unparalleled strength-to-weight ratio, excellent fatigue resistance, and stress corrosion resistance, far exceeding that of welded or cast rings.
Max Outer Diameter: Ф100 mm to Ф1500 mm
Max Ring Height: 50 mm to 400 mm
Tolerance Class: IT14 - IT15 Grade
Min Wall Thickness/Height: Min Wall Thickness 20 mm; Min Height 50 mm
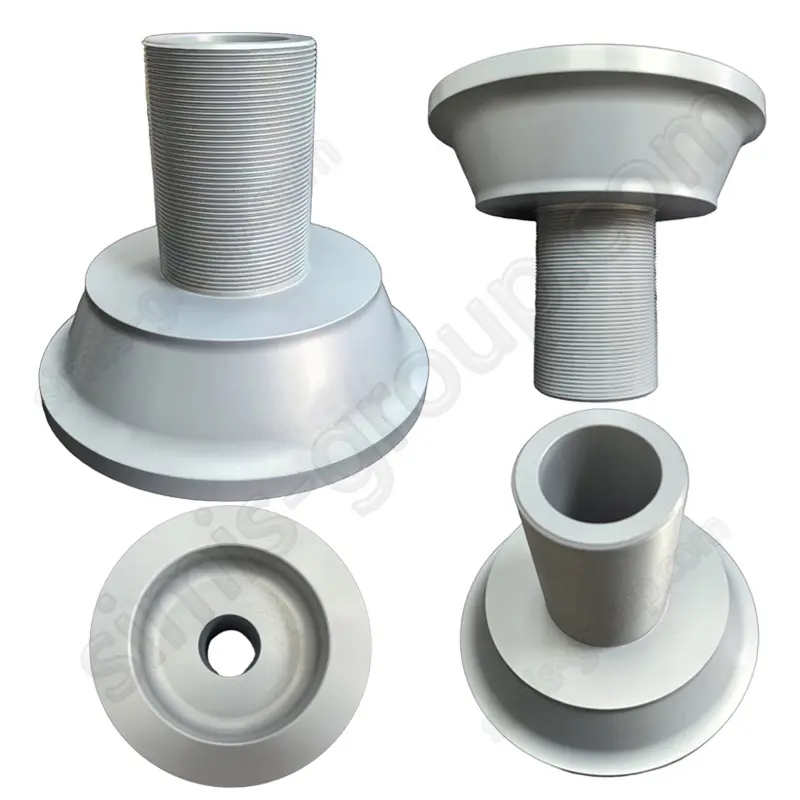
Aluminum Cold Forging
Aluminum alloys Cold forging involves applying extremely high pressure to an aluminum billet at room temperature to shape it. This results in forgings with extremely high dimensional accuracy and a smooth surface, significantly improving the strength and hardness of the aluminum alloy and enhancing the durability and reliability of the parts. This process is typically used for the mass production of small-volume aluminum alloy forgings with relatively simple shapes and extremely high requirements for dimensional and mechanical properties.
Forging Weight Range: 0.01 kg – 2 kg
Max Dimensions: Diameter ф100 mm/ Length 200 mm
Dimensional Tolerance: IT8 - IT10 Grade
Surface Finish (Ra): Ra 0.8 to 3.2 μm
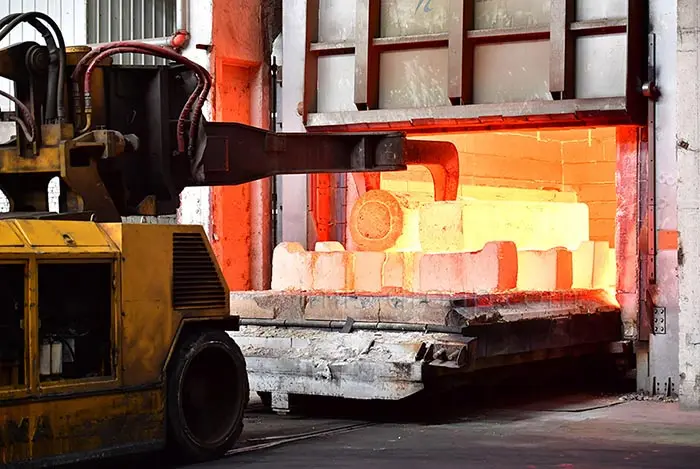

Heat Treatment
Aluminum heat treatment relies fundamentally on the mechanism of Precipitation Hardening, which precisely controls the precipitation of alloying elements. The process is highly standardized, centered on solutionizing, quenching, and aging (artificial or natural). The final properties are defined by the resulting T Temper Designation.
Solution Treatment: Dissolve alloy elements; prepare for aging.
Quenching: Rapid cooling; lock strengthening elements in matrix.
Natural Aging: Slow strengthening at room temperature; achieves T4 temper.
Artificial Aging: Accelerated strengthening at medium heat; achieves maximum strength (T6).
Under Aging: Enhance stress corrosion resistance; often results in T7 temper.
Stress Relief: Eliminate internal stress; ensure dimensional stability.

Machining
Machining enables forgings to achieve high precision, lightweight, and final geometry, ensuring surface finish and realizing the final functions of aluminum forgings, such as bearing fits, threads, sealing surfaces, and complex cavities.
Machining Tolerance: IT7 to IT6 Grade
Surface Finish (Ra): Ra 1.6 to 0.4 μm
Geometric Accuracy: True Position, Concentricity ≤ 0.01 mm

Surface Treatment
Surface treatment for aluminum forgings primarily focuses on Anodizing and Chemical Conversion Coating, aiming to form a dense, hard, chemically inert oxide or protective layer on the aluminum surface. The dense structure of aluminum forgings is highly conducive to forming uniform coatings with superior adhesion compared to castings.
Conventional Anodizing (Type II): Color and basic protection (5-25μm).
Hard Anodizing (Type III): Ultimate wear resistance (25-100μm)
Conversion Coating: Pre-treatment for painting; maintains electrical conductivity.
Powder Coating/Painting: Heavy-duty protection and color coding.
Blasting/Shot Peening: Removes oxides; achieves uniform texture.
OEM Custom Forged Aluminum Parts by Aluminum Forging Factory
Forged Aluminum Materials for Custom Forging Applications



Non-Heat-Treatable Aluminum Alloys Forging
These aluminum alloys get strength from cold shaping. They do not use heat to become strong. Their strength comes from working the metal when it is cold. This makes them great for parts needing good shape change and rust defense. They only need moderate strength.
Forged Non-Heat-Treatable Aluminum Parts from Simis:
Ship and marine parts;
Chemical gear;
Electrical power bars;
Cold storage tanks;
Car body panels;
Building structures;
Food gear.
Simis can forged non-heat-treatable aluminum alloys types:
Pure Aluminum Forgings (Low-Alloy): Electrical wire, heat exchangers, chemical tools, and decoration.
Al-Manganese (Al-Mn) Forgings: Cooking tools, heat exchangers, storage tanks, and building parts.
Al-Magnesium (Al-Mg) Forgings: Marine hardware, boat parts, pressure tanks, and transport gear.
Al-Mg-Silicon (Al-Mg-Si) Forgings: Building parts, car panels, and general use (some types are non-heat-treatable).
Aluminum-Copper Alloys Forging
Forged Aluminum-Copper alloys are produced by heating and mechanically pressing the aluminum and copper mixture. They are subsequently processed using heat treatment to achieve their maximum strength. These alloys are among the highest strength aluminum materials available, providing an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and good fatigue resistance. This makes them suitable for high-performance structural components.
Forged Al-Cu Components from Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
Aircraft body frames and structure parts;
Car suspension parts and wheels;
High-performance sports gear;
Robotic arms;
Machinery parts.
Simis can forged Al-Cu alloys types:
Binary Al-Cu Alloys: General high-strength structural parts, car parts, and machinery components.
Al-Cu with Magnesium Added: Aircraft structure parts, truck frames, and high-stress components.
Al-Cu with Lithium Added: High-performance car parts.
Highest-Strength Al-Cu Forgings: High-performance racing parts.
Aluminum-Magnesium-Silicon Alloys Forging
Forged Al-Mg-Si alloys are made by heating the metal and pressing it into shape. We then use special heat treatment to reach the best strength. These alloys offer a great balance of medium-to-high strength, good rust defense, and excellent ability to be extruded. This makes them one of the most useful and widely used aluminum alloy families.
Forged Al-Mg-Si Components from Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
Car chassis and body structures;
Bicycle frames and parts;
Building structures;
Heat exchanger parts;
Marine hardware;
Electrical conductors;
General machine parts.
Simis can forged Al-Mg-Si alloys types:
Balanced Mg₂Si Alloy Forgings: General structural parts, car parts, and building uses.
High-Silicon Alloy Forgings: High-strength structure parts, wear-resistant parts, and car suspension.
High-Magnesium Alloy Forgings: Marine structures, pressure tanks, and transport equipment parts.
Copper-Containing Alloy Forgings: High-strength structure parts, aerospace parts, and precision machines.
Aluminum-Zinc Alloys Forging
Forged aluminum-zinc alloys are shaped by heating and pressing billets. They get strong naturally, without a special heat treatment step. This makes them high in strength and cost-effective for structural uses. They are best for jobs needing high strength but simple processing.
Forged Al-Zn Components from Simis Aluminum Forging Factory:
Car engine mounts and brackets;
Structural hardware;
Machine parts and fittings;
Electrical hardware;
General engineering components;
Architectural fittings.
Simis can forged Al-Zn alloys types:
High-Zinc Aluminum Alloy Forgings: Car structure parts, high-strength machine parts, and structural fittings.
Zinc-Magnesium Alloy Forgings: General structural parts, marine hardware, and transport equipment.
Zinc-Copper Alloy Forgings: High-strength structural parts, aerospace parts, and precision machines.
Low-Zinc Alloy Forgings: Marine parts, building structures, and general engineering.
Industries Served by Our Aluminum Forging Factory
How to Customize Aluminum Forgings with Aluminum Forging Factory

Confirm customization requirements
Design Review and Samples
Simis engineers first check the 3D and plane drawings. This makes sure your design is ready for the forging process. If you have a sample part, we can make the new parts based on that sample.
Define Part Requirements
We confirm what the part needs to do. This includes things like its strength, hardness, wear, and rust resistance. We also set the exact size, tolerance, and finish quality needed for the forged part.
Confirm Forging Material
Our engineers help you pick the right aluminum material. This choice depends on where the part will be used and your technical needs. We give advice based on material cost, strength, and resistance to wear or rust.
Choose the Forging Process
We select the best forging process for your part. We base this choice on your price goal, the part’s shape, its required dimensional accuracy, and the material.
Make Dies and Samples
We build the forging dies (molds) using your approved drawings or samples. Then, we shape the aluminum material through the chosen process to produce the first batch of samples.
Full Sample Inspection
The finished samples go through a full check. This confirms they meet all design standards and your quality demands. We give you reports covering size and tolerance inspection, performance testing, chemical composition analysis, and non-destructive testing.
Production and quality control
7. Mass Production
After you check and approve the sample, we start the mass production plan. We get all the materials ready based on your order. We use the exact same forging equipment and process as we did for the sample. This makes sure every single part we make is the same.
8. Quality Control During Production
We run tight quality checks while making the parts. We pull parts for checks often during the process. We test their size, look, and strength. This ensures every batch of forged aluminum parts is consistent and meets your needs.
9. Final Product Quality Inspection
We use multiple inspectors for the final check. They do many tests on the finished product. These tests cover size accuracy, surface quality, and part strength. This step makes sure all forged aluminum parts meet your quality standards.
10. Packaging and Delivery
We securely package and ship all approved parts. We pick the right packaging to prevent damage during shipping. We also choose the best delivery method (air, sea, or land) to get your parts to you on time.




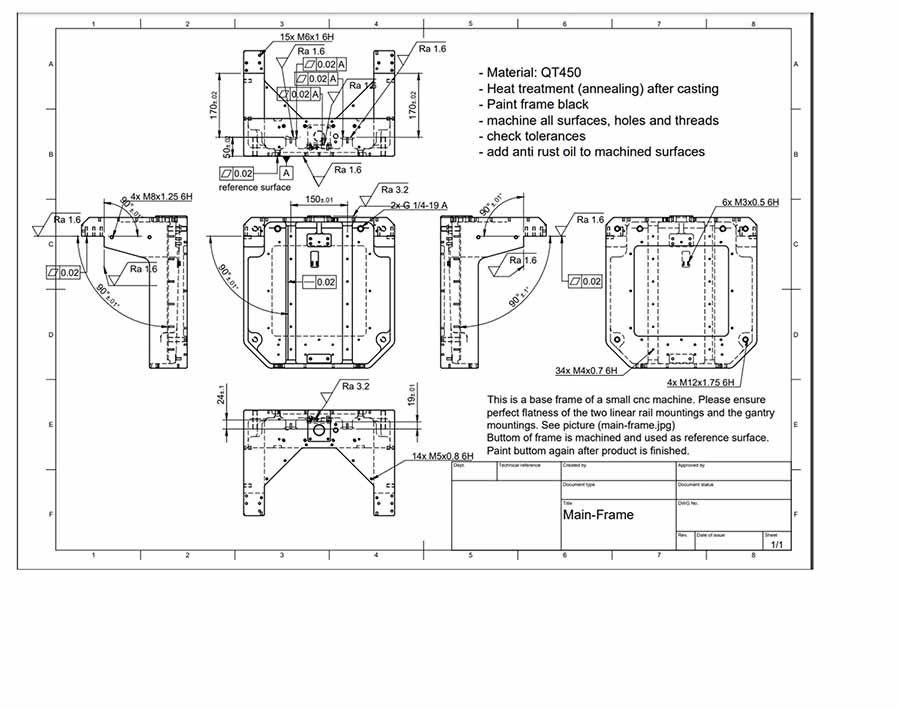
To order custom parts, please email us your design drawings and 3D models. Our team will review the detailed part parameters and the 3D model to provide you with an accurate quote.