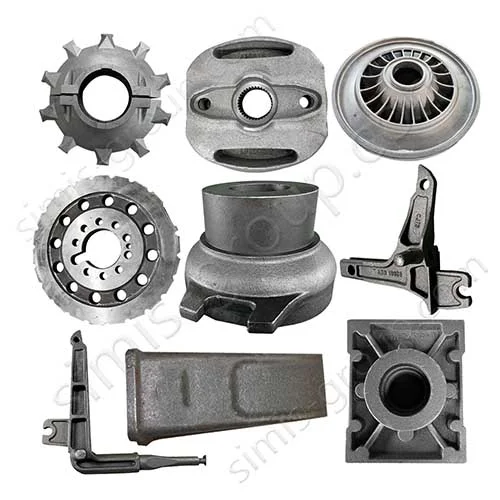
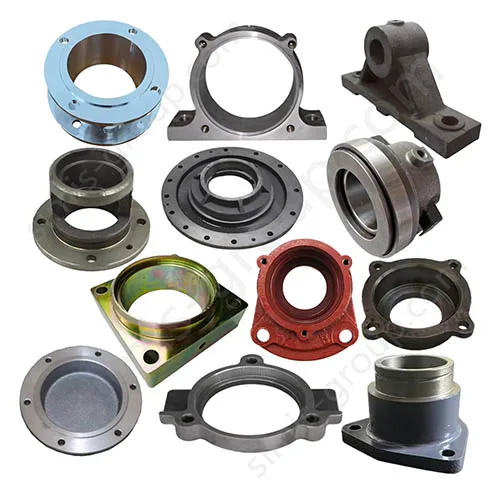
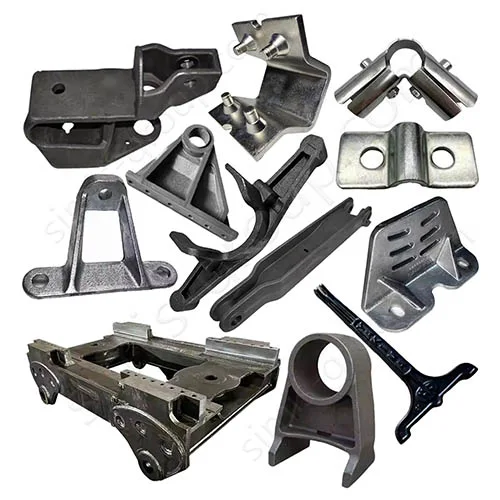
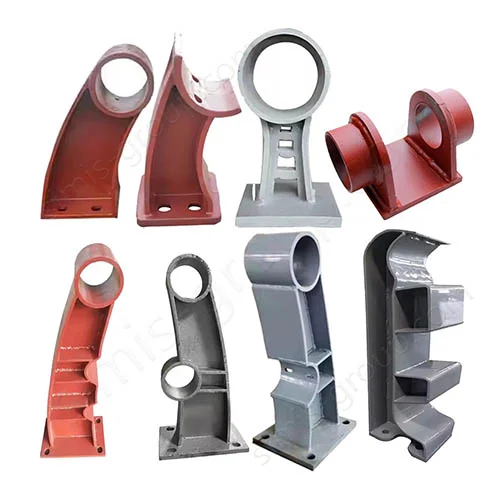
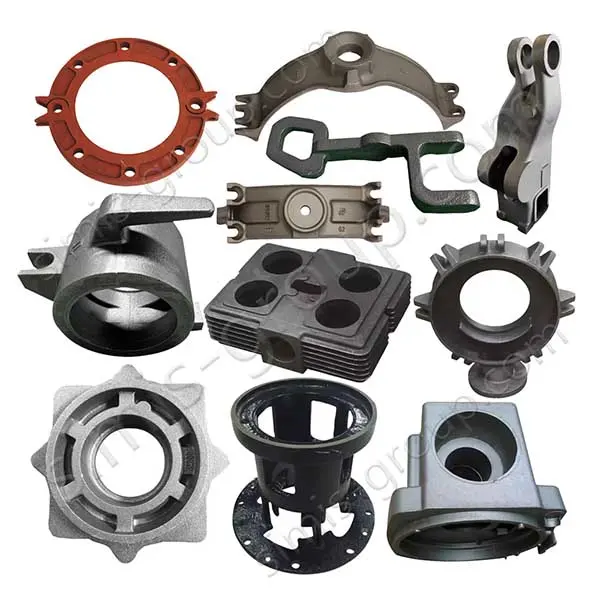
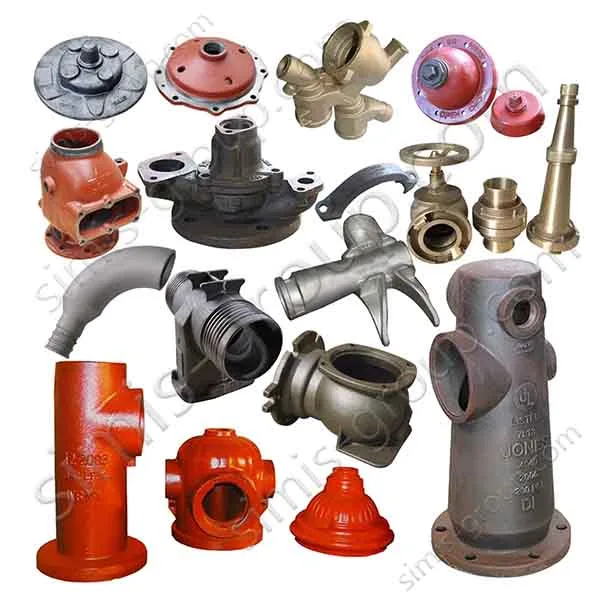
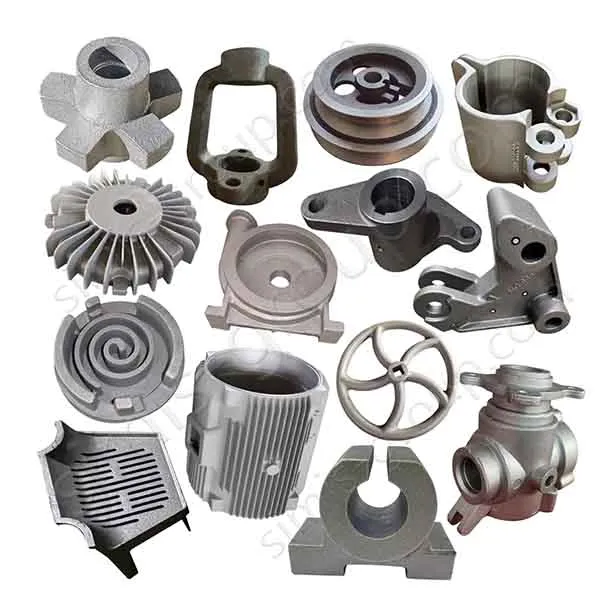
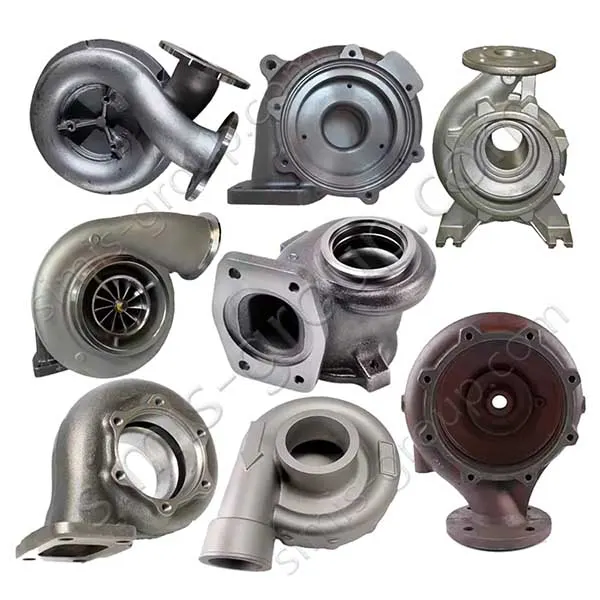
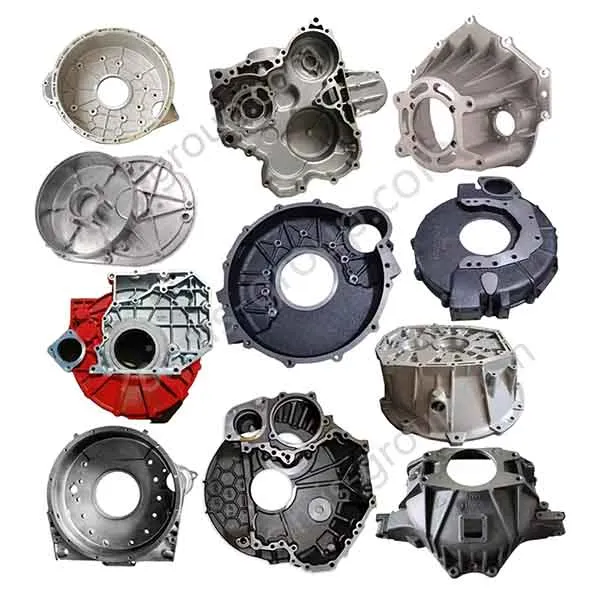
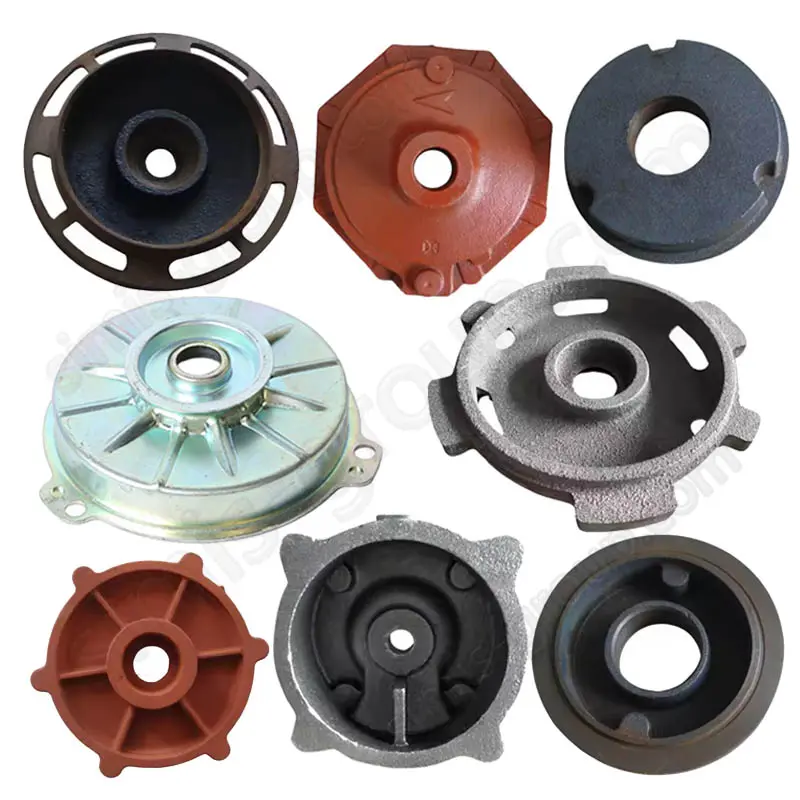
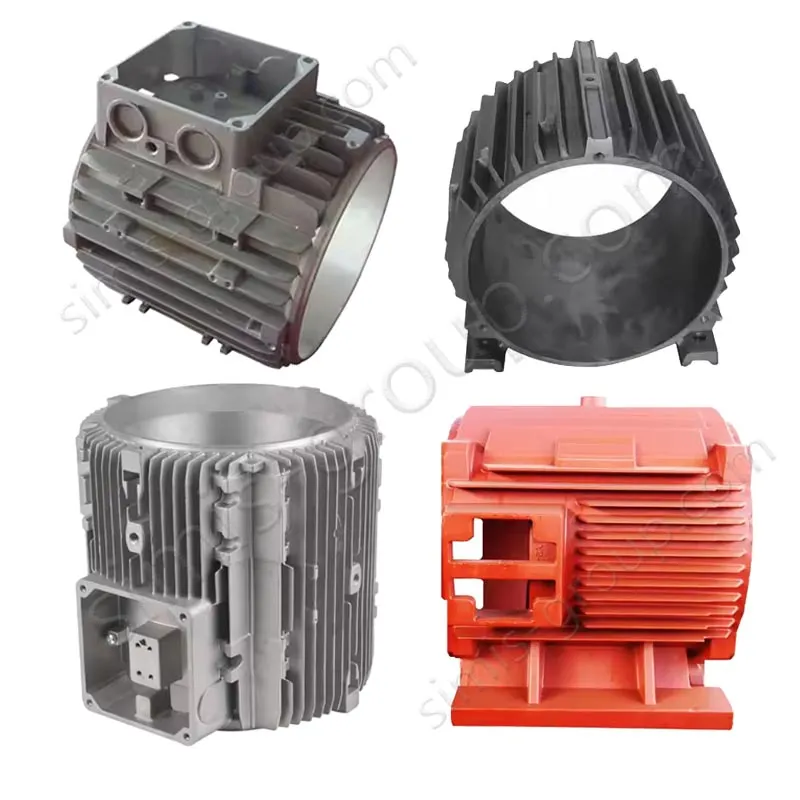
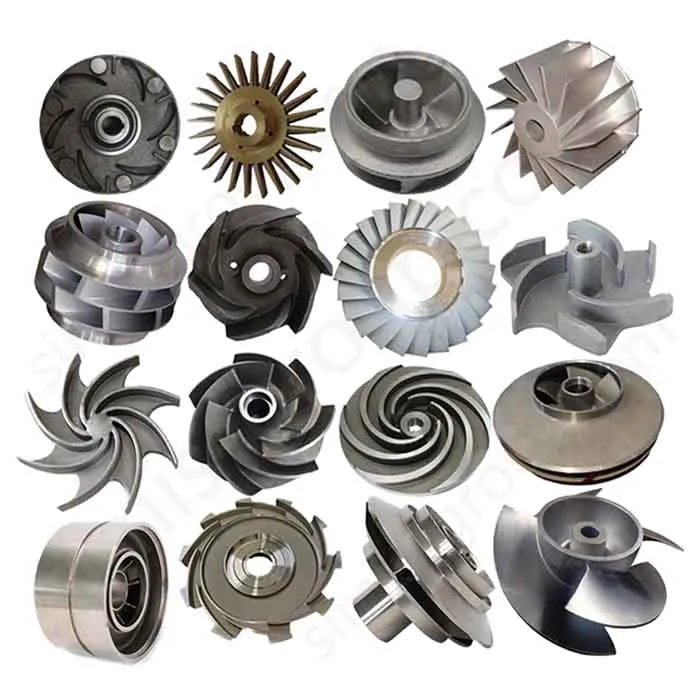
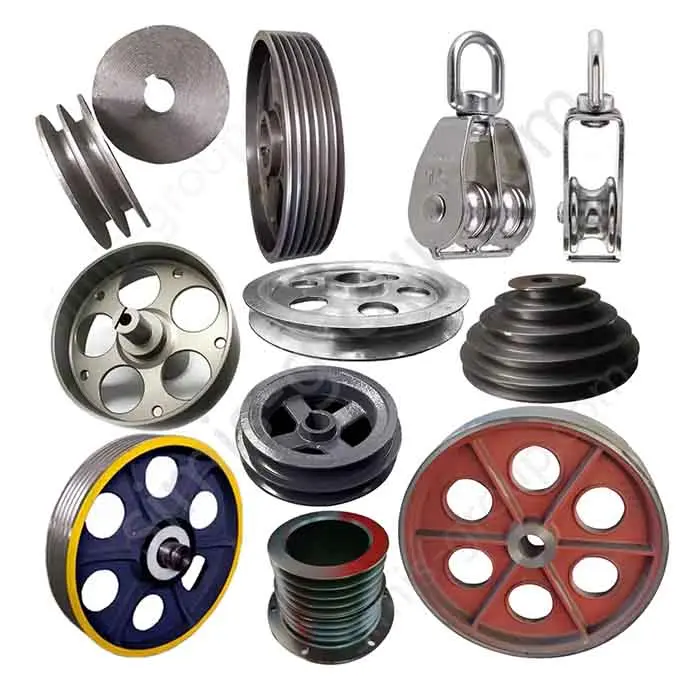
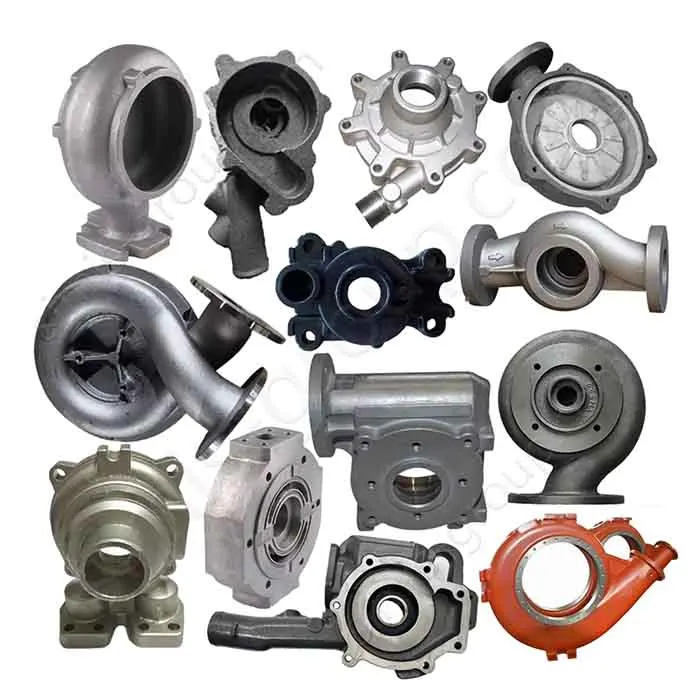
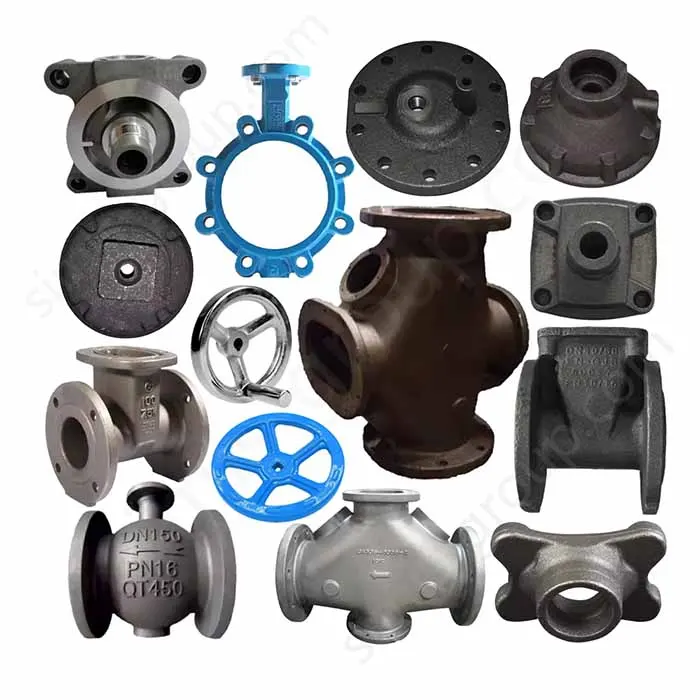
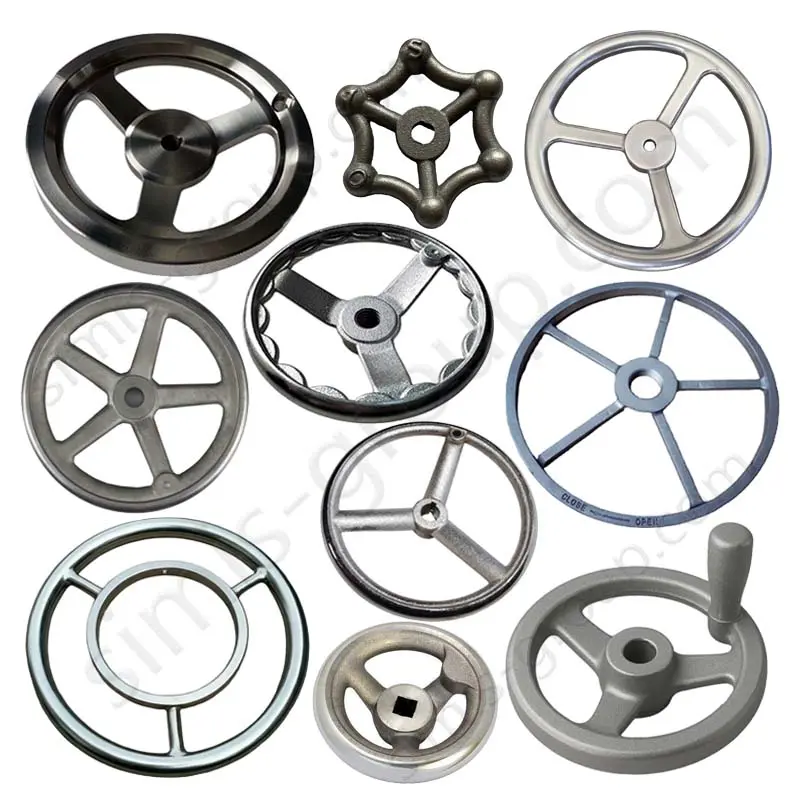
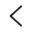Manufacturing Capabilities of Our Iron Casting Foundry

Iron Sand Casting
Simis Iron Sand Casting Foundry utilizes multiple molding techniques, including Static Pressure Molding, Automatic Molding, and Hand Molding, combined with the use of resin sand or clay sand. This results in low mold costs and high production flexibility, enabling us to meet the needs for cast iron parts production of all sizes and volumes, from small batches to large-scale production.
Cast Weight Range: 1 kg – 3,000 kg (Automatic Line); > 3,000 kg (Resin/Hand Molding)
Maximum Dimensions: Automatic Line: 2.5 m; Hand/Resin Molding: up to 4m
Dimensional Tolerance Grade: CT8 to CT13
Surface Roughness (Ra): Ra 12.5 to 50.0 μm (Depends on the mold type used)

Iron Shell Mold Casting
Iron shell mold casting involves pouring liquid iron into thin shell molds made from resin-coated sand. This process produces cast iron parts with high dimensional accuracy, superior surface finish, and high production efficiency. Suitable for the batch production of complex, small to medium-sized iron castings.
Cast Weight Range: 0.5 kg – 100 kg
Maximum Dimensions: 1.0 m × 0.8 m × 0.5 m
Dimensional Tolerance Grade: CT7 to CT9
Surface Roughness (Ra): Ra 6.3 to 12.5 μm
Machining Allowance: 1.0 mm to 2.5 mm

Iron Lost Foam Casting
Iorn lost foam casting (LFC) utilizes a foam pattern in place of traditional tooling; the iron vaporizes the foam upon pouring and solidifies into the final shape. Lost foam castings have no cores or parting lines, offering extreme design freedom, making the process suitable for manufacturing cast iron components with complex internal passages and fine structures.
Cast Weight Range: 0.5 kg – 1,000 kg
Maximum Dimensions: 1.5 m × 1.0 m × 1.0 m
Dimensional Tolerance Grade: CT6 to CT8
Surface Roughness (Ra): Ra 6.3 to 16.0 μm
Minimum Wall Thickness: 3 mm to 5 mm
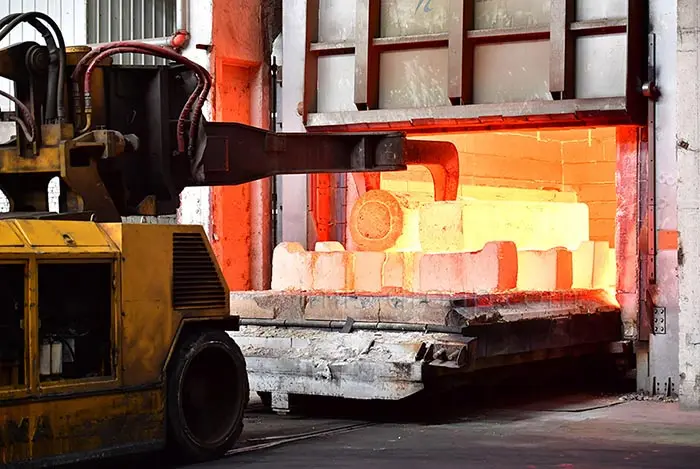

Heat Treatment
Heat treatment of cast iron parts is to improve their mechanical properties, eliminate casting stress, and improve the matrix structure. SIMIS Iron Foundry uses the following core heat treatment processes to meet customers' requirements for high strength, high toughness, or high wear resistance, depending on the different characteristics of gray cast iron and ductile iron.
Stress Relief Annealing: Eliminate internal stress; prevent part distortion.
Graphitization Annealing: Decompose cementite; increase ductility and toughness.(For white cast iron)
Normalizing: Homogenize matrix structure; enhance hardness and strength. (especially for ductile iron).
Quenching + Tempering (Q+T): Maximum strength and wear resistance; obtain martensitic matrix.
Austempering (ADI): Best combination of strength, toughness, and wear.(For ductile iron )

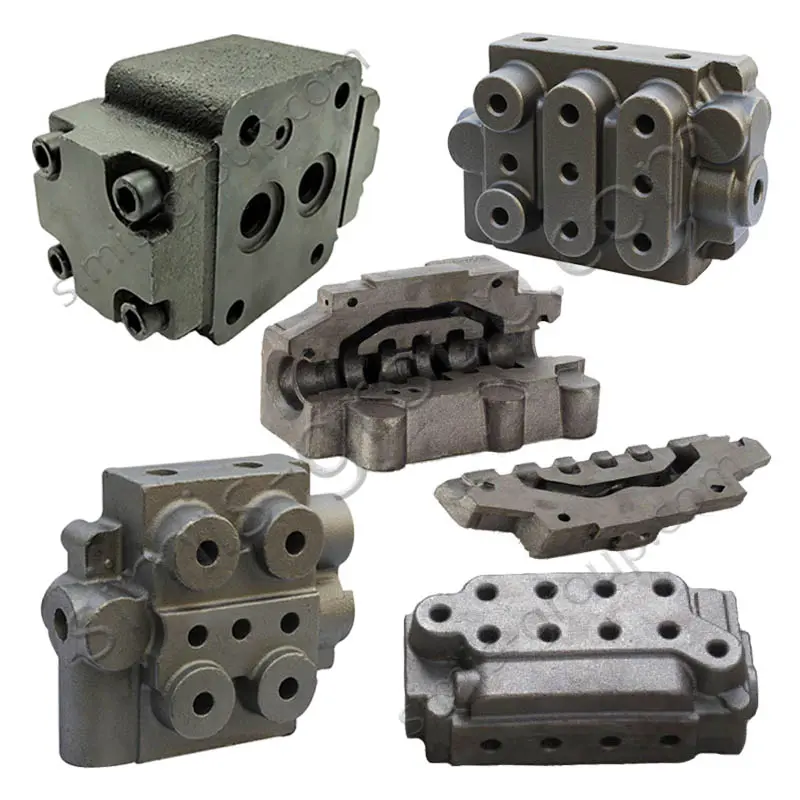
Machining
Machining ensures the final geometric accuracy and functional fit of iron castings. SIMIS Iron Foundry is equipped with high-precision CNC machine tools, enabling efficient handling of roughing, finishing, and ultra-finishing of all cast iron parts, ensuring that the flatness, coaxiality, and critical mating dimensions of the castings meet customers' stringent requirements.
Machining Tolerance: IT7 to IT4 Grade
Surface Finish (Ra): Ra 0.2 to 3.2 μm
Machined Part Weight Range: 1 kg – 5,000 kg
Quality Inspection Capability: CMM measurement accuracy up to ±0.005mm.

Surface Treatment
Surface treatment is used to improve the durability and environmental adaptability of cast iron parts. Because cast iron surfaces are prone to rust and some castings need to withstand friction, SIMIS Iron Foundry offers a variety of surface treatment processes to meet different customer requirements for corrosion resistance, increased hardness, and improved appearance.
Shot Blasting: Removes scale; surface stress relief.
Electroplating: Anti-corrosion and aesthetics; suitable for general use.
Hot Dip Galvanizing: Long-term, heavy-duty anti-corrosion; for outdoor heavy structure.
Painting/Coating: Basic corrosion protection; provides color coding.
Blackening/Phosphating: Short-term rust prevention; enhances coating adhesion.
Nitriding: Increases surface hardness and wear resistance.
OEM Custom Cast Iron Parts by Iron Foundry
Cast Iron Materials for Custom Casting Applications
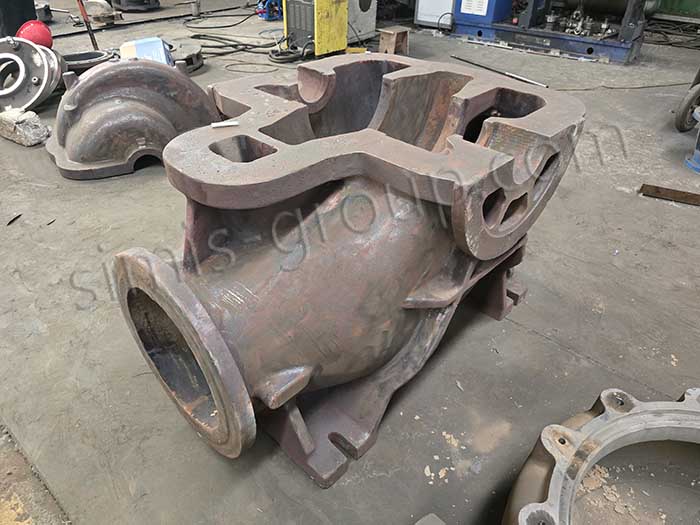



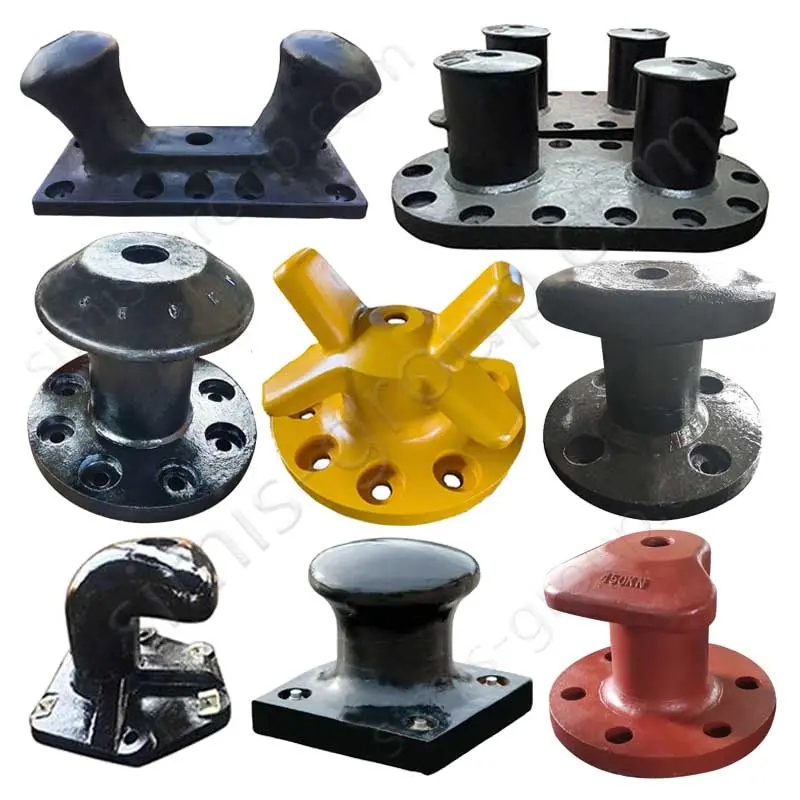
Gray Iron Casting
Grey Iron material with high compressive strength, good thermal conductivity, and easy machinability. Grey iron is valued for its high damping capacity, which effectively reduces operational vibration. This makes it a widely used, cost-effective material for manufacturing components like engine blocks, pump housings, and machine tool bases.
Simis Gray Iron Parts Include:
Brake discs
Engine cylinders
Machine tool beds
Pump housings
Valve bodies
Pipe systems
Ductile Iron Casting
Ductile iron achieves a combination of high strength, toughness, and good castability. It also maintains resistance to wear and processes well during machining. Ductile iron offers properties similar to steel but often at a lower material cost, making it suitable for complex parts that require high reliability.
Ductile Iron Parts from Simis:
Automotive parts (crankshafts, steering knuckles, differential housings)
Gears
Large farm machinery parts
Valves and pipe systems
Rollers
Pressure housings
Austempered Ductile Iron Casting
Austempered Ductile Iron (ADI) achieves high strength, toughness, and wear resistance from a post-casting heat treatment called austempering. ADI provides improved mechanical properties compared to standard ductile iron and is often used as a direct alternative to many forged and cast steels. This makes it suitable for parts that require a balance of high strength, reduced weight, and cost efficiency.
ADI Parts from Simis Iron Foundry:
Gears, suspension parts, and engine crankshafts for heavy trucks and rail lines
Track shoes, sprockets, and drive gears for construction equipment
Cutting tools and gears for farm machinery
High-performance reducer gears
Camshafts
Mining parts that need high safety
Alloy Cast Iron Casting
Alloy Cast Iron differs from standard iron due to the addition of one or more specific elements. These elements typically include chromium, nickel, molybdenum, and copper. This alloying enhances key properties, such as wear resistance, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance. The specific alloy composition is selected based on the component's service environment, such as the wear mechanism or the operating temperature.
Alloy Cast Iron Parts from Simis:
Wear-Resistant Parts(High Chromium Cast Iron/Nickel-Chromium Cast Iron): Rollers, Shot Blasting Blades, Liners, Slurry Pump Casings.
Heat-Resistant Parts: Boiler Grates, Heat Exchangers, Furnace Floors, Flue Gates.
Corrosion-Resistant Parts(High Silicon Cast Iron): Chemical Valves, Pump Casings, Pipes, Pickling Tanks.
Special-Use Parts: Machine Tool Guides, Cylinder Liners, Automotive Camshafts.
Industries Served by Our Iron Casting Foundry
How to Customize Iron Castings with Iron Foundry
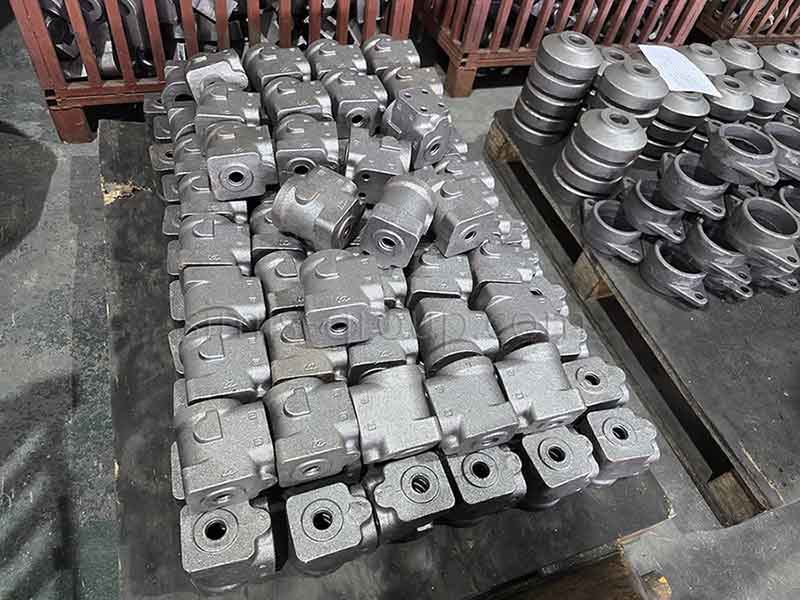
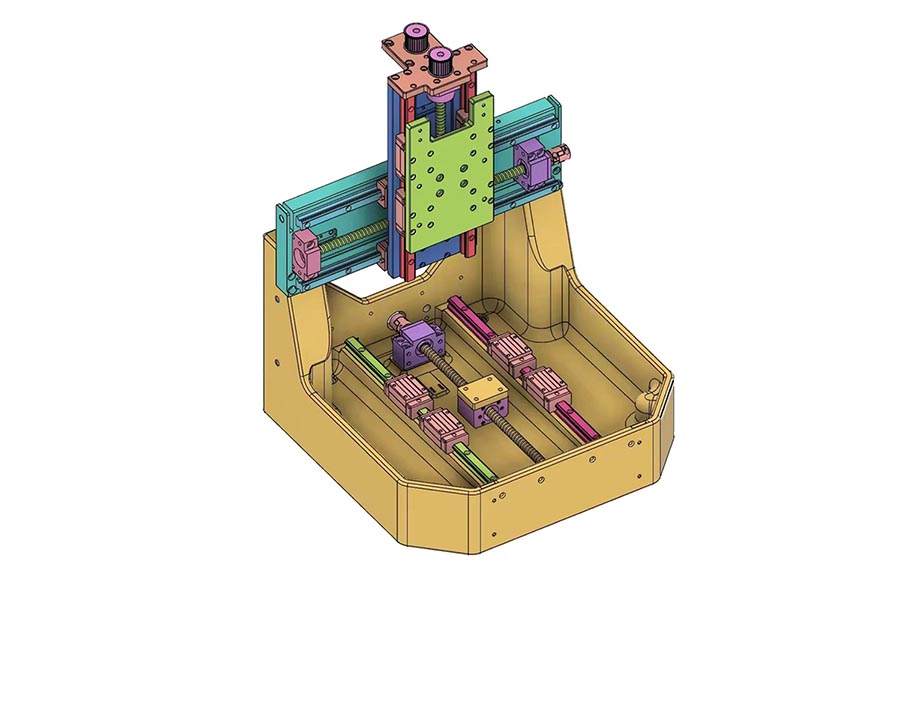

Confirm Manufacturing Requirements for Cast Iron Parts
Design Review and Samples
Simis engineers first check the 3D and plane drawings. This makes sure your design is ready for manufacturing. If you have a sample part, we can make the new parts based on that sample.
Define Part Requirements
We confirm what the part needs to do. This includes things like its strength, hardness, wear, and rust resistance. We also set the exact size, tolerance, and finish quality needed.
Confirm Casting Material
Our engineers help you pick the right cast iron material. This choice depends on where the part will be used and your technical needs. We give advice based on material cost, strength, and resistance to wear or rust.
Choose the Casting Method
We select the best casting process for your part. We base this choice on your price goal, the part’s shape, its required accuracy, and the material.
Make Molds and Samples
We build the casting molds using your approved drawings or samples. Then, we cast the first batch of samples using the chosen material and process.
Full Sample Inspection
The finished samples go through a full check. This confirms they meet all design standards and your quality demands. We give you reports covering size, performance, material makeup, and non-destructive testing.
Mass Production of Cast Iron Parts
Mass Production
After you check and approve the sample, we start the mass production plan. We get all the materials ready based on your order. We use the exact same machines and process as we did for the sample. This makes sure every single part we make is the same.
Quality Control During Production
We run tight quality checks while making the parts. We pull parts for checks often during the process. We test their size, look, and strength. This ensures every batch of cast iron parts is consistent and meets your needs.
Final Product Quality Inspection
We use multiple inspectors for the final check. They do many tests on the finished product. These tests cover size accuracy, surface quality, and part strength. This step makes sure all cast iron parts meet your quality standards.
Packaging and Delivery
We securely package and ship all approved parts. We pick the right packaging to prevent damage during shipping. We also choose the best delivery method (air, sea, or land) to get your parts to you on time.




To order custom parts, please email us your design drawings and 3D models. Our team will review the detailed part parameters and the 3D model to provide you with an accurate quote.