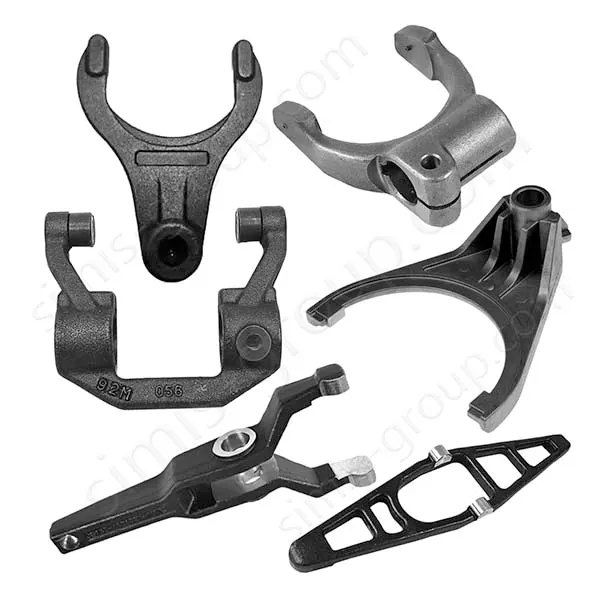
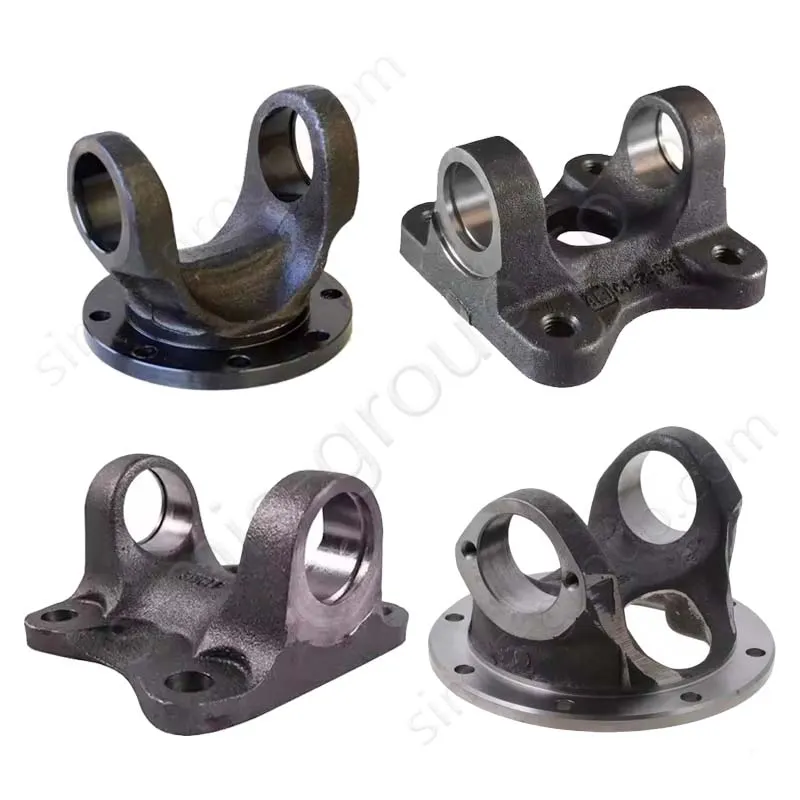
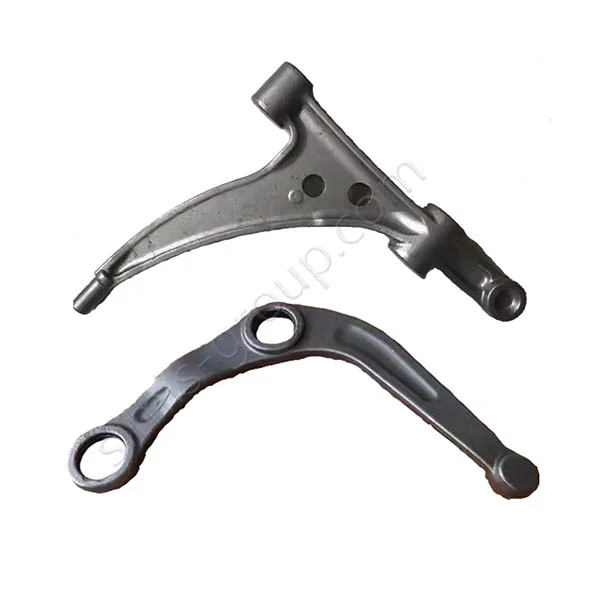
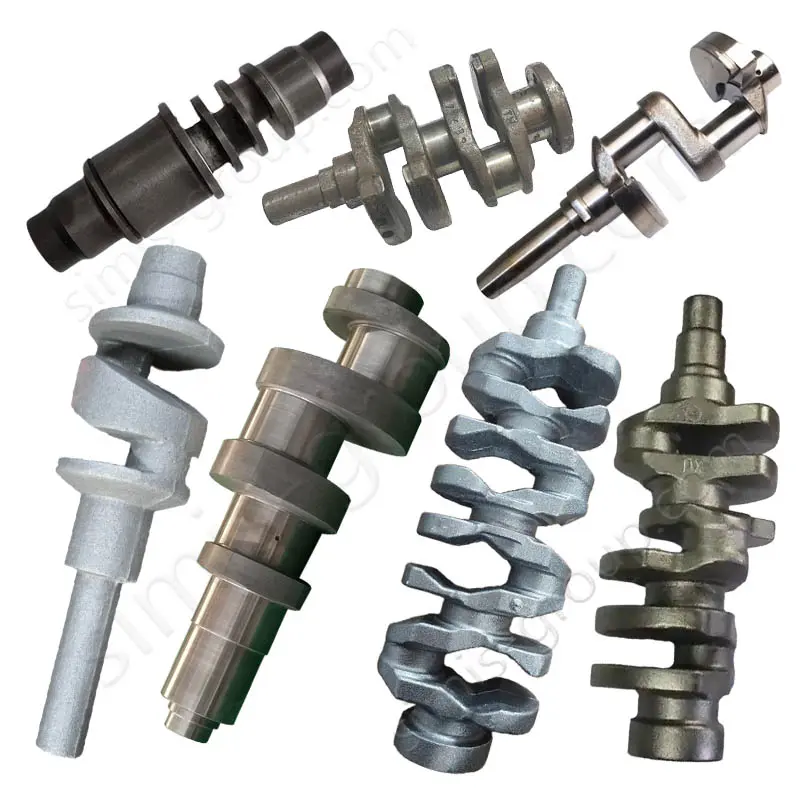
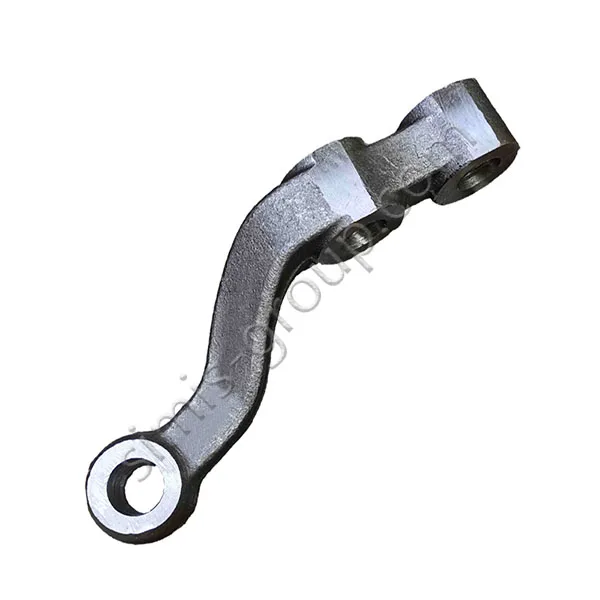
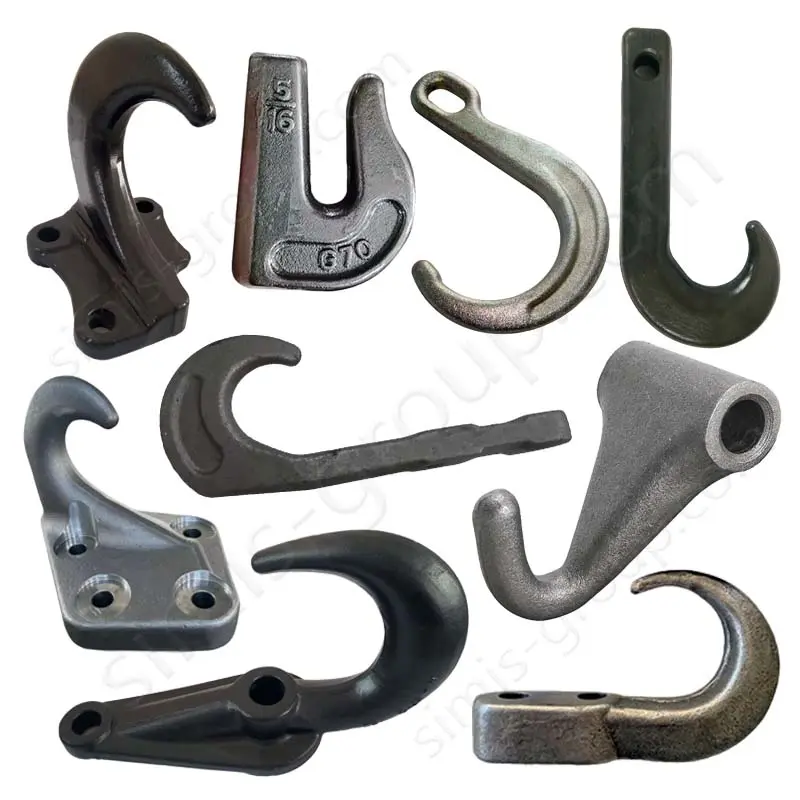
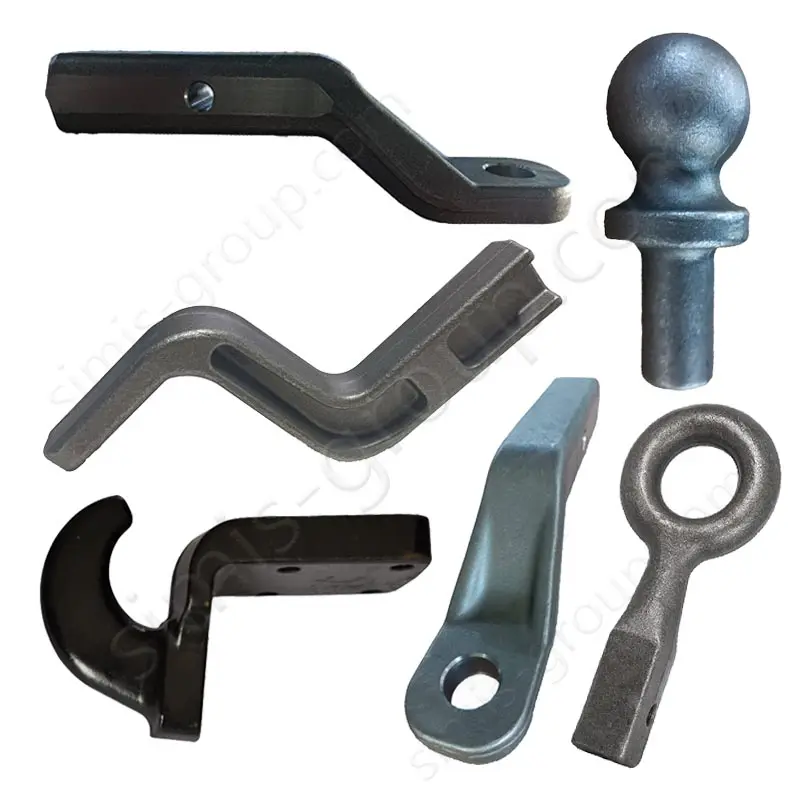
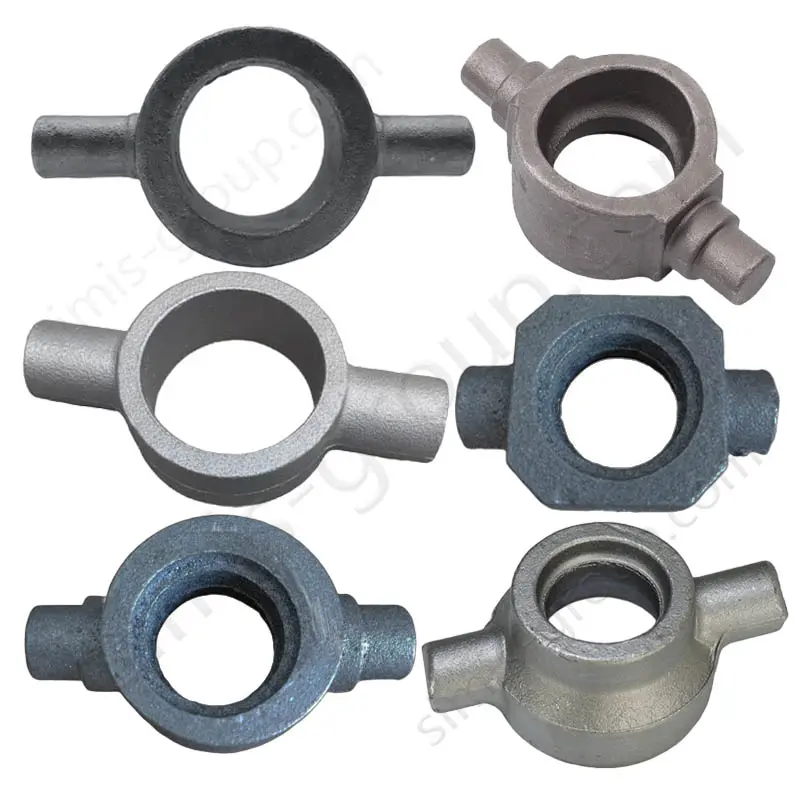
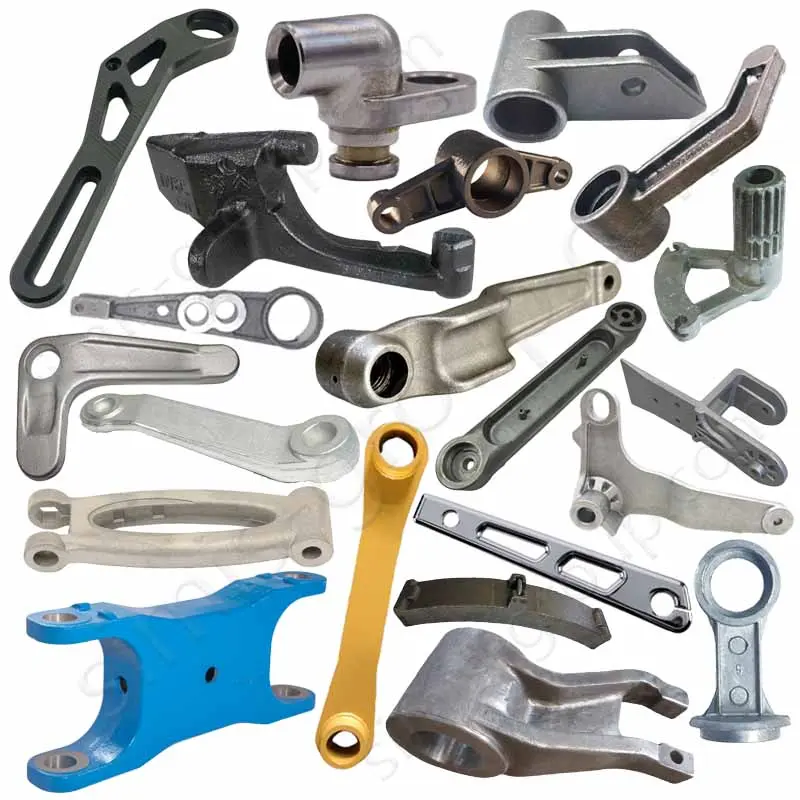
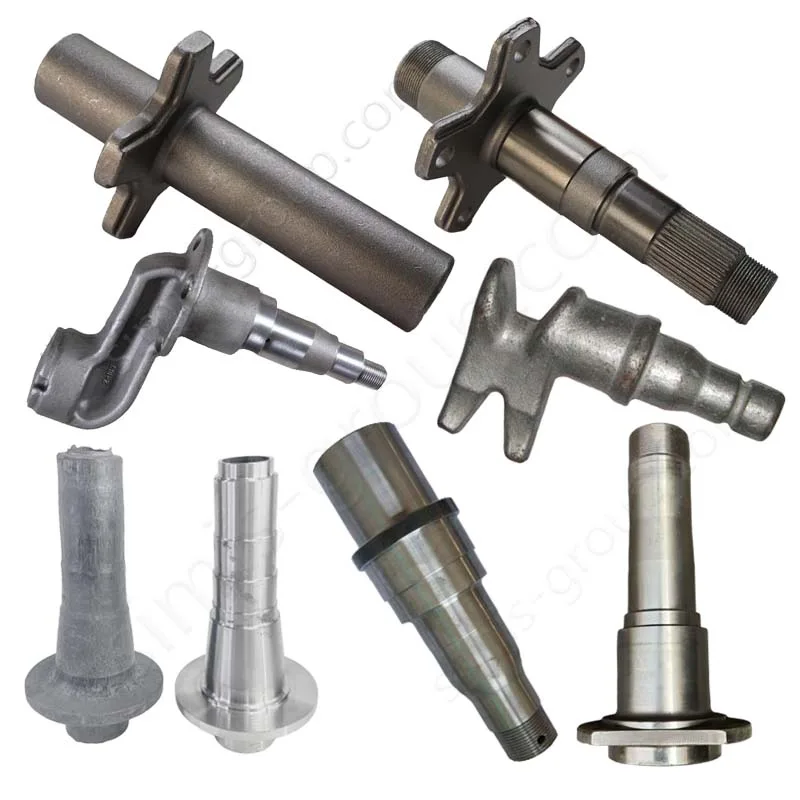
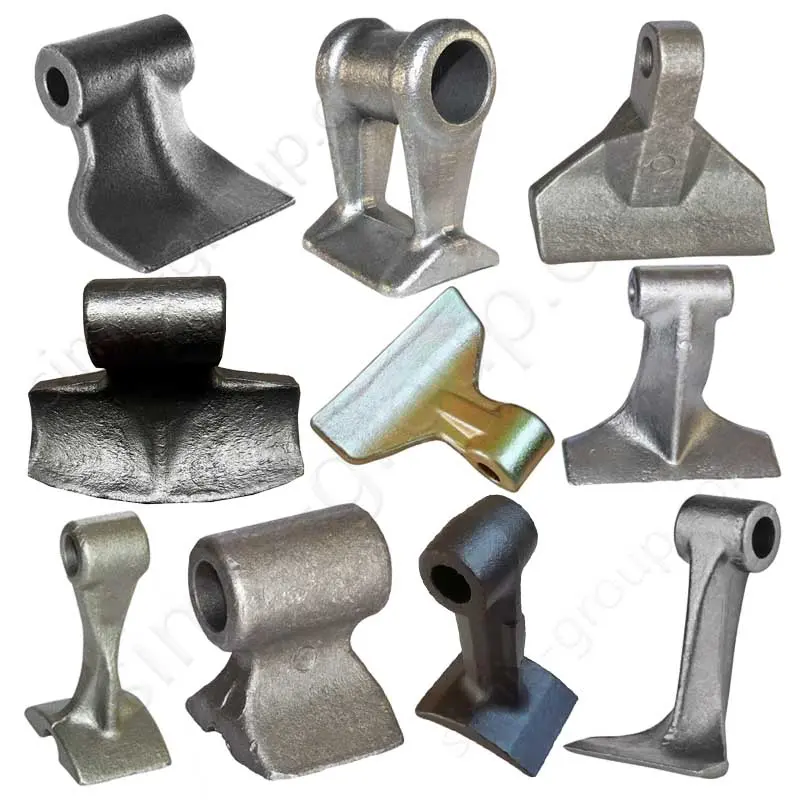
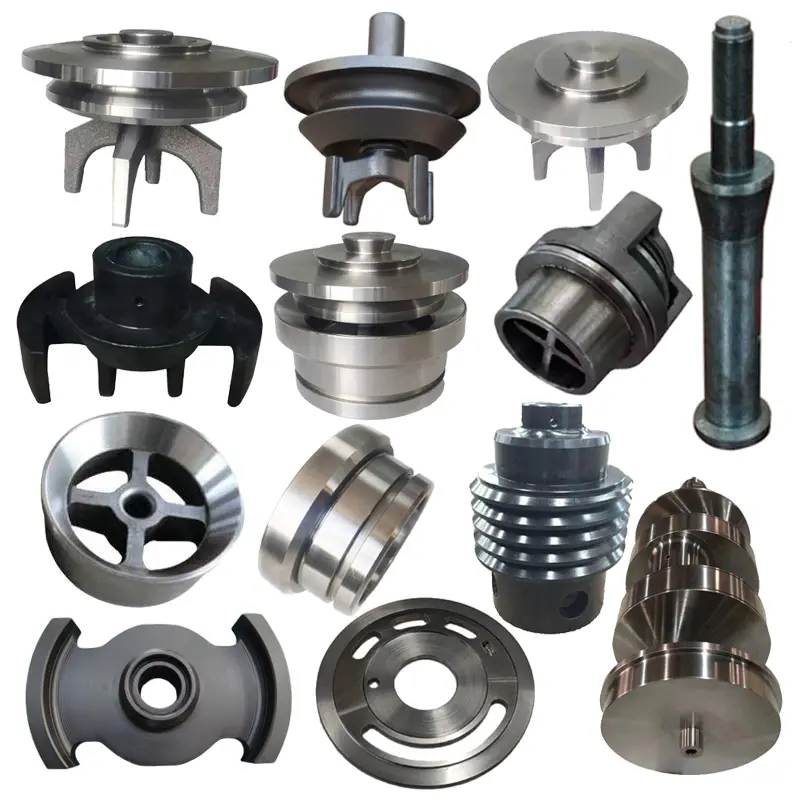
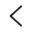Manufacturing Capabilities of Steel Forging Factory

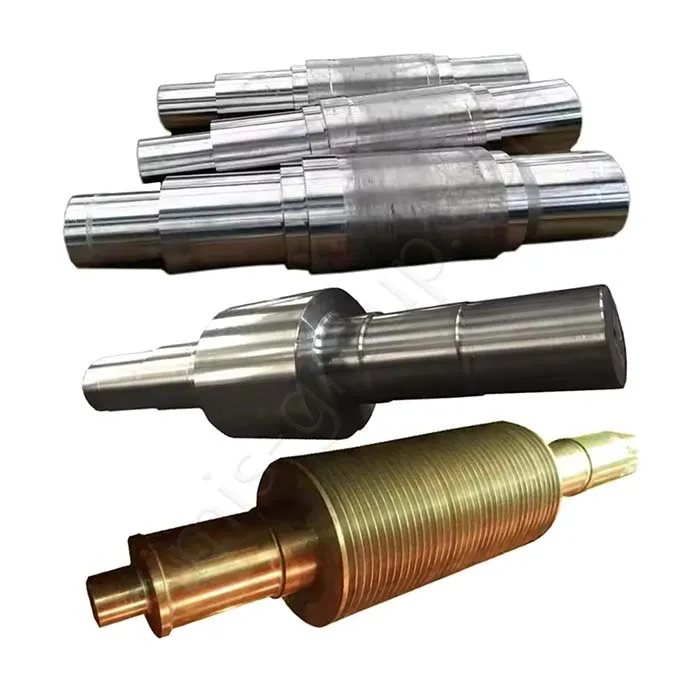
Steel Open-die Forging
Steel Open Die Forging (also known as Free Forging) involves placing a heated steel ingot or billet between two simple-shaped dies (typically flat or slightly contoured) and repeatedly shaping it through immense pressure or impact. This process is primarily used for the production of custom, large-scale shafts, cylinders, discs, and block-type components.
Max. Dimensions: Diameter ≤ 1.2 m, Length ≤ 6.0 m
Cranes Max. lifting capacity: 25 tons
Forging Weight Range: 50 kg – 8,000 kg
Tolerance Class: Loose (Further machining is required.)
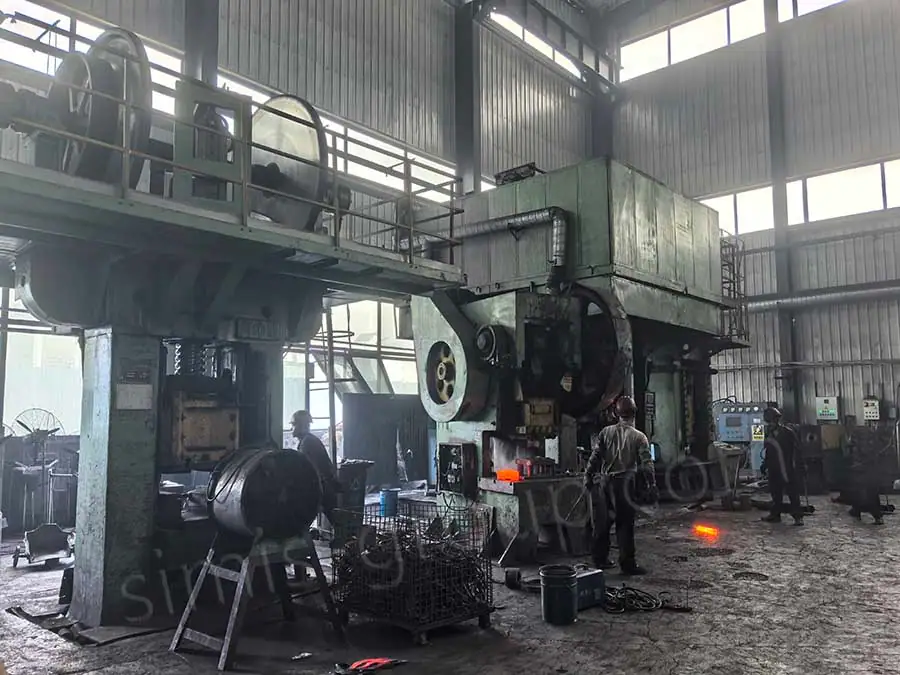

Steel Closed Die Forging
Steel Closed Die Forging (also known as Impression Die Forging) involves placing a heated steel billet into a die cavity of specific shape, where immense pressure forces the metal to flow and fill the enclosed impression. This process offers high production efficiency and, while maintaining the high strength and dense internal structure of the forgings, can achieve complex geometries and extremely high dimensional accuracy.
Forging Weight Range: 0.2 kg – 25 kg
Max Forged Dimensions: 0.6 m x 0.4 m x 0.2 m
High dimensional accuracy: tolerance up to ±0.3 mm
Dimensional Tolerance Grade: IT12 - IT14 Grade
Machining Allowance: 1.5 mm - 5 mm

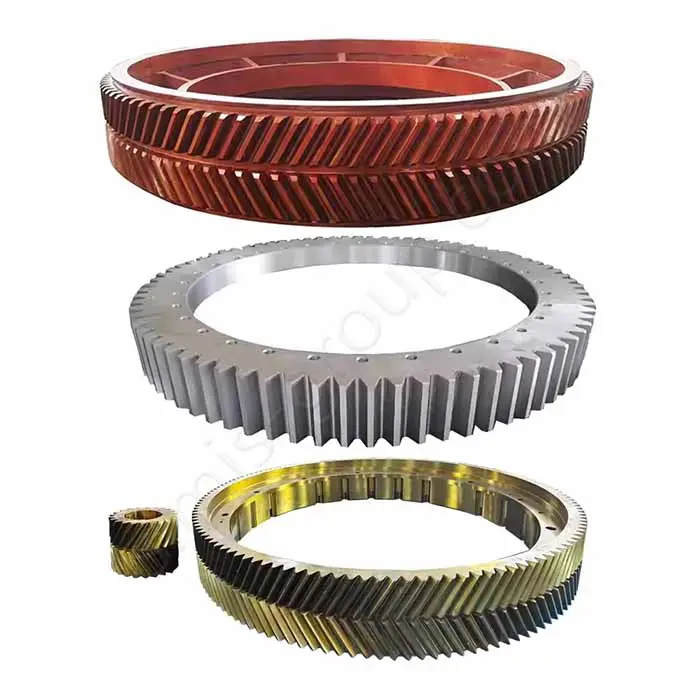
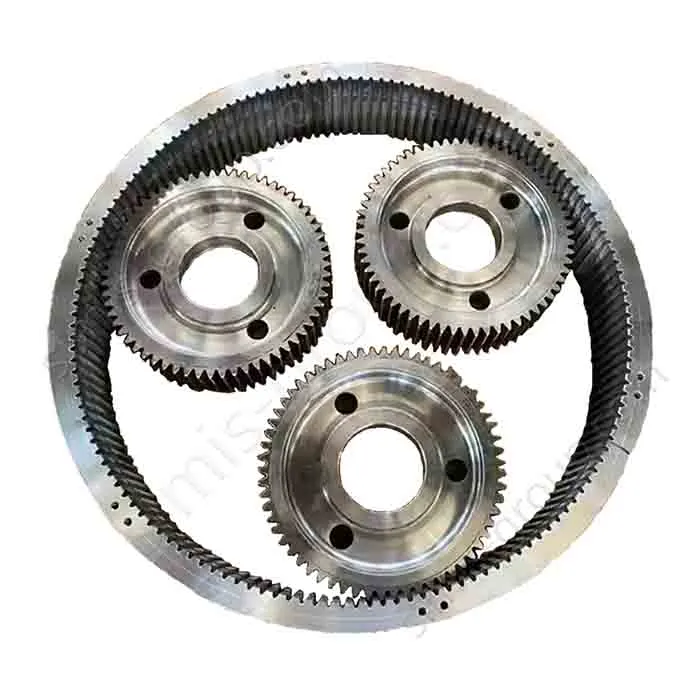
Steel Ring Forging
Steel ring forging (also called ring rolling) first involves forming a steel billet into a ring-shaped preform (cake) with a central hole, and then pressing it with radial and axial rolls to continuously increase its diameter and gradually decrease its wall thickness, eventually forming a seamless ring.
Product Size Range: Outer diameter Ø300–Ø6,000 mm; height ≤ 800 mm
Ring Characteristics: Seamless, Tangential Grain Flow
Single Piece Weight: 10 kg – 8,000 kg
Steel Cold Forging
Steel cold forging involves applying extremely high pressure to a steel billet at room temperature to shape it without heating. This significantly improves the strength and hardness of the forgings, resulting in forgings with extremely high dimensional accuracy and surface finish. This process is suitable for the mass production of small, high-precision, high-strength transmission steel forgings.
Forging Weight Range: 0.05 kg – 5 kg
Max Dimensions: Ф100 mm (Diameter)/200 mm(Length)
Dimensional Tolerance: IT8 - IT10 Grade
Surface Finish (Ra): Ra 0.8 to 3.2 μm
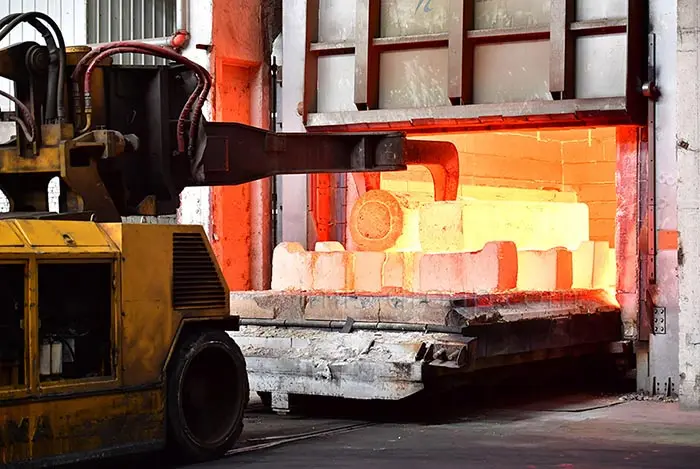

Heat Treatment
Heat treatment involves precisely controlling the heating and cooling of steel forgings to alter the internal structure of the steel, eliminate internal stress, and optimize mechanical properties. High-performance steel forgings must undergo heat treatment to meet customers' stringent requirements for strength, hardness, toughness, fatigue strength, and dimensional stability.
Normalizing: Refine grains; uniform structure.
Annealing: Soften material; improve cutting.
Quenching: Max strength; increase hardness.
Tempering: Increase toughness; reduce brittleness.
Quenching & Tempering: Optimal strength-toughness balance.
Stress Relief Annealing: Eliminate stress; dimensional stability.

Machining
Machining refers to removing forging allowances from steel forgings, correcting tolerances, and forming critical mating surfaces. SIMIS Steel Forging Factory uses high-rigidity, high-power CNC machine tools to complete the entire process from heavy roughing (removing allowances and oxide scale) to precision finishing (achieving critical fits), ensuring that critical parts of the forgings reach an accuracy level of IT7 or even IT5.
Machining Tolerance: IT7 to IT5 Grade
Surface Finish (Ra): Ra 3.2 to 0.4 μm
Geometric Accuracy: Concentricity, Parallelism < 0.01 mm
Handling Capacity: Covers Open Die Shafts up to 6000 mm long
OEM Custom Forged Steel Parts by Steel Forging Factory
Forged Steel Materials for Custom Forging Applications
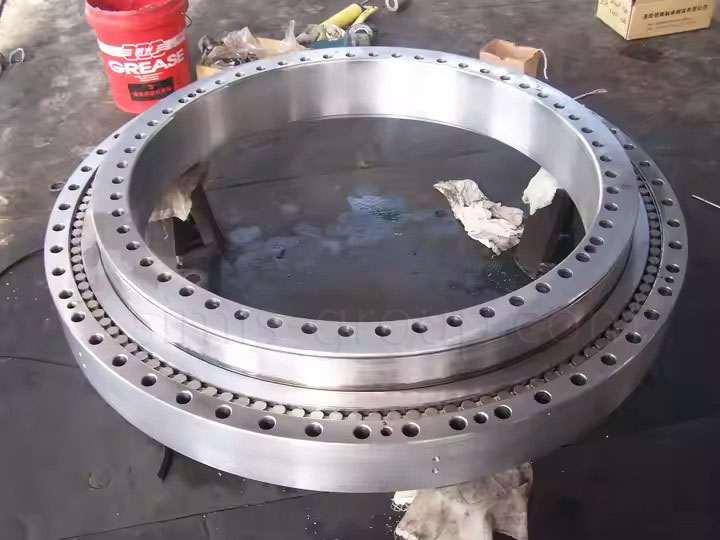
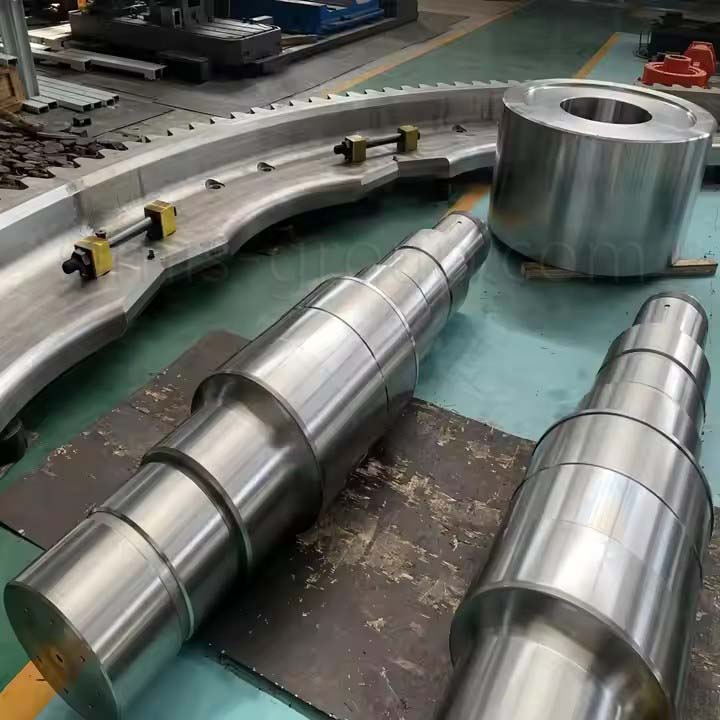
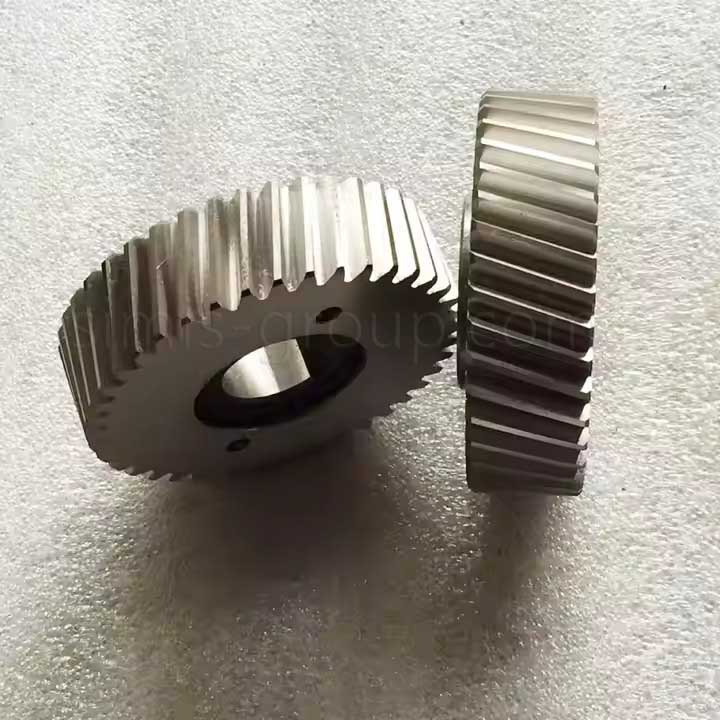



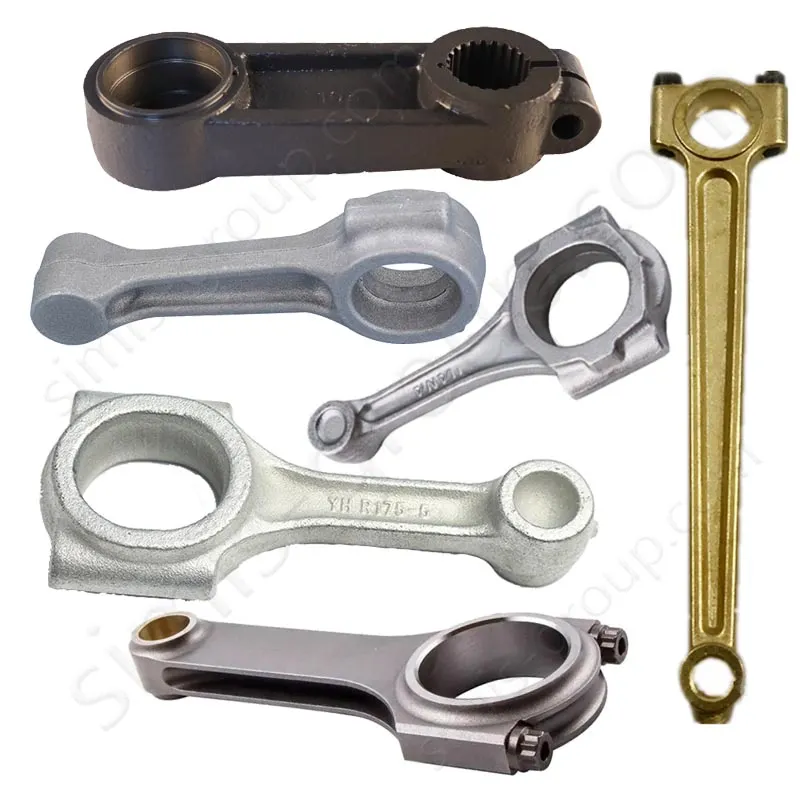
Carbon Steel Forging
Forging Carbon Steel improves the material's internal structure by refining the grain flow and eliminating internal discontinuities. Forging process results in components with maximized strength, high impact resistance, and enhanced fatigue life compared to cast parts.
Forged Carbon Steel Parts from Simis Steel Forging Factory:
Car crankshafts and connecting rods;
Gears and transmission shafts;
Hand tools (wrenches, hammers);
Construction machine parts;
Railway axles and wheels;
Industrial shafts and couplings.
Simis can forged carbon steel types:
Low Carbon Steel Forgings: General structural parts, car body parts, construction hardware, and case-hardened components.
Medium Carbon Steel Forgings: Car crankshafts, connecting rods, gears, axles, and strong structural parts.
High Carbon Steel Forgings: Cutting tools, springs, strong wire, wear parts, and railway wheels.
Free-Cutting Carbon Steel Forgings: High-volume parts that need a lot of machining, like fasteners, fittings, and car parts.
Stainless Steel Forging
Forging Stainless Steel refines the material's grain structure, which enhances its already strong properties. The forging process significantly increases the stainless steel's mechanical strength, improves its fatigue resistance, and maintains its high level of corrosion resistance across the entire component.
Forged Stainless Steel Components by Simis Steel Forging Factory:
High-pressure flanges and valves for oil and gas;
Important marine parts;
Surgical tools and medical implants;
Food processing parts;
Chemical tank components;
Turbine blades.
Simis can forged stainless steel types:
Austenitic Stainless Steel Forgings: Good for chemical, food, and medical parts.
Martensitic Stainless Steel Forgings: Good for strong tools and parts like surgical instruments.
Duplex Stainless Steel Forgings: Good for tough places like offshore oil rigs and chemical plants.
Alloy Steel Forging
Forging alloy steel adds specific elements like nickel and chromium to carbon steel before shaping it. The metal is heated and then pressed into form. This process boosts the steel's strength, hardening ability, and performance in harsh conditions.
Forged Alloy Steel Parts from Simis Steel Forging Factory:
Turbine and rotor shafts;
High-performance gears and pinions;
Heavy-duty axles;
Aircraft landing gear parts;
High-pressure valve bodies for oil and gas;
Specialized tools and dies.
Simis can forged alloy steel types:
Chromium-Molybdenum (Cr-Mo) Steels: Strong shafts, gears, tool joints, and parts needing good toughness in moderate heat.
Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum (Ni-Cr-Mo) Steels: Critical parts needing the highest strength, toughness, and fatigue life (e.g., aircraft gear and heavy crankshafts).
Bearing Steels (High Carbon Chromium): Parts needing extreme hardness and long rolling fatigue life (e.g., bearings and races).
Boron-Alloyed Steel: Good for fasteners and automotive parts that need good hardenability.
Special Purpose Forged Steel
Special purpose forged steel is designed for jobs with extreme demands. This includes high heat, high pressure, or special wear. These steels use complex alloys (like high nickel, cobalt, or tungsten) to achieve traits that standard steels cannot match.
Special Purpose Forged Steel Components by Simis Steel Forging Factory:
Turbine discs and blades;
Deep-sea drilling tools;
High-temperature fasteners;
Non-magnetic shafts;
Specialized tool steel dies.
Simis can forged special purpose steel types:
High-Nickel Alloys (Superalloys): Gas turbine components, furnace parts, and high-temperature pressure vessels.
Tool Steels (Hot Work / High Speed): Forging dies, hot shear blades, and cutting tools that run at high temperatures.
Maraging Steels: Parts needing ultra-high strength and good toughness with simple heat treatment.
Non-Magnetic Steels: Parts for mining and electrical gear where a magnetic field must be avoided.
Industries Served by Our Steel Forging Factory
How to Customize Steel Forgings with Steel Forging Factory

Confirm customization requirements
Design Review and Samples
Simis engineers first check the 3D and plane drawings. This makes sure your design is ready for the forging process. If you have a sample part, we can make the new parts based on that sample.
Define Part Requirements
We confirm what the part needs to do. This includes things like its strength, hardness, wear, and rust resistance. We also set the exact size, tolerance, and finish quality needed for the forged part.
Confirm Forging Material
Our engineers help you pick the right steel material. This choice depends on where the part will be used and your technical needs. We give advice based on material cost, strength, and resistance to wear or rust.
Choose the Forging Process
We select the best forging process for your part. We base this choice on your price goal, the part’s shape, its required dimensional accuracy, and the material.
Make Dies and Samples
We build the forging dies (molds) using your approved drawings or samples. Then, we shape the steel material through the chosen process to produce the first batch of samples.
Full Sample Inspection
The finished samples go through a full check. This confirms they meet all design standards and your quality demands. We give you reports covering size and tolerance inspection, performance testing, chemical composition analysis, and non-destructive testing.
Production and quality control
7. Mass Production
After you check and approve the sample, we start the mass production plan. We get all the materials ready based on your order. We use the exact same forging equipment and process as we did for the sample. This makes sure every single part we make is the same.
8. Quality Control During Production
We run tight quality checks while making the parts. We pull parts for checks often during the process. We test their size, look, and strength. This ensures every batch of forged steel parts is consistent and meets your needs.
9. Final Product Quality Inspection
We use multiple inspectors for the final check. They do many tests on the finished product. These tests cover size accuracy, surface quality, and part strength. This step makes sure all forged steel parts meet your quality standards.
10. Packaging and Delivery
We securely package and ship all approved parts. We pick the right packaging to prevent damage during shipping. We also choose the best delivery method (air, sea, or land) to get your parts to you on time.




To order custom parts, please email us your design drawings and 3D models. Our team will review the detailed part parameters and the 3D model to provide you with an accurate quote.