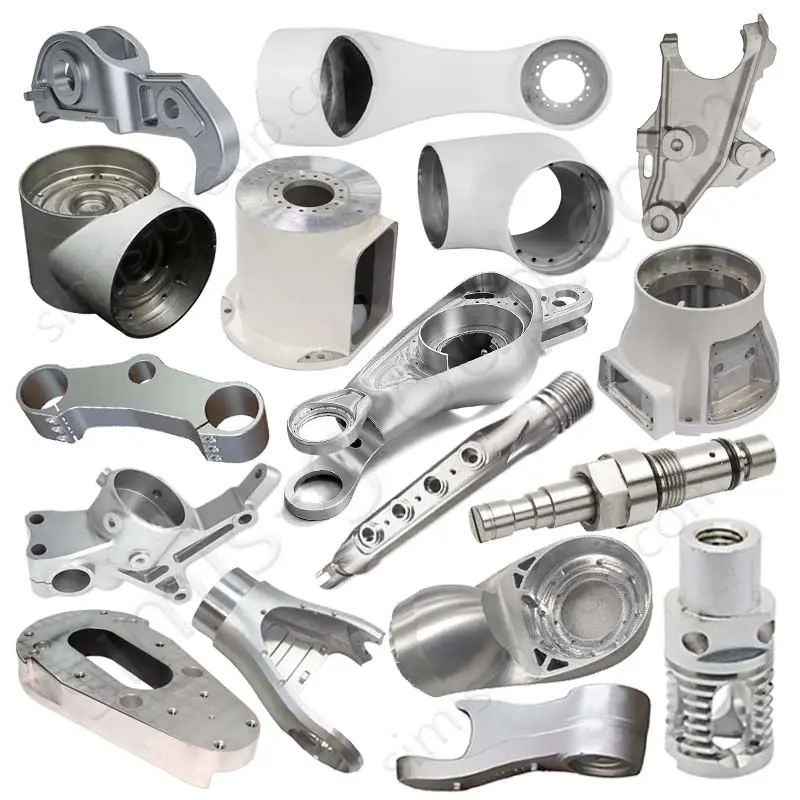
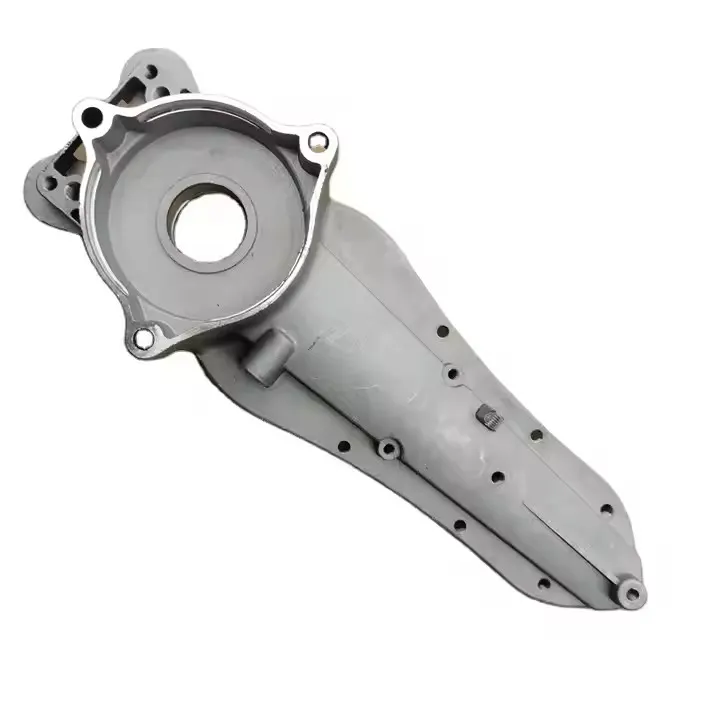
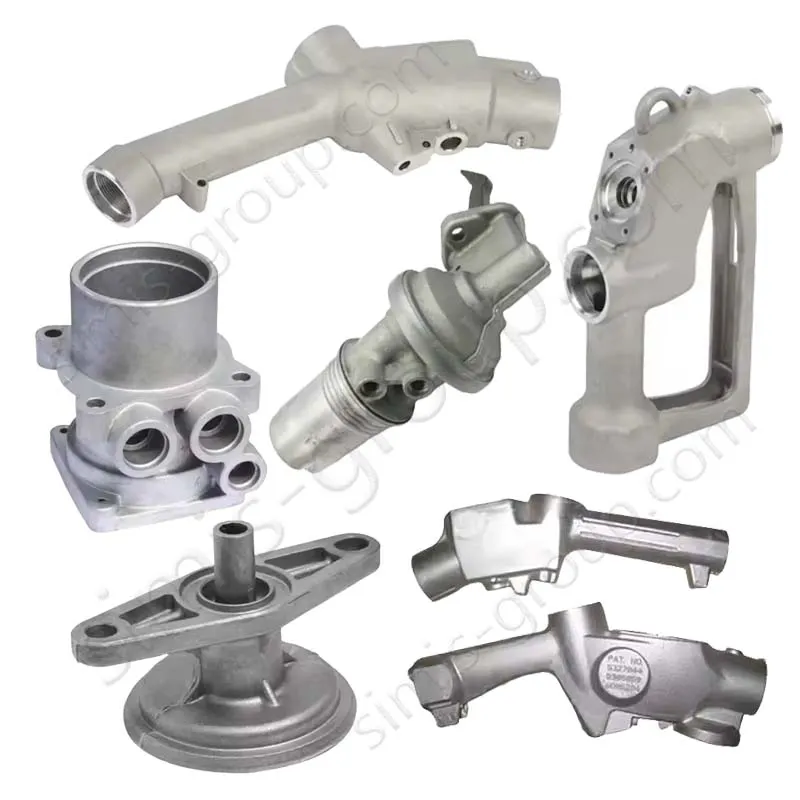
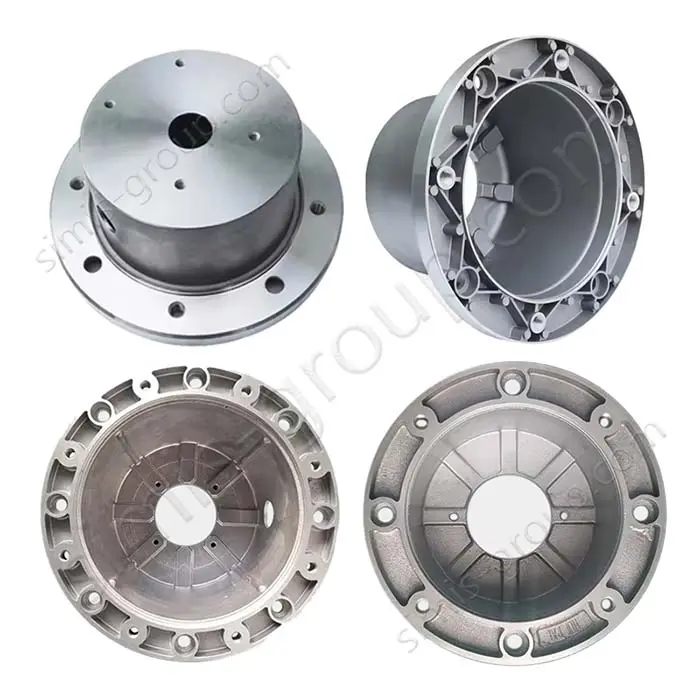
Gravity Permanent Mold Casting Foundry for OEM Custom Manufacturing
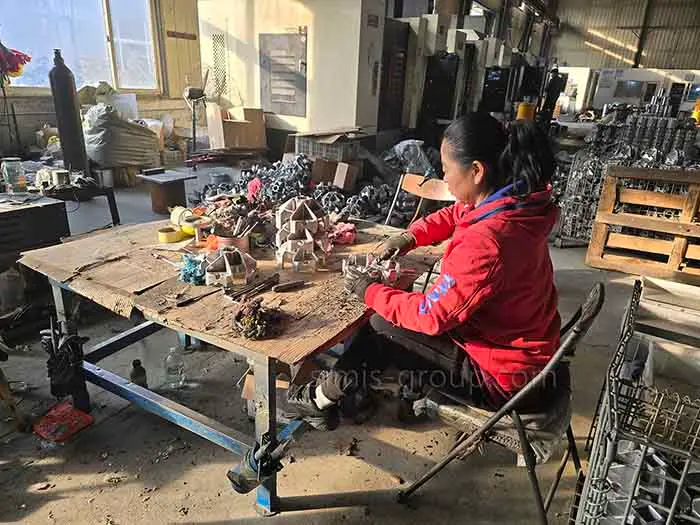
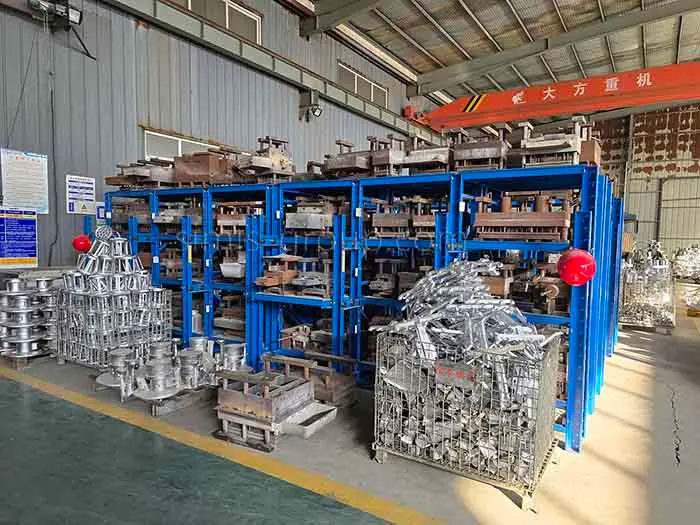
Gravity Permanent Mold Casting Factory Introduction
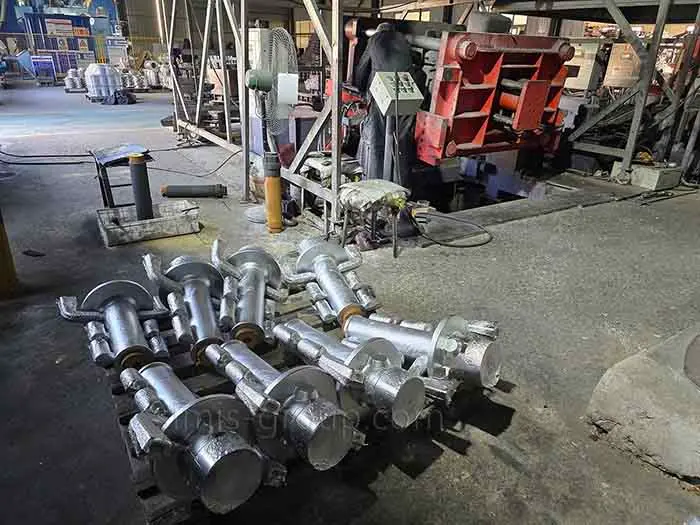
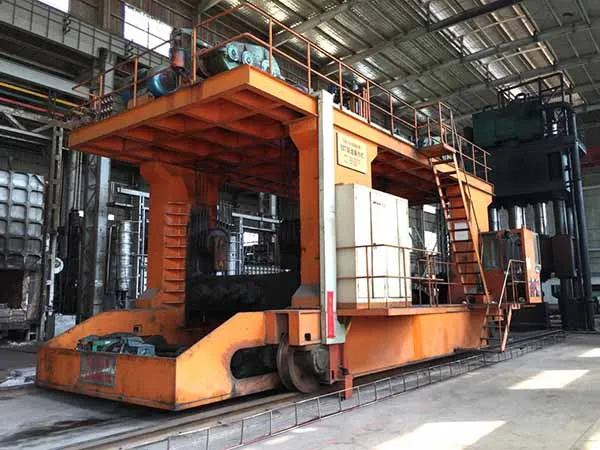
The SIMIS Gravity Permanent Mold Foundry focuses on producing high-quality aluminum, copper, and magnesium alloy castings. We use advanced gravity die casting (permanent mold casting) technology, which relies on reusable metal molds to pour molten alloys under the force of gravity.This specialized process delivers excellent dimensional accuracy and superior surface quality, making it the ideal choice for medium-to-high volume production where consistency and precision are critical.
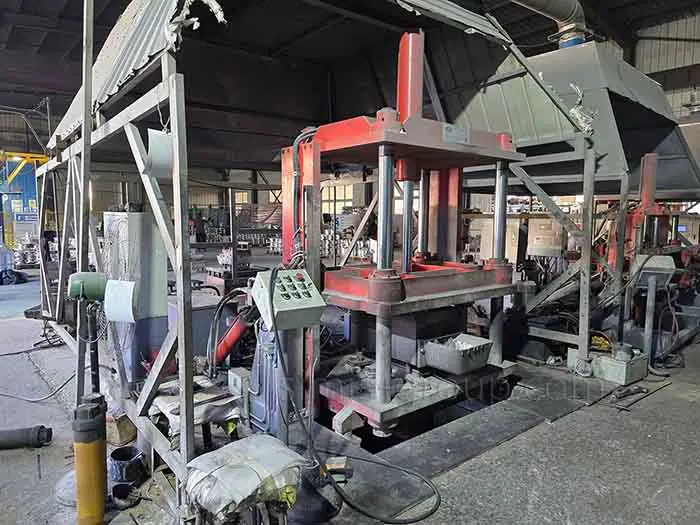
Melting Capacity: We utilize multiple Medium-Frequency Induction and Resistance Furnaces (ranging from 300 kg up to 1 ton) for flexible alloy handling and precise temperature control.
Pouring Automation: Semi-Automatic Gravity Pouring Machines with adjustable tilt control ensure smooth, controlled mold filling, minimizing turbulence and internal defects.
Mold Management: Advanced Mold Heating and Cooling Systems use circulating oil/water to regulate temperature, which is essential for maximizing mold life and achieving consistent casting microstructure.
Casting Weight: 0.1 kg – 100 kg
Maximum Dimensions: 800 mm × 800 mm × 400 mm
Min Wall : 3.5 mm
Dimensional Accuracy: CT6 – CT8
Surface Roughness (Ra): 3.2 – 6.3 μm
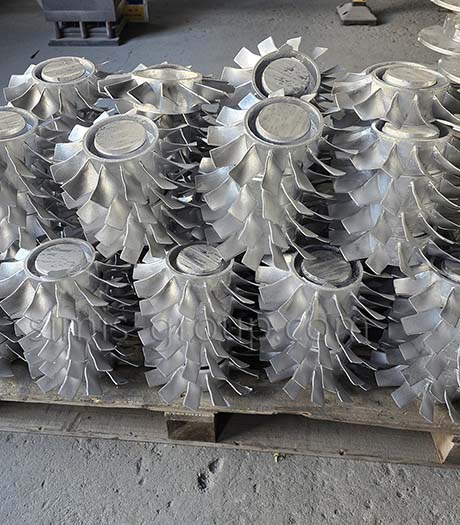
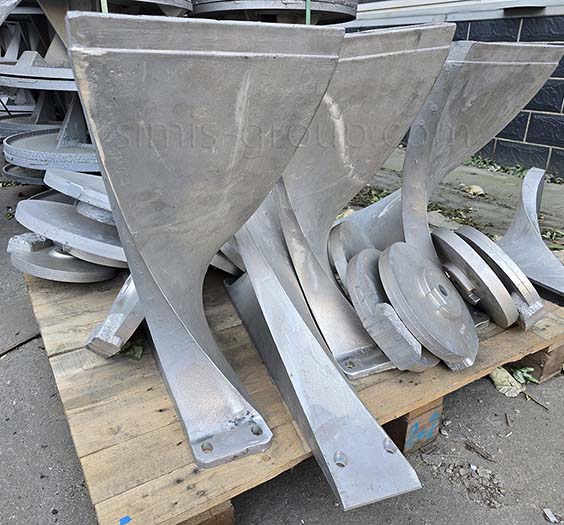
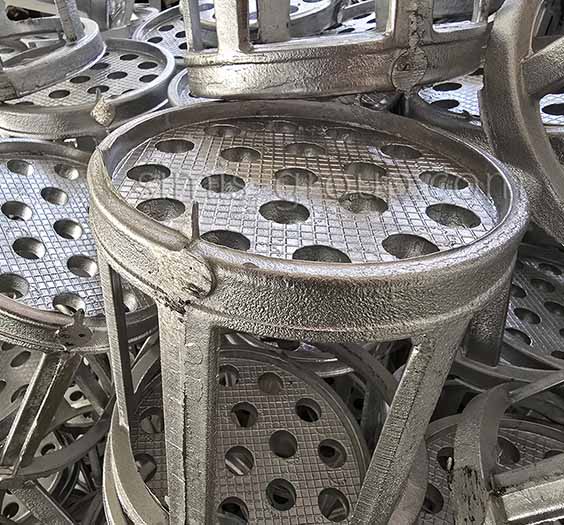
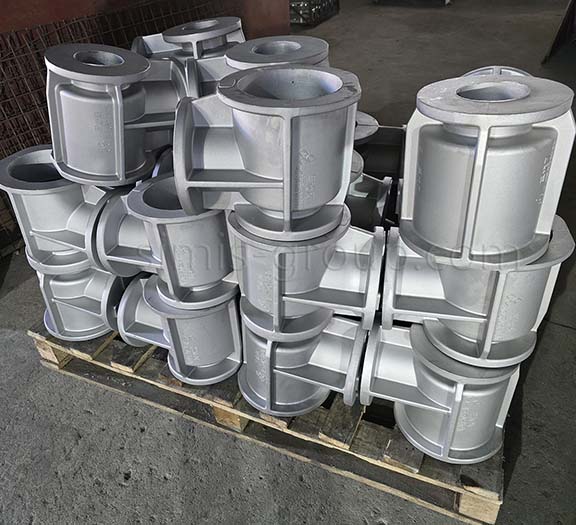
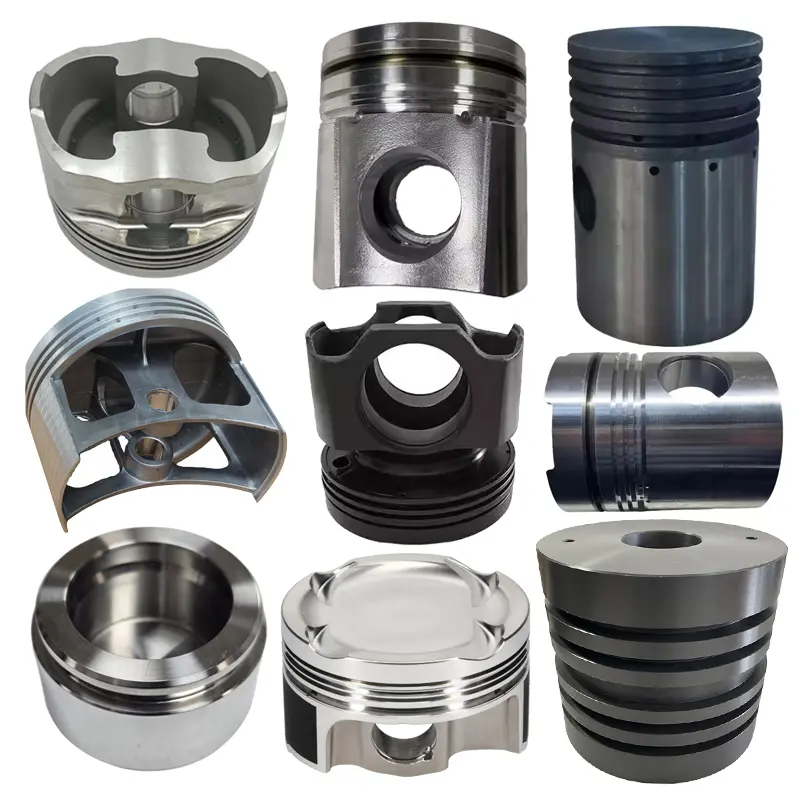
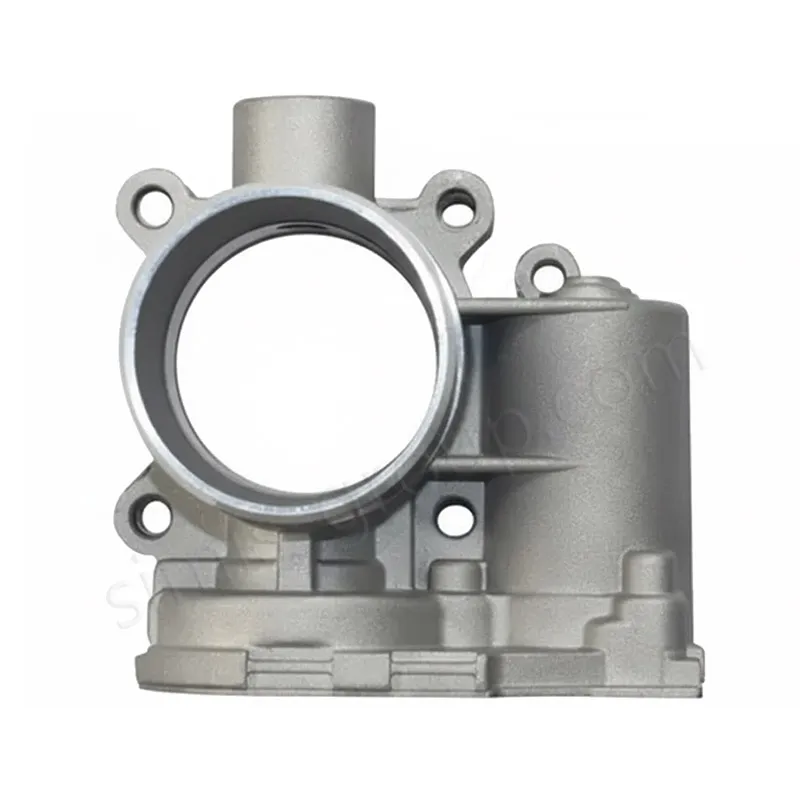
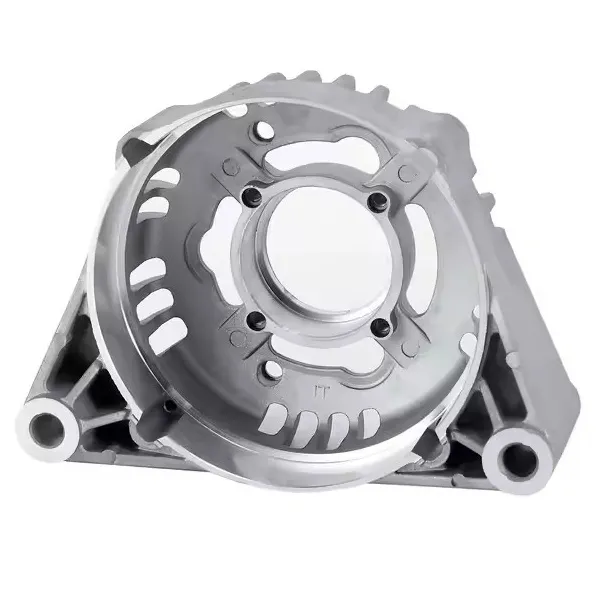
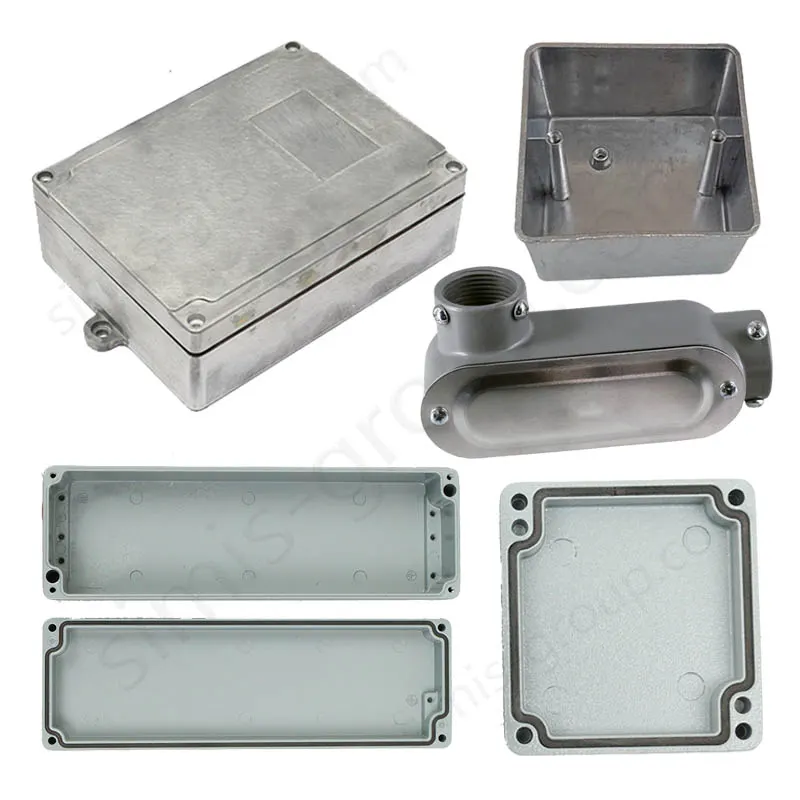
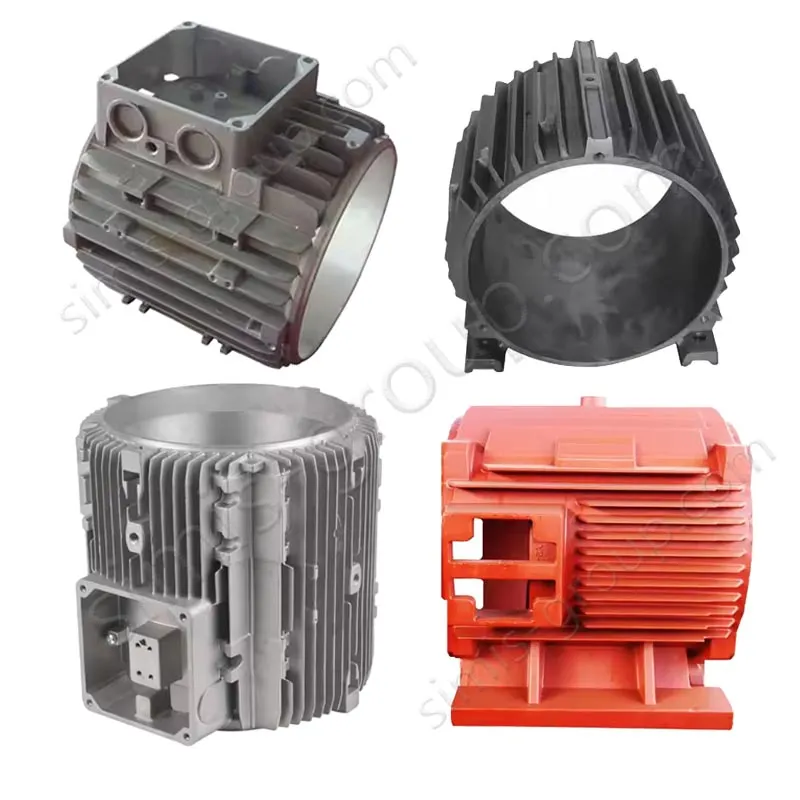
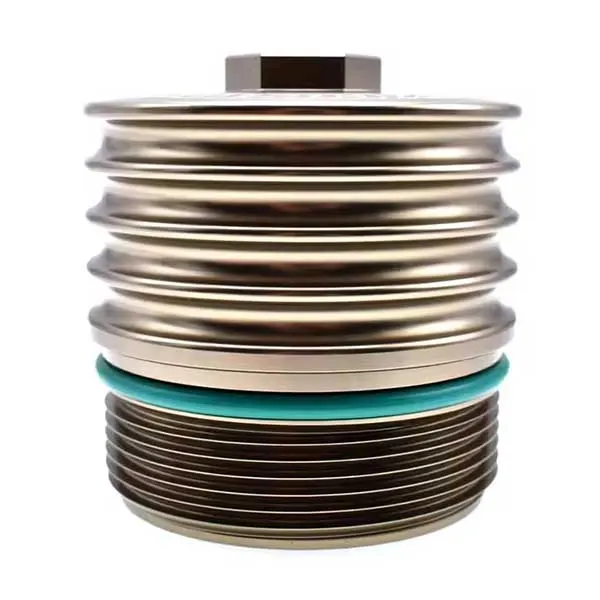
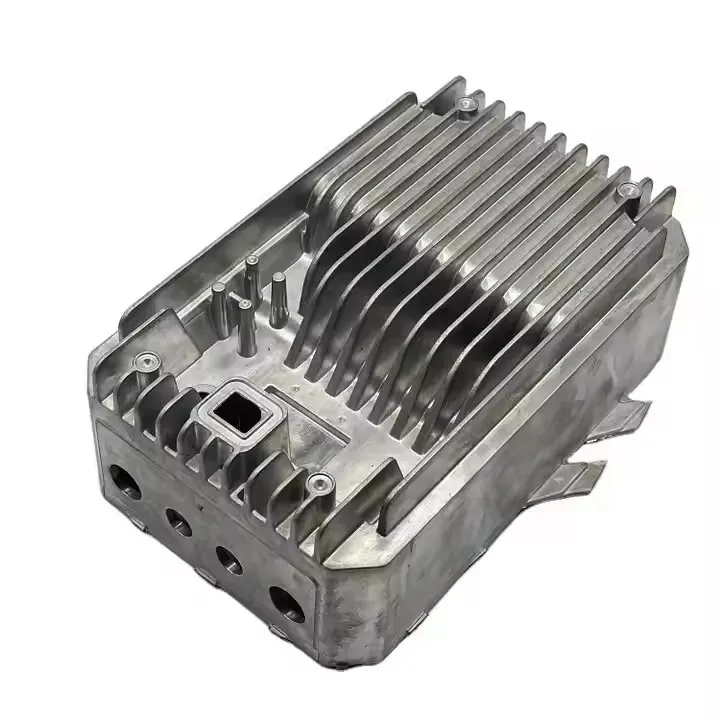
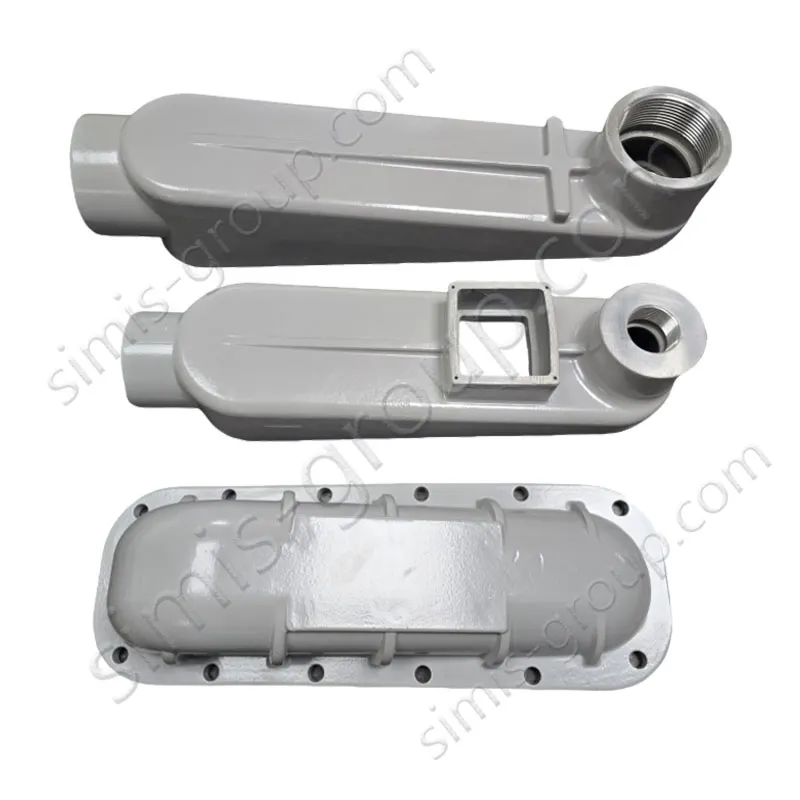
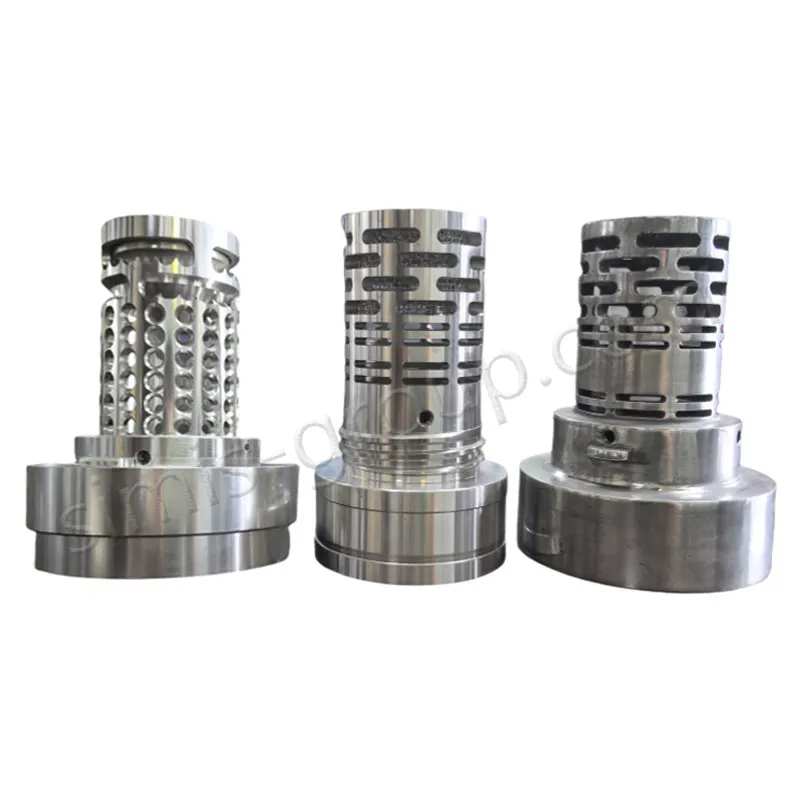
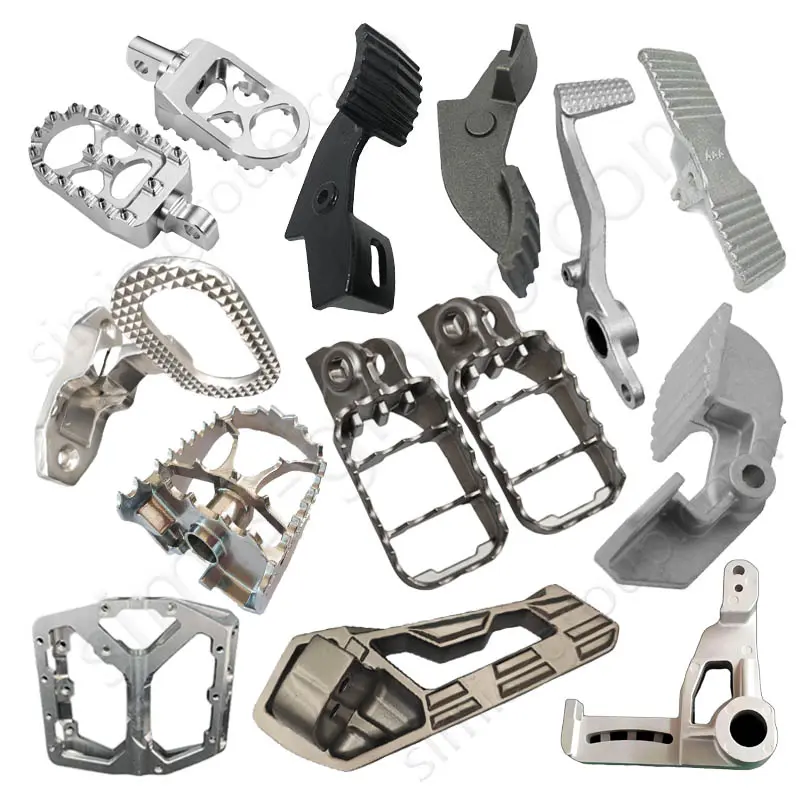
OEM Custom Gravity Casting Parts
Gravity Permanent Mold Casting Process for Custom Metal Parts
Gravity permanent mold casting process overview
Gravity Permanent Mold Casting uses gravity to pour molten metal into a prepared reusable metal die (mold). The casting is formed after cooling and solidification within this metal die. This process is highly effective for producing castings that require high precision and simple to moderately complex structures, offering benefits like low cost and ease of operation for medium-to-high volume runs.
1. Die Preparation
Permanent molds are constructed from durable metal or ceramic materials. The mold design process must carefully account for the metal's fluidity, the cooling rate, and the complex geometry of the final casting.
2. Melting Metal Materials
The specific metal alloy is heated in a high-temperature furnace until it is completely molten, ensuring the temperature is well above its melting point for optimal pouring.
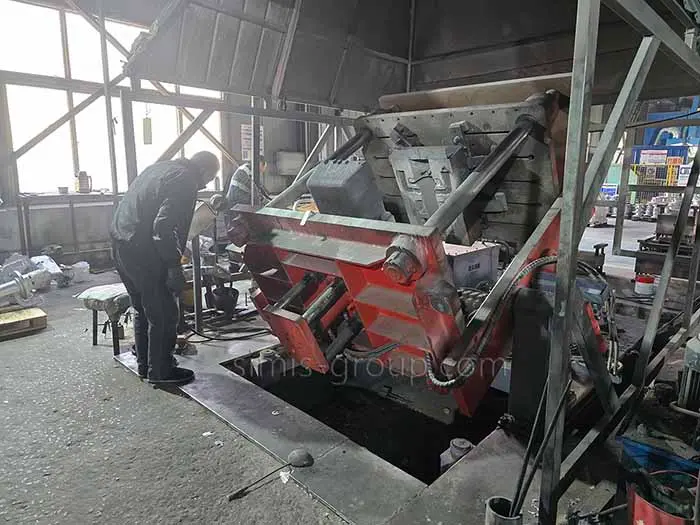
3. Pouring
During pouring, the molten metal flows by gravity from the holding furnace or ladle, through the mold's runner system, and enters the mold cavity via the gate. Gravity ensures the cavity is fully filled to form the shape of the desired casting.
4. Cooling and Solidification
Once inside the metal die, the molten metal begins to cool and solidify rapidly. The metal mold extracts heat efficiently, promoting a fine, dense microstructure in the casting.
5. Permanent Mold Demolding
After the casting has fully solidified and cooled, the reusable metal die is opened (disassembled), and the casting is mechanically ejected or removed.
6. Casting Cleaning
The castings is removed from the die, and excess material, such as gates, risers, and flash, is trimmed and removed. The casting surface is cleaned in preparation for further processing.
7. Post-Processing and Testing
The cleaned casting undergoes necessary post-processing steps, such as specialized heat treatment and precision machining, to achieve the required mechanical performance and final dimensions for the customer's design.
8. Quality Inspection
Comprehensive quality inspection is performed. This includes surface quality inspection, dimensional checks, and mechanical property testing to ensure the finished permanent mold castings strictly adhere to the requirements of the design drawings.




Available Materials for Gravity Casting Applications
What metal parts can be cast in Simis Gravity die Factory?
Gravity permanent mold casting process is particularly suited for metals with relatively low melting temperatures and good fluidity, allowing the production of medium- to high-volume components with consistent quality. Gravity permanent mold casting is predominantly applied to aluminum and magnesium alloys due to their low pouring temperatures, but it can also be used in limited cases for copper alloys or selected low-melting-point zinc alloys. The process enables thin-walled, complex, and high-repeatability components with reduced post-machining requirements.
| Material Category | Why It Is Suitable for Gravity Permanent Mold Casting | Simis Gravity Die Casting Foundry Typical Applications | Simis Gravity Die Casting Foundry Common Grades |
| Aluminum Alloys | Low melting temperature, excellent fluidity, and good fillability make aluminum alloys ideal for permanent metal molds. The process produces smooth surfaces, thin walls, and consistent dimensional accuracy with minimal post-machining | Automotive components, gearbox housings, engine brackets, structural housings | ASTM A356, A319, EN AC-42100 (AlSi7Mg) |
| Magnesium Alloys | Extremely low melting temperature and good castability allow magnesium alloys to be poured safely into metal molds. The process supports lightweight, thin-walled components with good dimensional repeatability | Aerospace structural parts, automotive lightweight brackets, housings | AZ91D, AM60, AZ31 |
| Copper Alloys (limited) | Certain low-melting copper alloys can be cast in permanent molds when part size and geometry are suitable. Careful mold and gating design is required to control cooling and prevent porosity | Bushings, pump parts, impellers (small to medium size) | ASTM B62, C83600 |