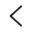Manufacturing Capabilities of Our Steel Casting Foundry

Steel Sand Casting
Steel sand casting involves pouring molten steel into a sand mold to produce cast steel parts with high strength, high toughness, impact resistance, and wear resistance. We use specialized silica sand or chromite sand in conjunction with resin binders for molding to ensure the quality and internal density of the steel castings.
Cast Weight Range: 1 kg – 5,000 kg
Maximum Dimensions: up to 3 m.
Dimensional Tolerance Grade: CT10 to CT13
Surface Roughness (Ra): Ra 25.0 to 60.0 μm
Minimum Wall Thickness: 8 mm to 25 mm

Steel Investment Casting
Steel investment casting (lost-wax casting) uses a fusible wax model to create a complex mold cavity, which is then encased in multiple layers of refractory slurry to form a hard outer shell. This allows steel castings to achieve extremely high dimensional accuracy, excellent surface finish, and great design freedom.
Cast Weight Range: 0.01 kg – 50 kg
Maximum Dimensions: 0.5 m × 0.5 m × 0.4 m
Dimensional Tolerance Grade: CT3 to CT6
Surface Roughness (Ra): Ra 0.8 to 3.2 μm
Minimum Wall Thickness: 1 mm to 3 mm

Steel Shell Mold Casting
Steel shell mold casting is a process that uses thin-shell molds made of coated sand for pouring. The resulting castings have higher dimensional accuracy and surface finish than sand casting, with moderate mold costs and high production efficiency. It is suitable for mass production of small to medium-sized steel castings with relatively complex structures.
Cast Weight Range: 0.5 kg – 50 kg
Maximum Dimensions: 0.5 m × 0.4 m × 0.3 m
Dimensional Tolerance Grade: CT7 to CT9
Surface Roughness (Ra): Ra 6.3 to 12.5 μm
Minimum Wall Thickness: 4 mm to 8 mm

Steel Lost Foam Casting
Steel lost foam casting (LFC) of steel utilizes foam models and dry sand, and completes the molding by instantly vaporizing the foam in molten steel. It has no sand core, no parting surface, and a high degree of design freedom, and can be used for integrated mass production of medium and large steel castings with complex internal cavities, manifold structures and fine details.
Cast Weight Range: 1 kg – 500 kg
Maximum Dimensions: 1.5 m × 1.0 m × 0.8 m
Dimensional Tolerance Grade: CT6 to CT8
Surface Roughness (Ra): Ra 6.3 to 16.0 μm
Minimum Wall Thickness: 5 mm to 10 mm

Heat Treatment
Because internal stress, uneven microstructure, and coarse grains can occur during the solidification process of molten steel, optimization through heat treatment is necessary. SIMIS Steel Foundry employs various heat treatment processes depending on the different steel grades and customer requirements.
Annealing: Relieve internal stress; maximum softening.
Normalizing: Homogenize structure; balance strength and toughness.
Normalizing + Tempering (N+T): Enhance toughness; adjust to target strength level.
Quenching + Tempering (Q+T): Highest strength, hardness; improve wear resistance.
Solution Treatment: Eliminate intergranular corrosion; maximize stainless steel resistance.

Machining
Machining is the process of applying high precision, strict tolerances, and functional surfaces to steel castings after casting. SIMIS Steel Foundry is equipped with a full set of high-rigidity, high-power CNC equipment, capable of machining all cast steel parts, from small precision components to large structural parts, and employs a coordinate measuring machine (CMM) for rigorous quality verification.
Machining Tolerance: IT7 to IT5 Grade
Surface Finish (Ra): Ra 0.4 to 3.2 μm
Machined Part Weight Range: 1 kg – 5,000 kg
Quality Inspection Capability: CMM measurement accuracy up to ±0.005mm.
OEM Custom Cast Steel Parts by Steel Foundry
Cast Steel Materials for Custom Casting Applications



Carbon Steel Casting
Carbon steel exhibits good castability, offering high strength and reliable toughness. This material provides significantly higher ductility than cast iron and allows for the formation of complex shapes more easily than forging. This makes it suitable for casting components with intricate designs that are subjected to heavy operational loads or impact forces.
Carbon Steel Parts from Simis Steel Foundry:
Power plant gear (valves, pump cases, turbine cases),
Mining machines (track shoes, shovel teeth),
Heavy machines (gears, mill frames, rollers),
Ship parts (anchor chains, rudder stocks),
Train parts (couplers, side frames).
Simis can cast carbon steel types:
Low Carbon Cast Steel (Carbon ≤0.25%): Parts needing high toughness and good welding. Examples: engine bases, ship parts, and pressure vessels.
Medium Carbon Cast Steel (Carbon 0.25% - 0.60%): Parts under heavy load, fatigue, and some impacts. Examples: gears, connecting rods, and heavy mill frames.
High Carbon Cast Steel (Carbon ≥0.60%): Parts needing very high hardness and wear resistance. Examples: rolls and crusher jaws.
Alloy Steel Casting
Alloy Steel Casting involves adding specific elements such as nickel, chromium, and molybdenum to carbon steel. This modification enhances the steel's strength, hardenability, and mechanical performance. Alloy steel exhibits higher strength, increased toughness, and better wear resistance than plain carbon steel. By utilizing specific elemental combinations and customized heat treatments, we create components with the precise characteristics required for the energy, mining, and heavy industries.
Alloy Steel Castings from Simis Steel Foundry:
Gears, pinions, and sprockets for heavy equipment;
High-pressure valve bodies and pump cases for oil and gas;
Crusher liners, shovel teeth, and mining components;
Turbine cases for power generation;
High-strength parts for ships.
Simis can cast alloy steel types:
High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steels: Structural parts, truck frames, crane arms, and mining gear where being light is important.
Heat-Treatable Alloy Steels (Cr-Mo / Ni-Cr-Mo): Parts under high stress like gears, crankshafts, and pressure parts for hot service.
Wear-Resistant Alloy Steels: Crusher rolls, pulverizer hammers, and grinding parts.
Low-Temperature Nickel Alloy Steels: Parts for storing and moving liquid gas, and offshore platforms.
Stainless Steel Casting
Stainless Steel Casting provides high resistance to corrosion and performs well across a wide range of hot and cold service temperatures. This combination of characteristics exceeds the general performance of carbon or low-alloy steels. Stainless steel castings suitable for parts utilized in chemically aggressive settings, high-temperature environments, or those requiring precision in complex shapes.
Stainless Steel Castings from Simis Steel Foundry:
Valves, pumps, and fittings for chemical plants;
Impellers and turbine blades;
Gear for food and drink processing;
Marine hardware;
Parts for medical tools.
Simis can cast stainless steel types:
Austenitic Stainless Steels: Pump and valve bodies, chemical gear, and food processing parts.
Martensitic Stainless Steels: Pump shafts, valve trim, turbine parts, and mechanical parts needing high strength and some rust resistance.
Duplex (Austenitic-Ferritic) Steels: Pumps, valves, and fittings for offshore oil, chemical ships, and water removal plants.
Ferritic Stainless Steels: Car exhaust parts (manifolds), heat exchangers, and gear used in strong acids. Good for fighting chloride stress cracking.
Tool Steel Casting
Tool Steel Casting produces highly hard, wear-resistant, and thermally stable components for tooling applications. Casting methods allow for the precise placement of strong material and the integration of internal features, such as cooling channels, making them suitable for complex molds, dies, and high-wear parts.
Tool Steel Castings from Simis Steel Foundry:
Die casting dies and cores;
Forging dies and punches;
Cutting tools and blades;
Wear plates and liners;
Cold-work punches;
Trimming dies;
Hot-work extrusion dies.
Simis can cast tool steel types:
Cold-Work Tool Steels: Dies for punching and cutting, shearing blades, thread rolling dies, and gauges.
Hot-Work Tool Steels: Dies for die casting, extrusion dies, forging dies, and hot punches.
Plastic Mold Steels: Mold cores and cavities, compression molds, and mold bases.
High-Speed Tool Steels: Complex cutting tools, drill bits, and milling cutters. We cast them for near-net-shape parts.
Industries Served by Our Steel Casting Foundry
How to Customize Steel Castings with Steel Foundry
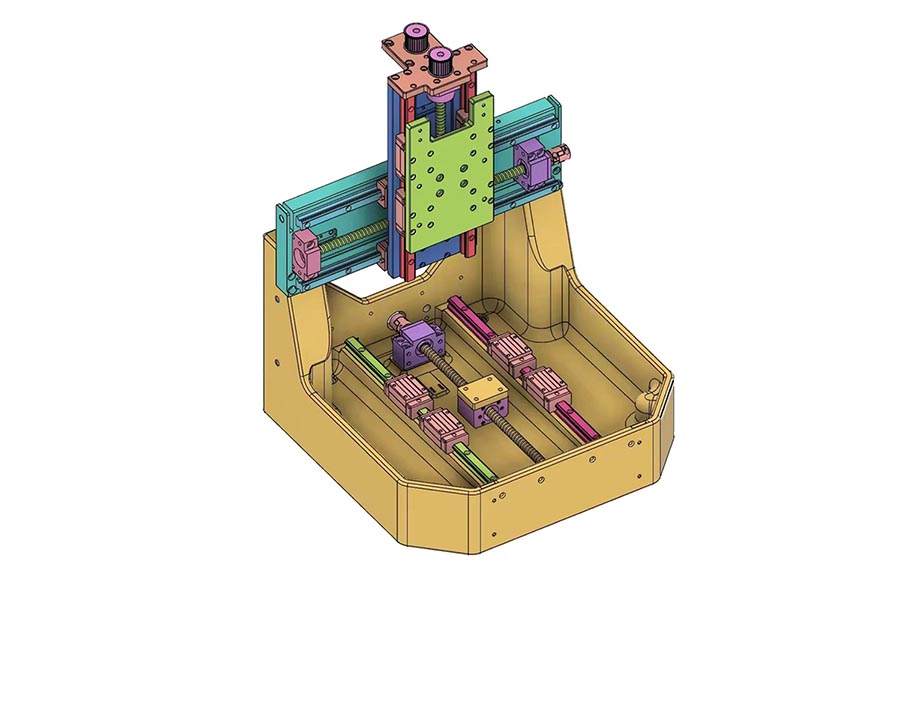
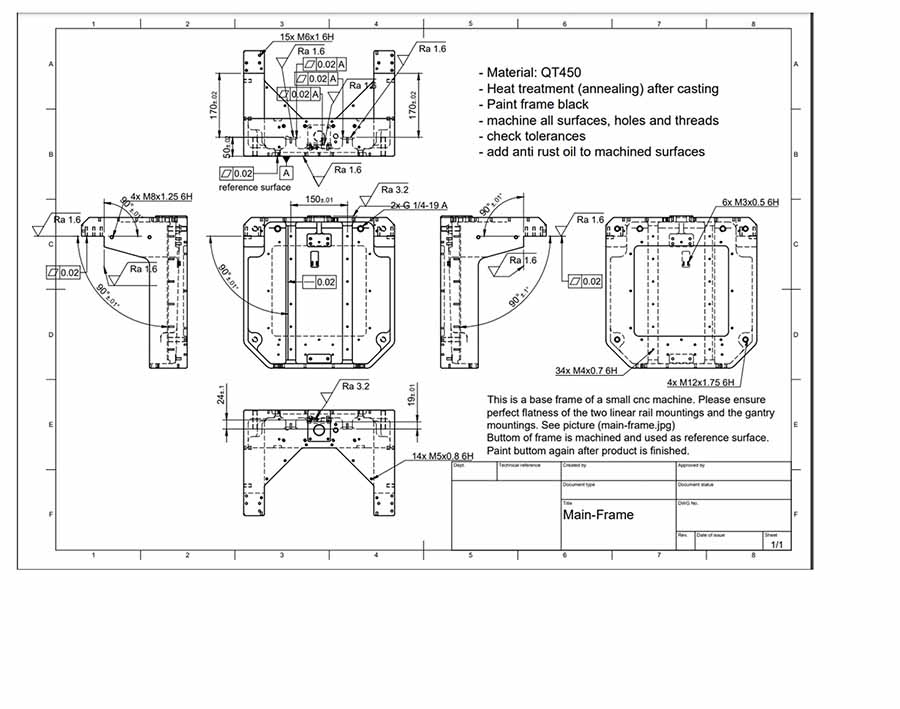

Confirm Manufacturing Requirements for Cast Steel Parts
Design Review and Samples
Simis engineers first check the 3D and plane drawings. This makes sure your design is ready for manufacturing. If you have a sample part, we can make the new parts based on that sample.
Define Part Requirements
We confirm what the part needs to do. This includes things like its strength, hardness, wear, and rust resistance. We also set the exact size, tolerance, and finish quality needed.
Confirm Casting Material
Our engineers help you pick the right cast steel material. This choice depends on where the part will be used and your technical needs. We give advice based on material cost, strength, and resistance to wear or rust.
Choose the Casting Method
We select the best casting process for your part. We base this choice on your price goal, the part’s shape, its required accuracy, and the material.
Make Molds and Samples
We build the casting molds using your approved drawings or samples. Then, we cast the first batch of samples using the chosen material and process.
Full Sample Inspection
The finished samples go through a full check. This confirms they meet all design standards and your quality demands. We give you reports covering size, performance, material makeup, and non-destructive testing.
Mass Production of Cast Steel Parts
Mass Production
After you check and approve the sample, we start the mass production plan. We get all the materials ready based on your order. We use the exact same machines and process as we did for the sample. This makes sure every single part we make is the same.
Quality Control During Production
We run tight quality checks while making the parts. We pull parts for checks often during the process. We test their size, look, and strength. This ensures every batch of cast steel parts is consistent and meets your needs.
Final Product Quality Inspection
We use multiple inspectors for the final check. They do many tests on the finished product. These tests cover size accuracy, surface quality, and part strength. This step makes sure all cast steel parts meet your quality standards.
Packaging and Delivery
We securely package and ship all approved parts. We pick the right packaging to prevent damage during shipping. We also choose the best delivery method (air, sea, or land) to get your parts to you on time.




To order custom parts, please email us your design drawings and 3D models. Our team will review the detailed part parameters and the 3D model to provide you with an accurate quote.