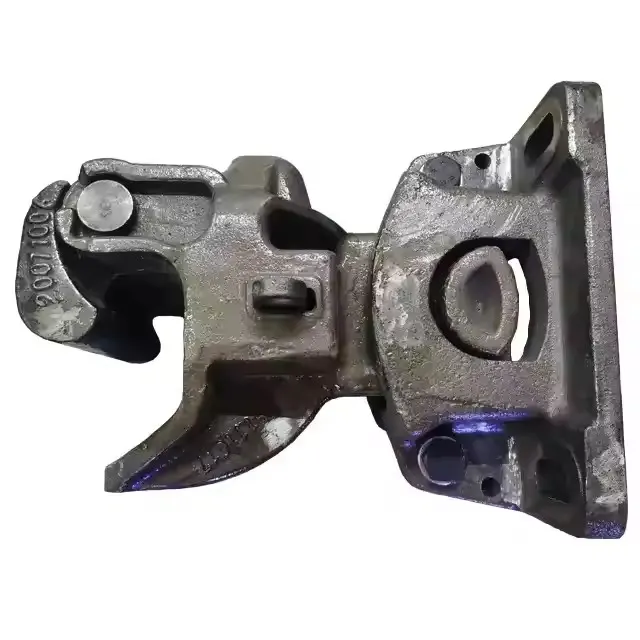
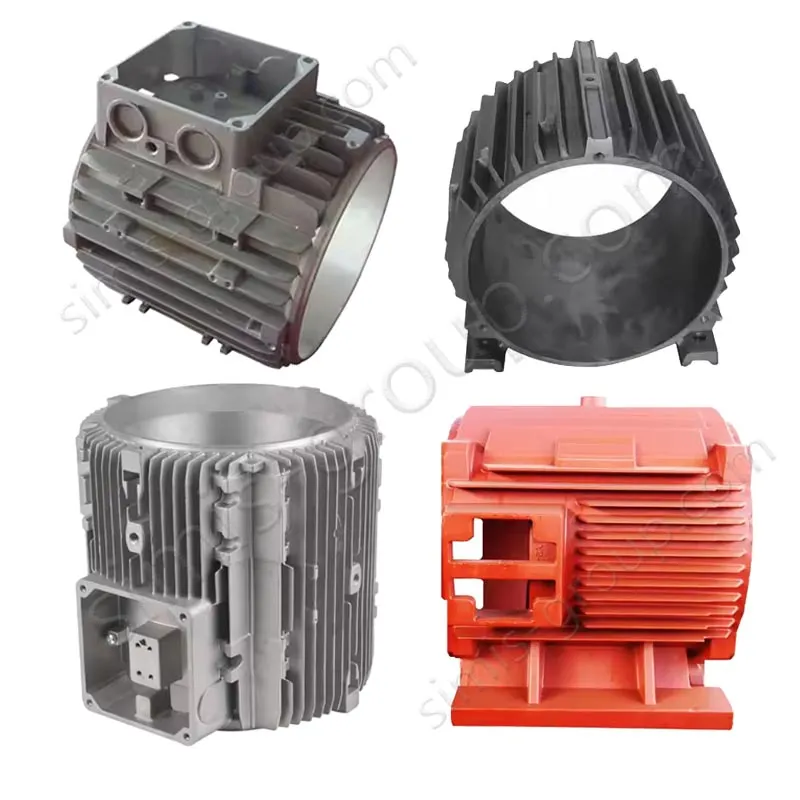
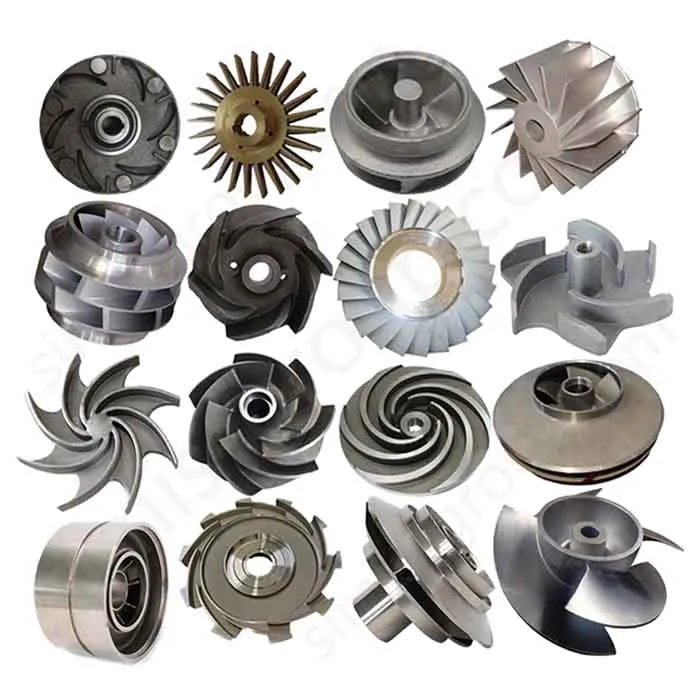
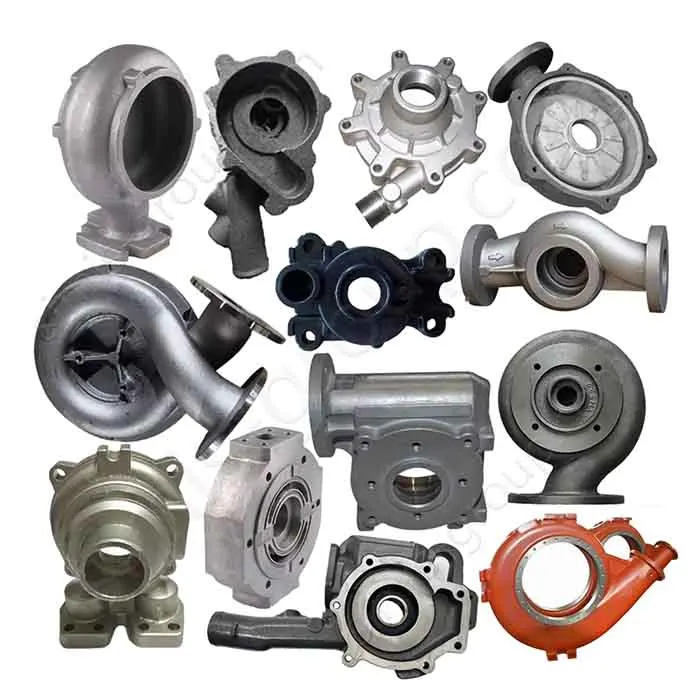
Sand Casting Foundry for OEM Custom Manufacturing
Simis Sand Casting Foundry Introduction
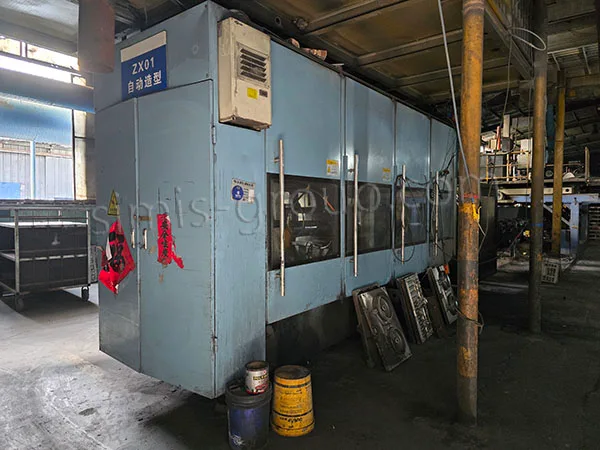
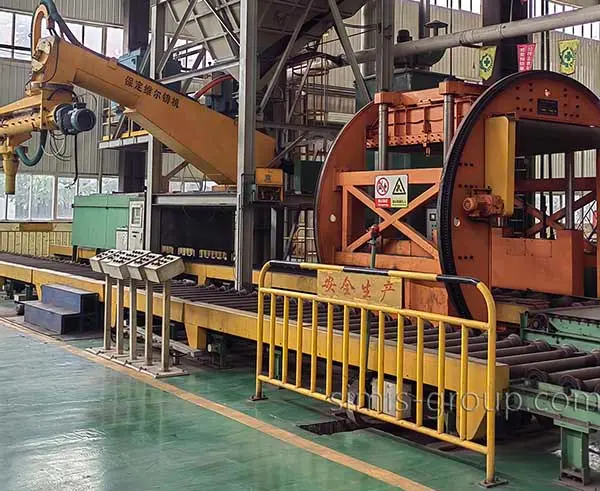
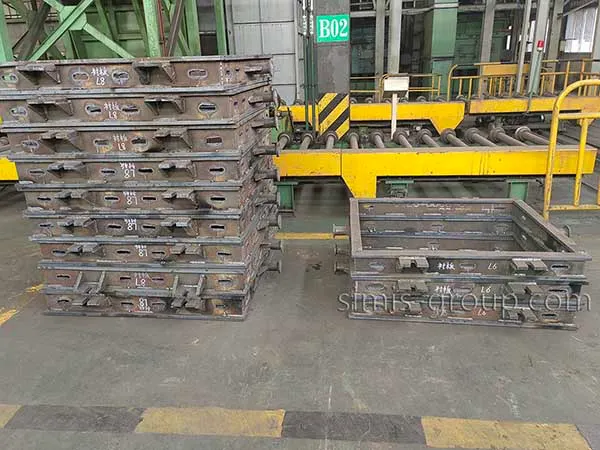
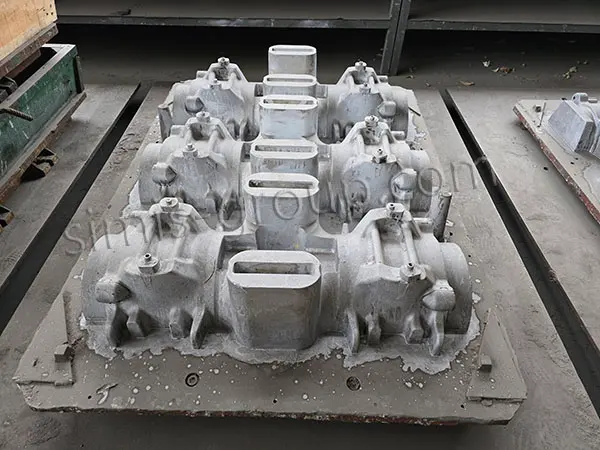
SIMIS Sand Casting Foundry is a modern, high-capacity facility specializing in precision sand casting for ferrous and non-ferrous metals. The foundry employs multiple molding techniques, including Static Pressure Molding, Automatic Molding, and Hand Molding, combined with the use of resin-bonded sand or clay-bonded sand, offering both low mold cost and high production flexibility.
This diverse approach enables SIMIS to meet the demands of all cast iron part sizes and production volumes, from small batches to large-scale production runs.
| Process | Weight Range | Max Dimensions | Min Wall | Tolerance | Surface Roughness (Ra) | Ideal For |
| Automatic Line | 0.5kg - 100kg | 800 x 600 x 300 mm | 3.5 - 4.0 mm | CT8 - CT9 | 12.5 – 25 μm | High-volume production & high-precision components. |
| Static Pressure | 5kg - 500kg | 1500 x 1200 x 500 mm | 4.5 - 5.0 mm | CT9 - CT10 | 12.5 – 25 μm | Complex, heavy-duty parts requiring uniform mold density. |
| Resin / Hand | 10kg - 1,000kg | Up to 3.0 m | 8.0 - 10.0 mm | CT11 - CT13 | 25 – 50 μm | Custom, oversized, or low-volume specialized castings. |
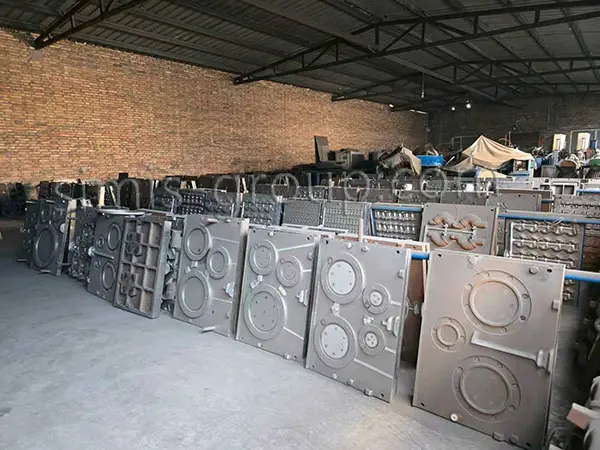
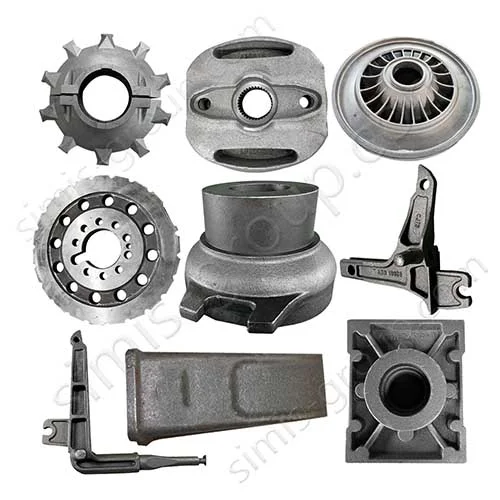
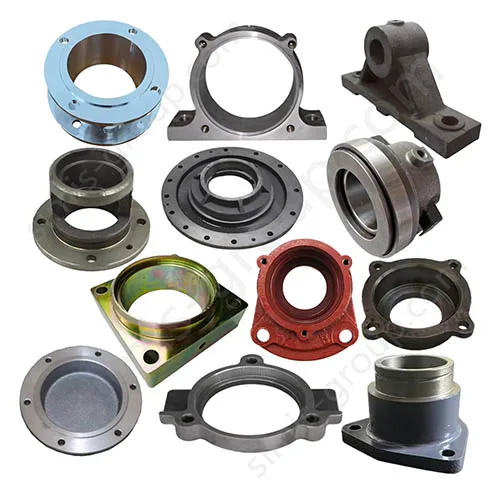
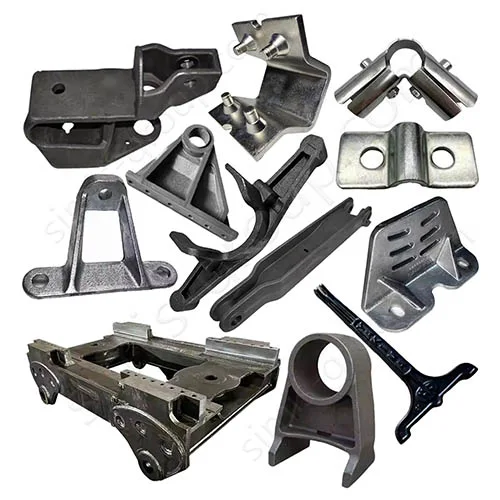
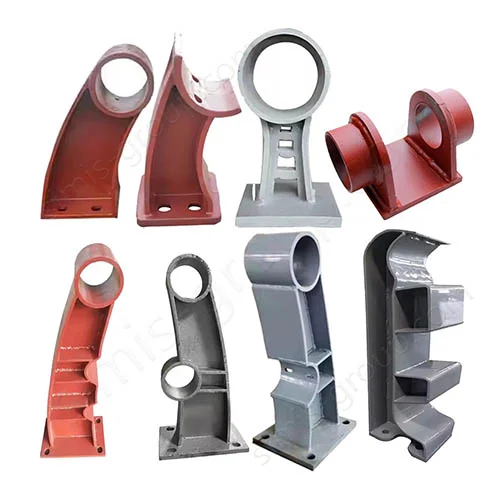
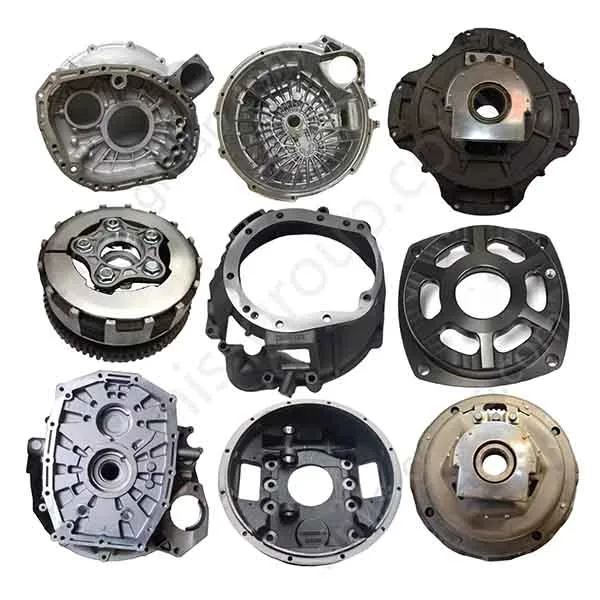
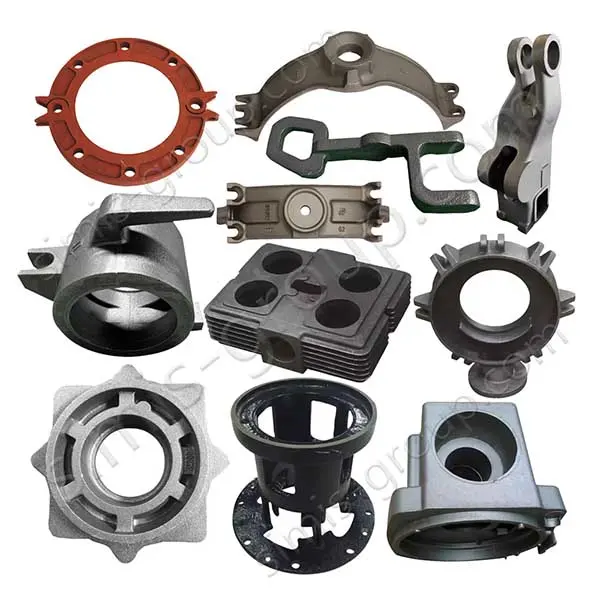
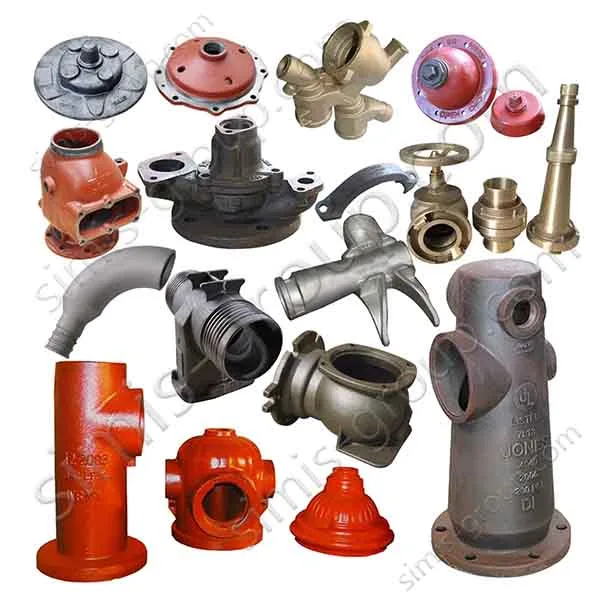
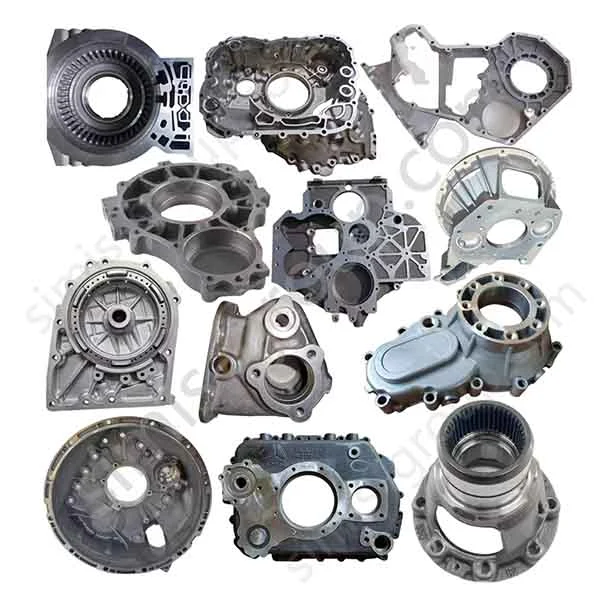
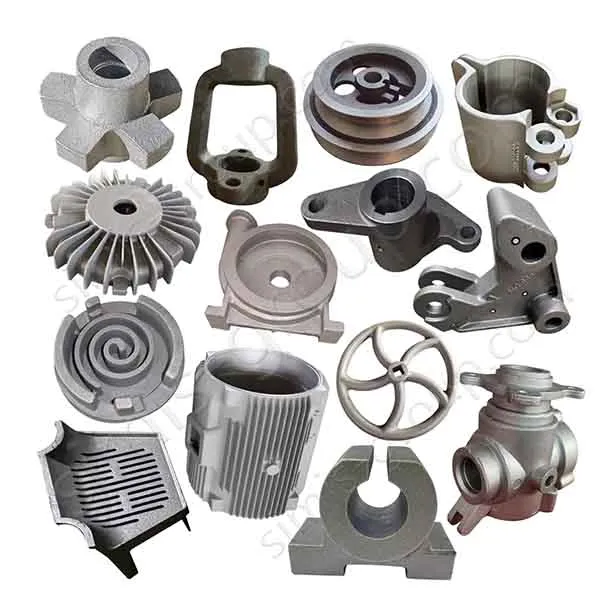
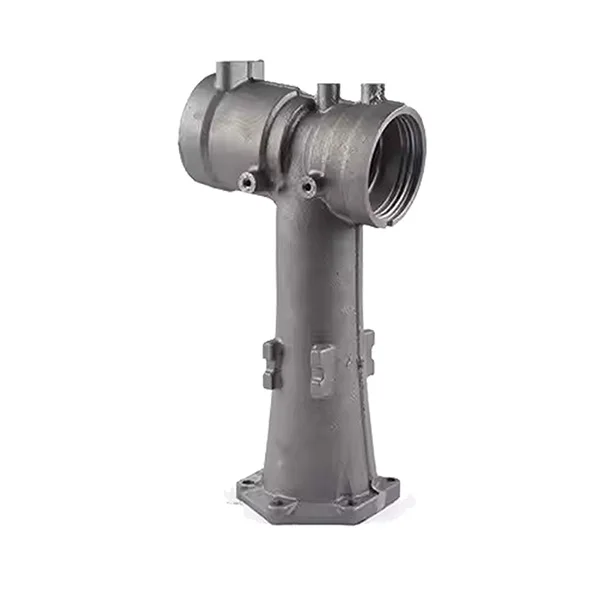
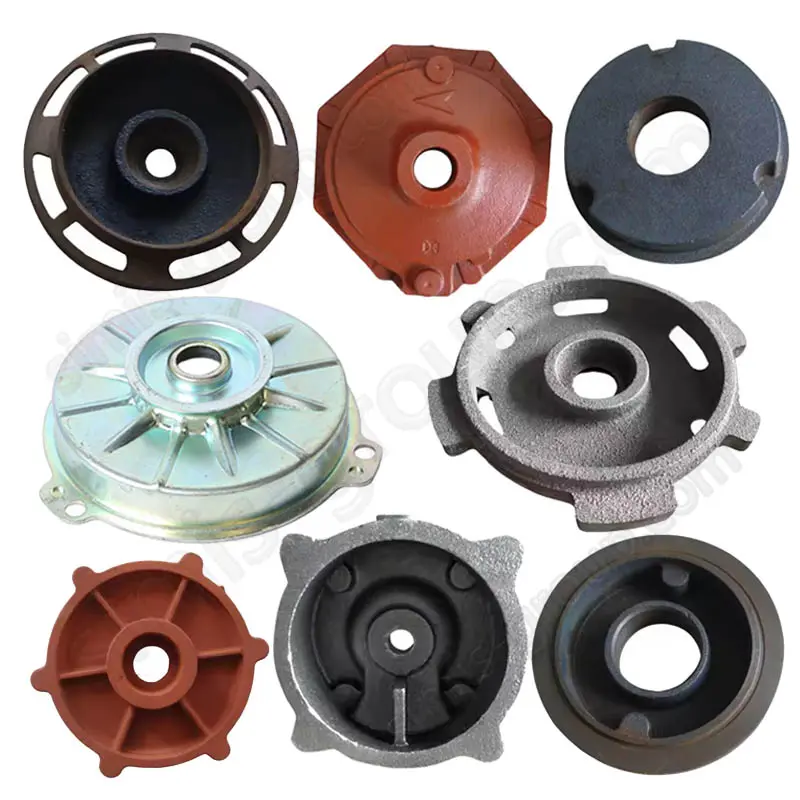
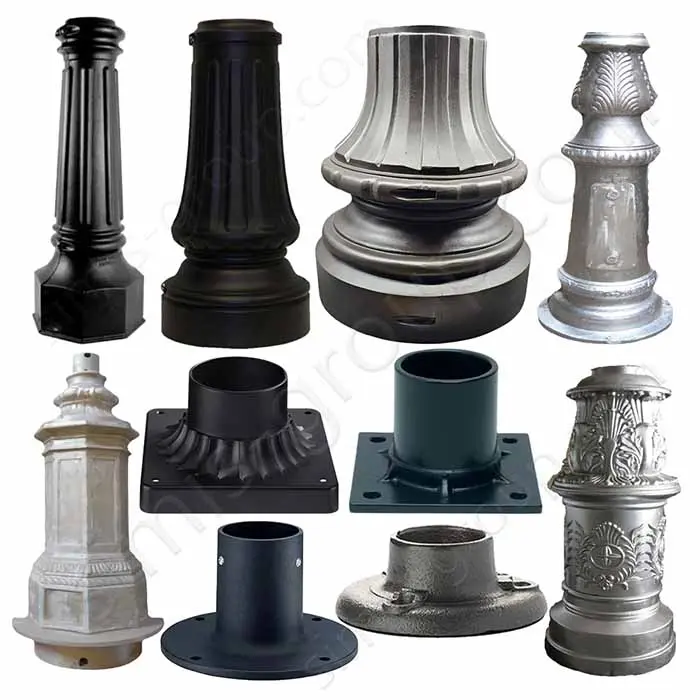
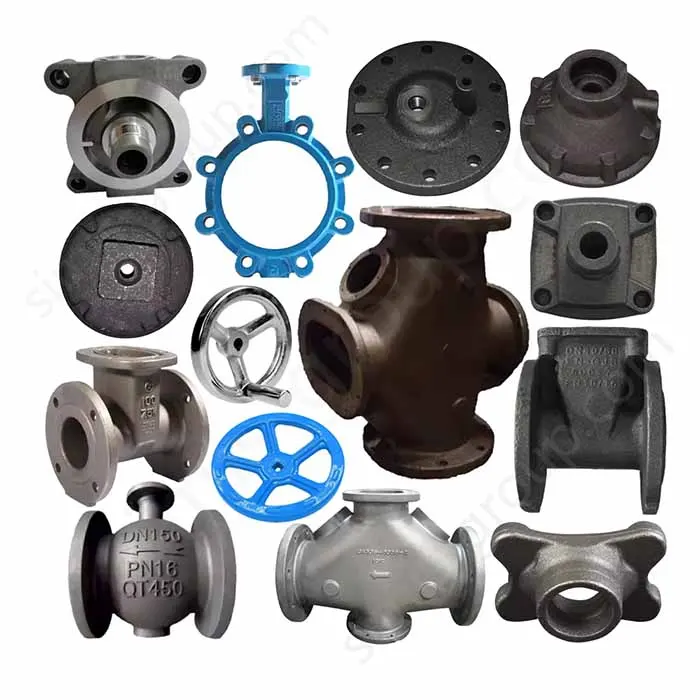
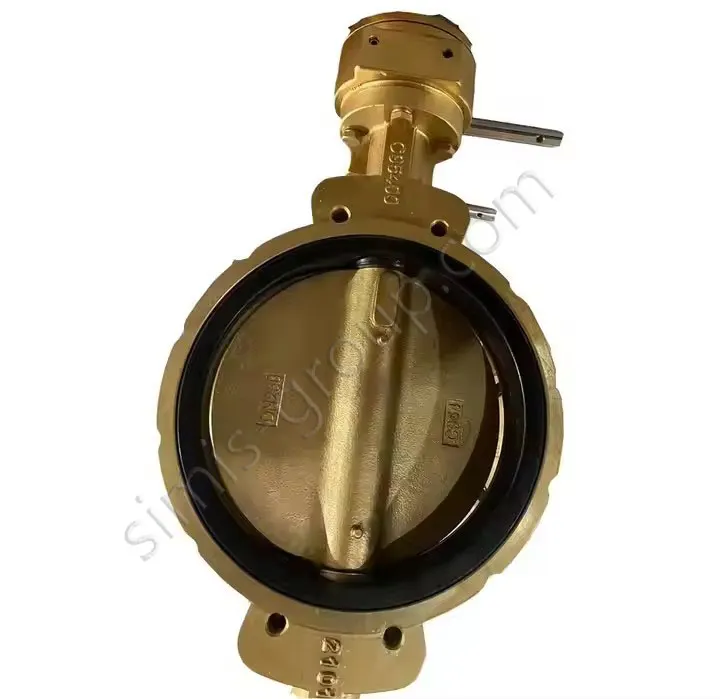
OEM Custom Sand Casting Parts
Sand Casting Process for Custom Metal Parts
Sand Casting Process Overview
Sand casting involves pouring molten metal into a mold made from sand and a binder. The process relies on the sand mold's plasticity and permeability to form the desired part. Sand casting is highly flexible, capable of producing castings with complex shapes and large sizes with a relatively short production cycle.
1. Prepare Sand Mold
The basic raw materials are river, silica, or fine sand. This sand is mixed with binders (like bentonite, resin, or clay) and additives (such as water or oil).
Note: The two common mold types are resin sand casting and clay sand casting. The mixed sand is then packed into a flask (mold box) to form the mold structure.
2. Core Making
The core is used to form the internal spaces or complex cavities of the casting. It is generally created by mixing fine sand and a binder, then compressing and often baking the mixture.
3. Mold Closing and Core Loading
The top and bottom sections of the mold (cope and drag) are assembled to form the complete mold cavity. Before closing, the finished core is secured inside the mold to prevent shifting during pouring, which is critical for maintaining casting quality.
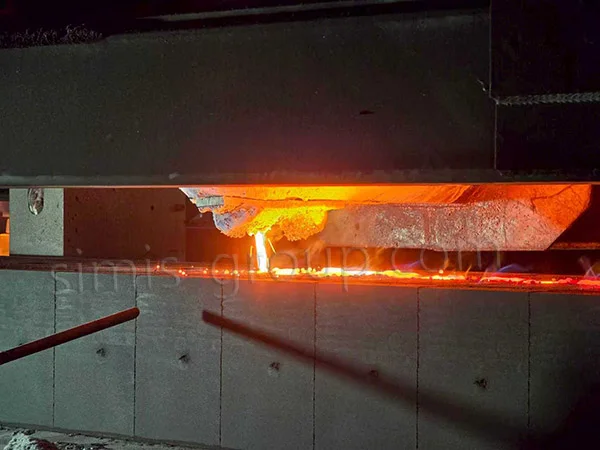
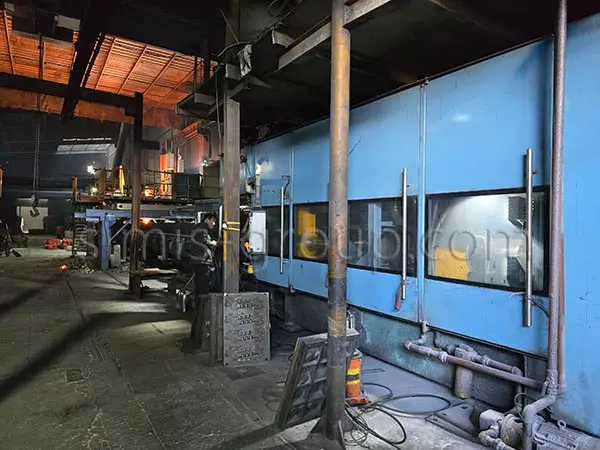
4. Pouring
The required metal is melted at high temperatures. The molten metal is then poured and enters the sand mold through the gate and riser. Gravity forces the metal into the mold cavity, filling the entire space to form the initial shape of the part.
5. Cooling and Solidification
Once the molten metal is in the mold, it begins to cool and turn solid. The time needed for cooling depends on the size, shape, and specific properties of the metal material used.
6. Mold Removal and Casting Cleaning
After the metal has completely solidified, the sand mold is broken away, and the casting is extracted (shakeout). All attached material, including sand particles, risers, gates, and cores, is removed from the casting surface.
7. Inspection and Quality Control
The cleaned castings undergo strict quality checks. This includes dimensional inspection, surface flaw detection, and mechanical property testing to ensure the product meets all customer standards.
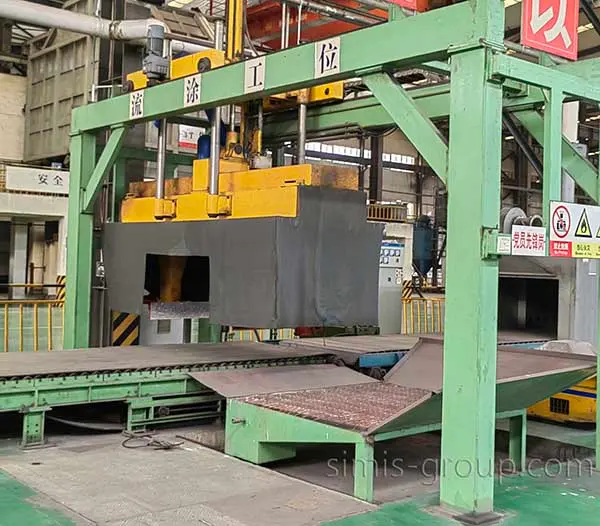
8. Post-Processing
Final treatments are applied to optimize the part:
Heat Treatment: Processes like annealing, normalizing, or quenching are used to enhance the part's mechanical properties and eliminate any internal stress.
Machining: Finishing processes like drilling, tapping, or precision machining are performed as needed to achieve the final, strict dimensional requirements.




Available Materials for Sand Casting Applications
What metal parts can be cast in Simis sand casting process?
The Simis Sand Foundry provides custom sand casting solutions in a wide array of ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Owing to the excellent refractoriness, permeability, and configurability of sand molds, this process is well suited for casting materials with significantly different melting temperatures and solidification behaviors. Simis sand casting capabilities cover gray iron, ductile iron, carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloys, copper alloys, and selected special alloys, accommodating both small and large components with complex geometries, internal cavities, and varying wall thicknesses.
| Material Category | Why It Is Suitable for Sand Casting | Simis Sand Foundry Typical Applications | Simis Sand Foundry Common Grades |
| Gray Iron | High carbon and silicon content promotes excellent melt fluidity and low solidification shrinkage. The flake graphite structure improves feeding behavior and provides natural stress relief, making gray iron highly tolerant of sand mold cooling rates, dimensional variability, and large section thicknesses | Engine blocks, machine bases, housings, valve bodies, pump casings | ASTM A48 Class 30/35/40, EN-GJL-250, EN-GJL-300 |
| Ductile Iron | Good inherent castability combined with controlled spheroidization allows sand molds to accommodate higher shrinkage compared to gray iron. Sand casting provides sufficient solidification time and feeding flexibility to ensure nodularity, mechanical properties, and internal soundness in complex or thick-walled components | Crankshafts, suspension components, hydraulic parts, structural brackets | ASTM A536 65-45-12, 80-55-06, EN-GJS-500-7 |
| Alloy Cast Iron | Alloying elements (Cu, Ni, Cr, Mo, W) enhance strength, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and hardenability. Sand casting accommodates solidification shrinkage and allows control of internal structure, suitable for both low-alloy and high-alloy cast iron, with proper gating, feeding, and cooling to manage porosity and hot cracking. | Automotive structural parts, pump and valve bodies, machinery housings, wear-resistant liners, heat-resistant machine parts | Low-alloy Cast Iron: EN-GJL / EN-GJS, ASTM A439; High-alloy Cast Iron: ASTM A532 Class I/II, Ni-Resist ASTM A439, EN-GJN-Ni series |
| Carbon Steel | High pouring temperature and significant solidification shrinkage require molds with high refractoriness, permeability, and collapsibility. Sand molds can be tailored through sand composition and binder systems to withstand thermal loads while allowing gas evacuation and controlled feeding | Valve bodies, flanges, pipe fittings, structural components | ASTM A216 WCB, WCC |
| Alloy Steel | Alloy additions increase strength but also raise sensitivity to hot cracking and shrinkage defects. Sand casting enables adjustable mold strength, feeding design, and cooling control to manage metallurgical stresses and ensure dimensional stability in medium to large components | Gears, shafts, pressure components, mining and machinery parts | ASTM A217 WC6, WC9, C12 |
| Stainless Steel | High chromium and nickel content results in high pouring temperature and strong reactivity with molds. Sand casting offers high-temperature resistance, good permeability, and flexible gating design to control gas evolution, oxidation, and solidification behavior in corrosion-resistant alloys | Pump bodies, valves, chemical equipment, marine components | ASTM A351 CF8, CF8M, CF3M |
| Aluminum Alloys | Low melting temperature and good fluidity make aluminum alloys compatible with sand molds, while sand casting allows flexible mold geometry, economical tooling, and accommodation of varying wall thicknesses. Controlled sand systems reduce gas entrapment and shrinkage porosity | Housings, brackets, heat sinks, automotive components | ASTM A356, A355, EN AC-42100 (AlSi7Mg) |
| Copper Alloys | Relatively high pouring temperature and density require molds with adequate refractoriness and strength. Sand casting provides controlled cooling rates and feeding capability, making it suitable for copper alloys where dimensional stability and internal soundness are critical | Bushings, bearings, impellers, valve components | ASTM B62 (Bronze), C83600 |