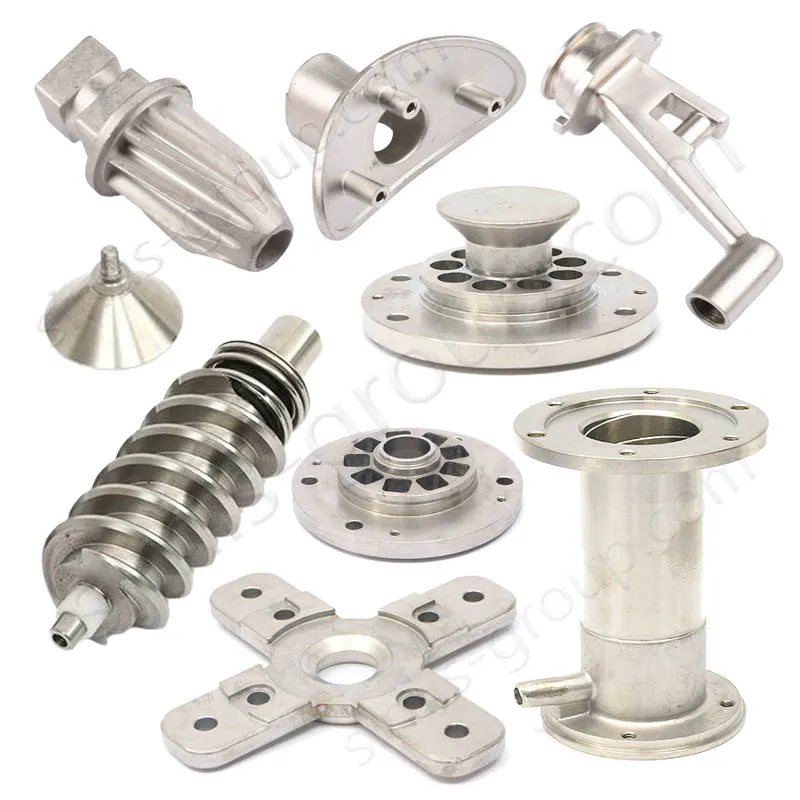
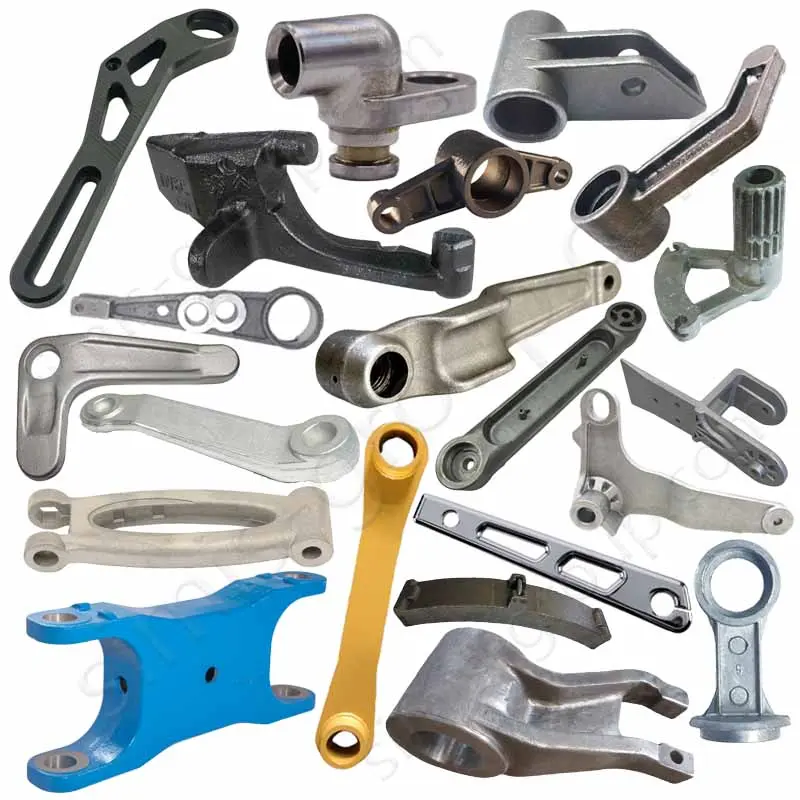
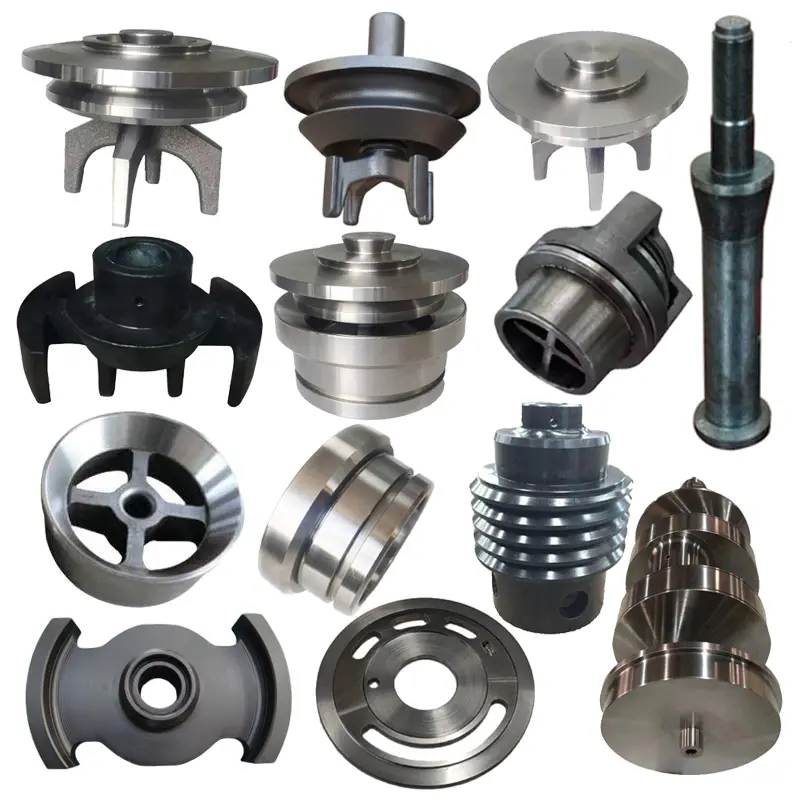
Custom Metal Parts For Industrial Machinery
In industrial machine making, castings make parts with complex shapes. They are used for large, complicated, and rust-resistant parts. Forgings have great mechanical properties and high strength. They fit parts that need high strength, good wear resistance, and high precision. Custom castings and forgings make machines more reliable and last longer. They also meet performance needs in many extreme work places.
Industrial Machinery Parts Classification
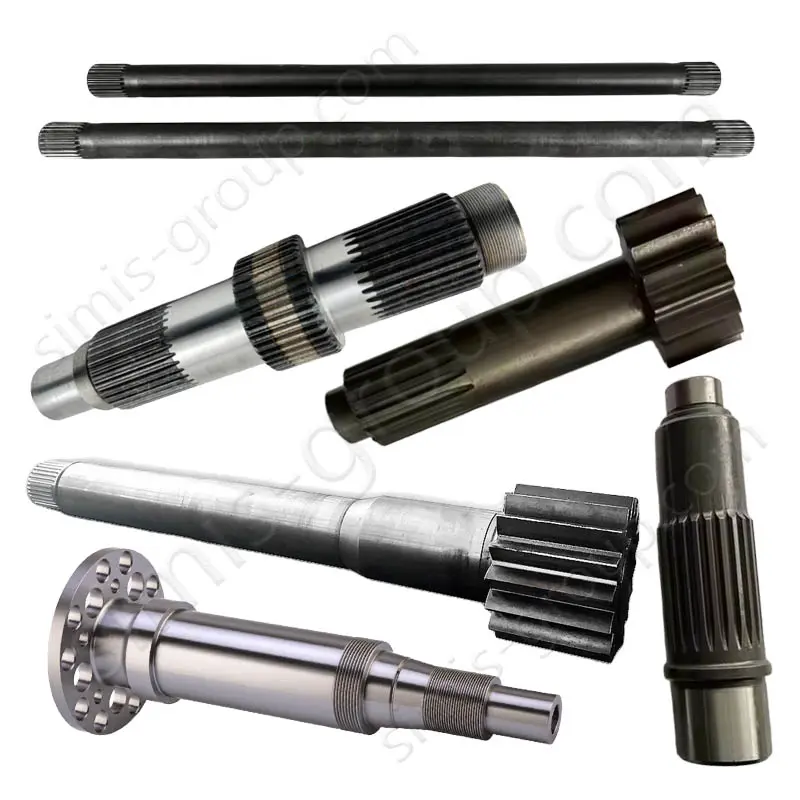
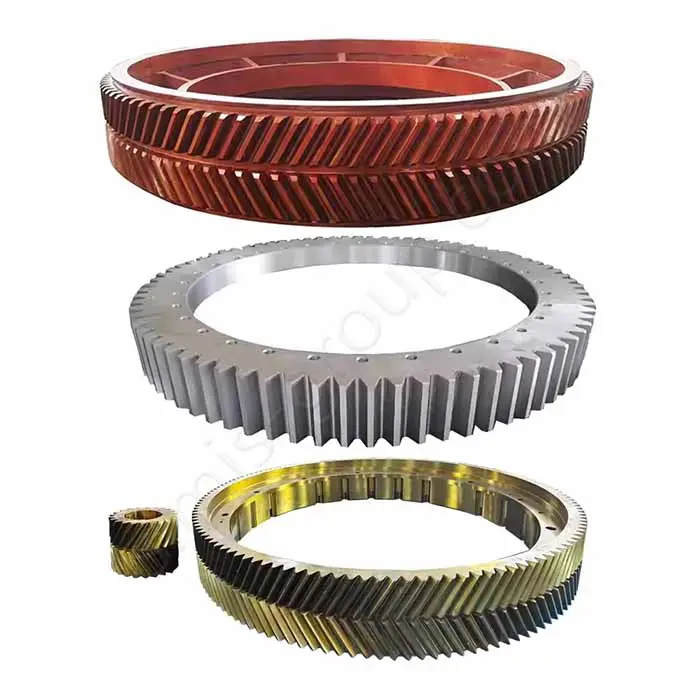
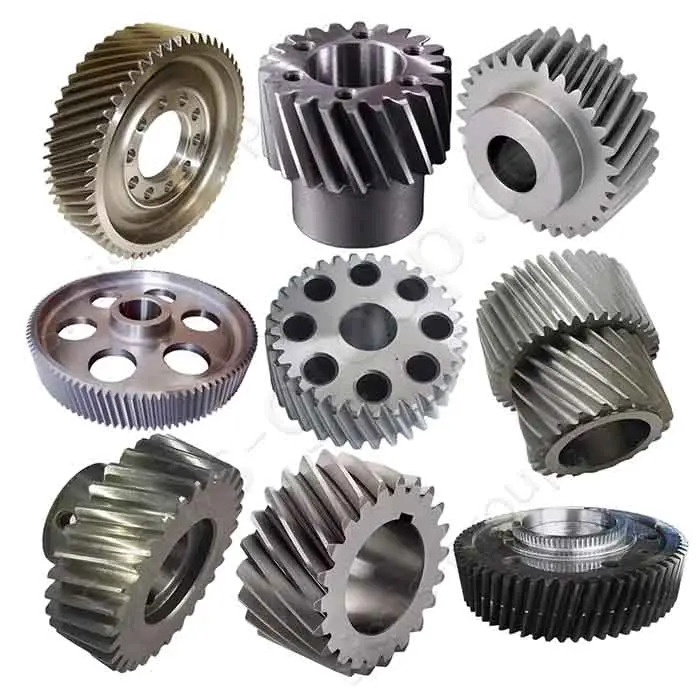
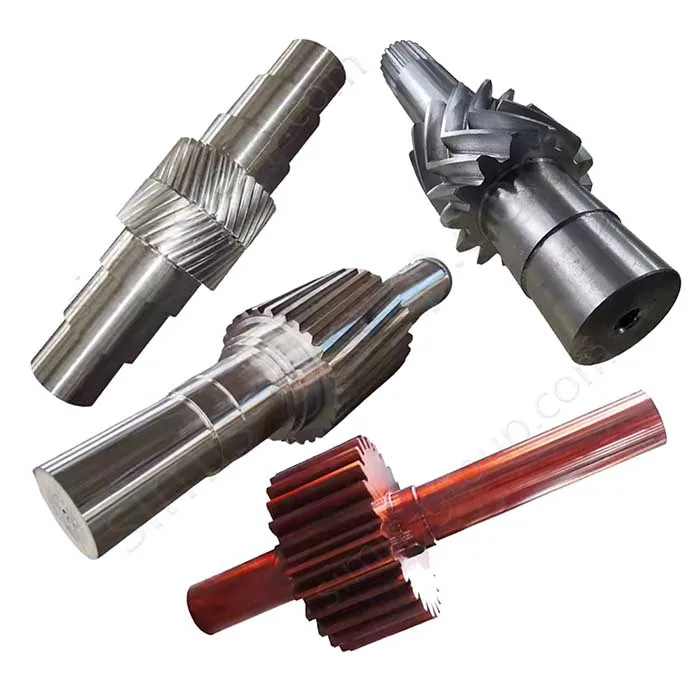
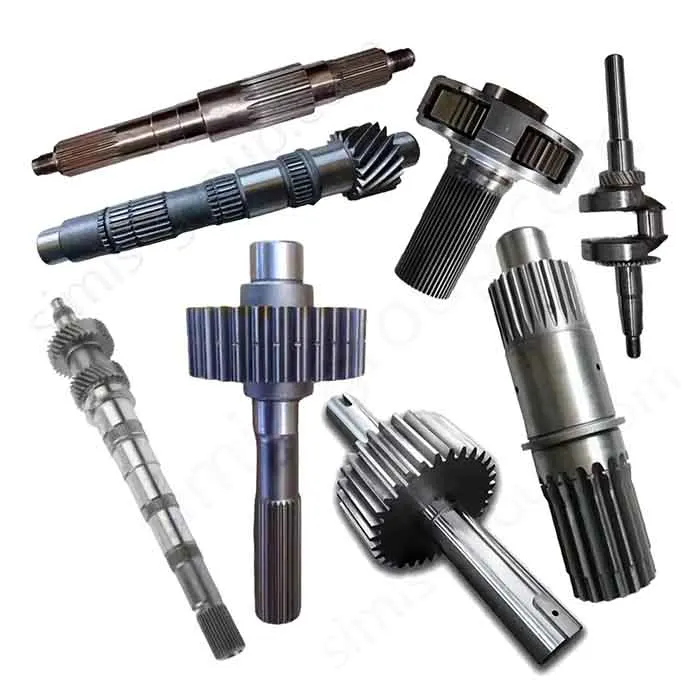
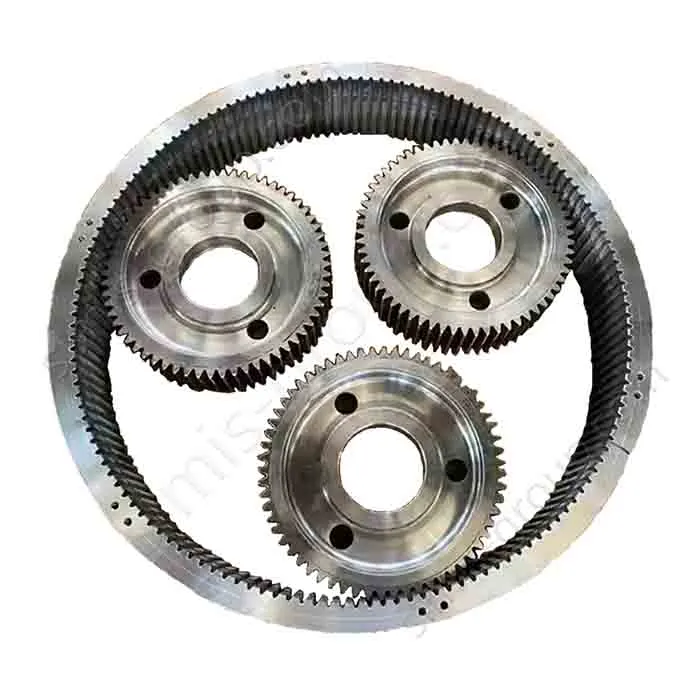
1. Transmission system
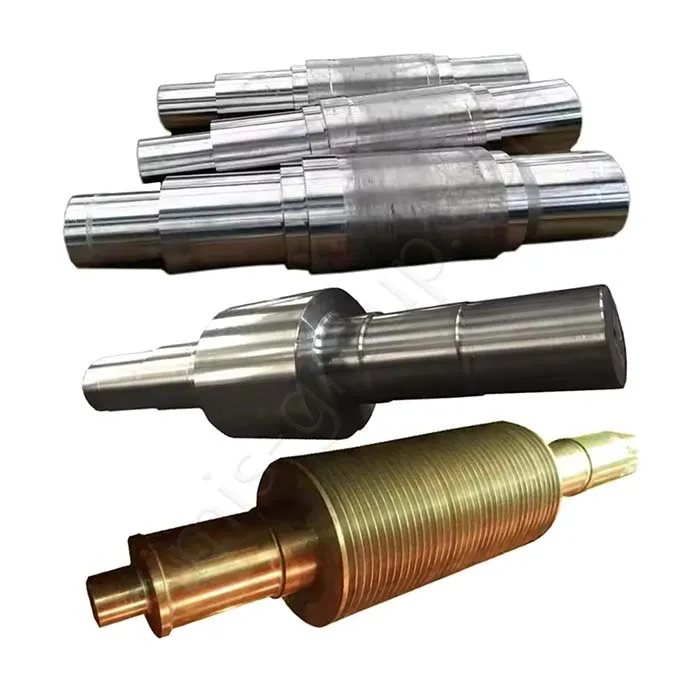
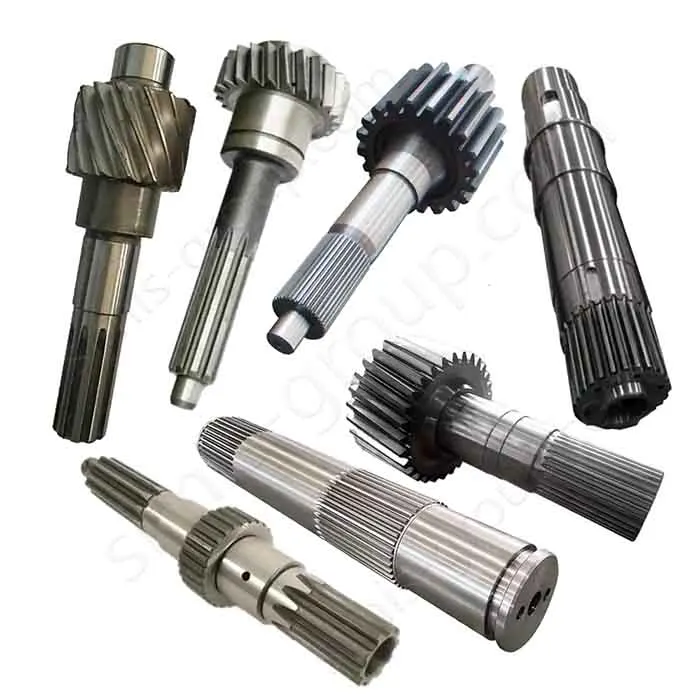
The transmission system is the core of machine operation. It moves power from the source to the working parts well. Castings make complex housings and bases. They give good structural stability. Forgings handle torque transfer and dynamic loads. They ensure the system has high precision, reliability, and durability.
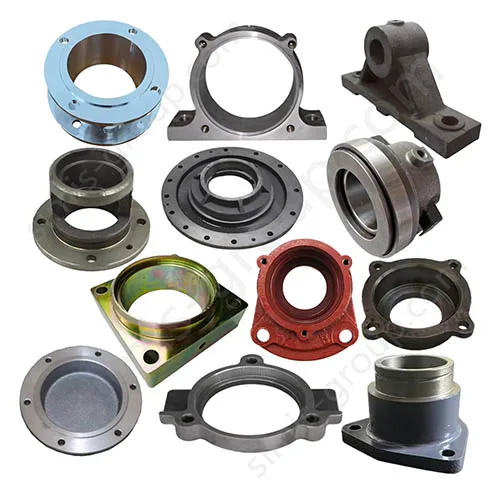
Castings: Gearbox housing, Clutch housing, Sprocket seat
Forgings: Gear, Transmission shaft, Universal joint, Sprocket
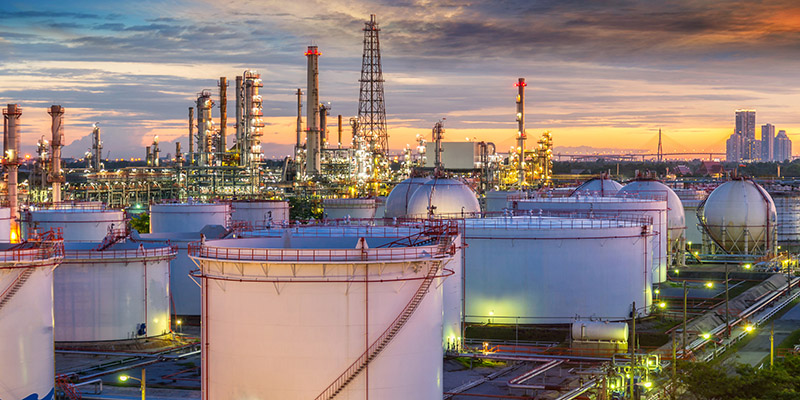

2. Power system
The power system is the "heart" of the machine. It gives continuous energy. Castings make complex parts that resist high heat, like housings and cylinders. Forgings are for core parts that handle high-intensity movement.
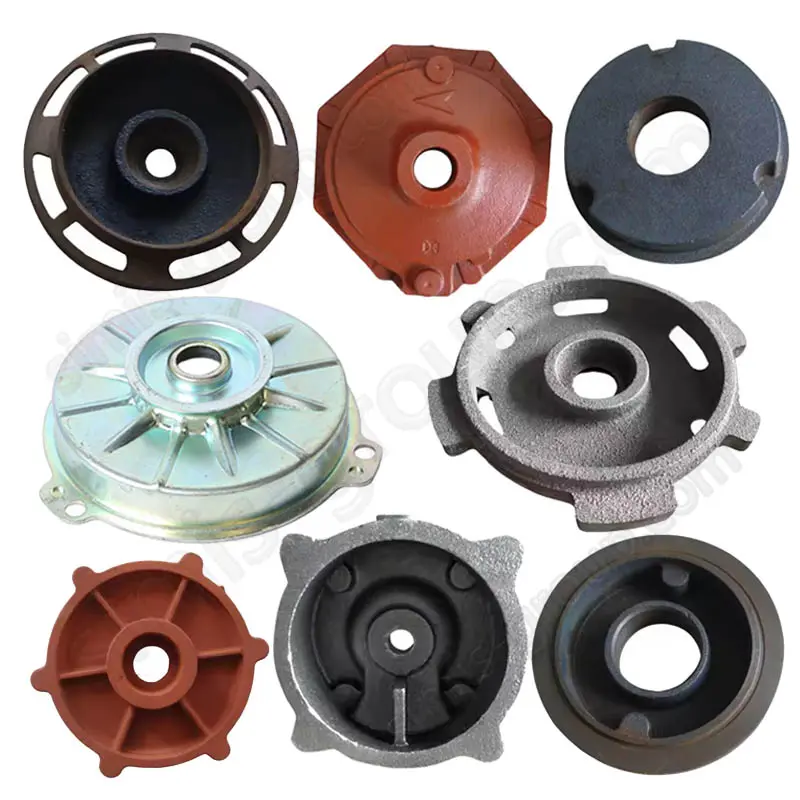
Castings: Engine cylinder block and cylinder head, Turbine housing, Oil pan
Forgings: Crankshaft, Connecting rod, Flywheel, Camshaft
3. Hydraulic system
The hydraulic system manages precise power transfer and control in industrial machines. Castings make parts with complex inner spaces, like pump housings and valve bodies. This ensures hydraulic fluid flows efficiently. Forgings are for parts that handle high-pressure loads, like piston rods and joints. They provide great durability and impact resistance.
Castings: Hydraulic valve body, Pump housing, Cylinder end cover
Forgings: Piston rod, Gear pump gear, Hydraulic joint
4. Chassis and Travel System
The chassis and travel system gives the machine movement and support. It is the base for stable operation. Castings make large support parts like wheel hubs and track rollers. They provide stability and resist impact. Forgings are used for key parts that need high strength and wear resistance, like drive shafts and pins.
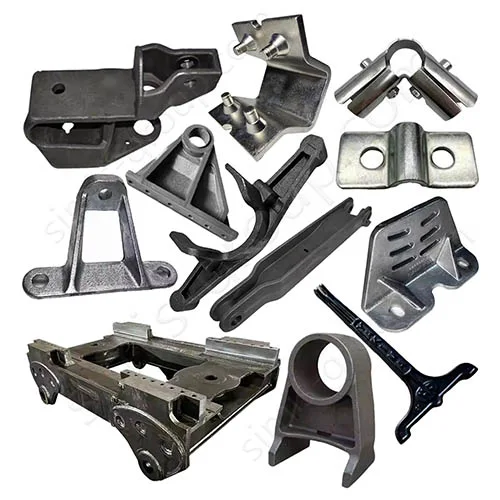
Castings: Track rollers, idler wheels, chassis frames
Forgings: Track shoes, drive wheels, pins and bushings
5. Lifting and load-bearing system
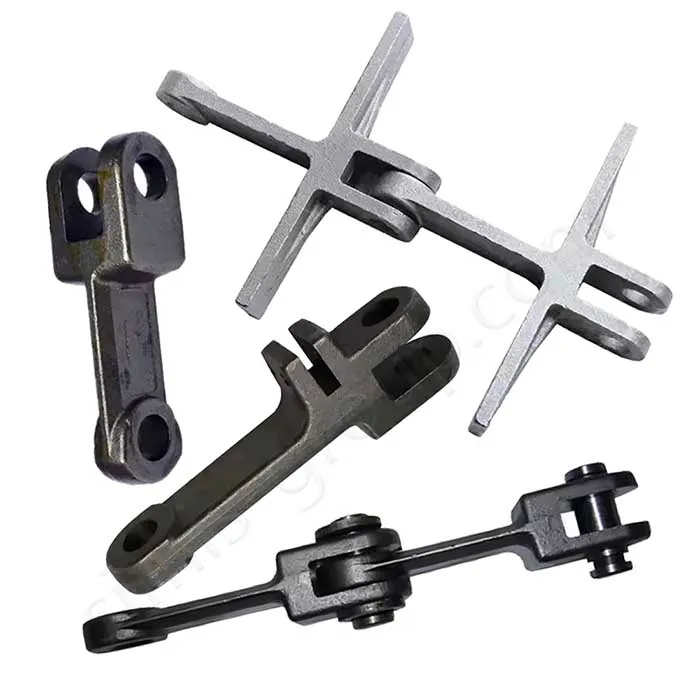
The lifting and load-bearing system moves and raises heavy objects. Castings mainly provide large bases and structural supports. Forgings are for key parts that handle dynamic loads, like hooks and pulley shafts.
Castings: Crane base, Pulley housing
Forgings: Hooks, Pulley shafts, Connecting pins
6. Braking and safety systems
The braking and safety system is key for running machines safely. Castings are mainly used for parts that resist wear, like brake discs and housings. Forgings are used for high-strength parts such as brake shafts and connecting rods.
Castings: Brake discs, Brake caliper brackets
Forgings: Brake shafts, Brake connecting rods, Brake calipers
7. Working devices and structural parts
Structural parts are the skeleton and frame of industrial machines. They support and hold other parts. Working devices touch the materials or workpieces directly. Castings make large frames and bases that need high stiffness and stability. They also make complex parts like buckets and booms for strong support. Forgings are used for high-load shafts and connectors. They also make parts that take high impact, like bucket teeth and pins.
Castings: Excavator buckets, Bucket arm articulation seats, Frames and bases
Forgings: Bucket teeth, Main arm pins, Main beam pins, Bucket arm pins, Flanges, Structural connecting shafts
Available Materials For Industrial Machinery Parts
Cast Iron in Industrial Machinery
Cast iron is used in industrial machines for frames, housings, and wear-resistant parts. Casting and processing create complex shapes and stable sizes.
Gray Cast Iron
Gray cast iron is sand-casted into machine tool beds, pump bodies, compressor housings, and bases. It absorbs vibration very well. This helps keep machining precise.
Gray Cast Iron Parts: Machine tool beds, Pump bodies, Compressor housings
Ductile Iron
Ductile iron is cast and heat-treated. It makes gearbox housings, couplings, and valve bodies. It is strong and tough. It can handle impact and fatigue loads.
Ductile Iron Parts: Gearbox housings, Couplings, Valve bodies, Heavy-duty support components
Alloy Cast Iron
Alloy cast iron is made stronger with alloying and heat treatment. It is used in wear-resistant bushings, guide rails, and mill liners. It fights wear and heat well. This fits high-temperature friction work.
Alloy Cast Iron Parts: Wear-resistant bushings, Guide rails, Mill liners
Steel in Industrial Machinery
Steel is used in power transfer, load-bearing, and safety parts of industrial machines. Casting, forging, stamping, welding, and machining ensure strength and precision.
Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is often forged into shafts, gears, cranks, and connecting rods. Machining ensures they fit precisely and transfer power reliably.
Carbon Steel Parts: Shafts, Gears, Cranks, Connecting rods
Low-Alloy Steel
Low-alloy steel makes high-strength frames, lifting arms, and crane supports. Welding and heat treatment make them last longer against fatigue.
Low-Alloy Steel Parts: High-strength frames, Lifting arms, Crane supports
Cast Steel
Cast steel is used for pump bodies, large valves, frames, and planetary reducer housings. After casting, machining ensures the parts fit together well.
Cast Steel Parts: Pump bodies, Large valves, Frames, Planetary reducer housings
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel fights rust very well. It is used in chemical valve bodies, food machine parts, piping, and fasteners. It is good for wet and corrosive places.
Stainless Steel Parts: Valve bodies for chemical equipment, Food processing machinery parts
Wear-Resistant Steel
Wear-resistant steel is used in hopper liners, conveyor scrapers, and crusher hammers. This makes the time between equipment fixes longer.
Wear-Resistant Steel Parts: Hopper liners, Conveyor scrapers, Crusher hammers
Aluminum Alloy in Industrial Machinery
Aluminum alloys are used in industrial machines for lightweight parts and cooling (heat dissipation). Complex parts are made using die-casting, extrusion, and machining.
Aluminum-Silicon Alloys
These alloys are die-cast into pump casings, compressor covers, and motor housings. They offer great heat transfer and make the parts light.
Aluminum-Silicon Alloys Parts: Pump casings, Compressor end covers, Motor housings
Aluminum-Magnesium Alloys
These alloys resist rust well. They are good for making transport casings, storage tanks, and brackets. This makes them last longer.
Aluminum-Magnesium Alloys Parts: Transportation equipment casings, Storage tanks, Brackets
High-Strength Aluminum Alloys
These alloys are treated and machined. They are used for robotic arms, positioning fixtures, and load beams. They reduce weight while staying rigid.
High-Strength Aluminum Alloys Parts: Robotic arms, Positioning fixtures, Load beams
Aluminum Extrusions
Extrusion makes these into production line frames, conveyor rails, and equipment brackets. They are easy to cut, assemble, and surface-treat.
Aluminum Extrusions Parts: Production line frames, Conveyor rails, Equipment brackets
Other Metal Alloys in Industrial Machinery
For special work conditions, industrial machines use other alloys. These meet needs for wear resistance, rust resistance, or electrical flow.
Copper and Copper Alloys
These alloys ensure good conductivity and lubrication. They are used in motor windings, conductive bars, slip rings, and wear-resistant bushings.
Bronze
Bronze fights wear well. It is used in worm gears, plain bearings, and bushings. This fits slow-speed, high-load work.
Brass
Brass is easy to cut. It is often used for valve bodies, fittings, and pipe connections. This makes assembly simple.
Nickel-Based Alloys
These alloys resist high heat and rust. They are used in chemical reactor linings and gas turbine parts.
Titanium Alloys
Titanium alloys are lightweight and resist rust. They are used in specialty pumps, seawater equipment, and air-related industrial machines.
How To Customize Industrial Machinery Parts
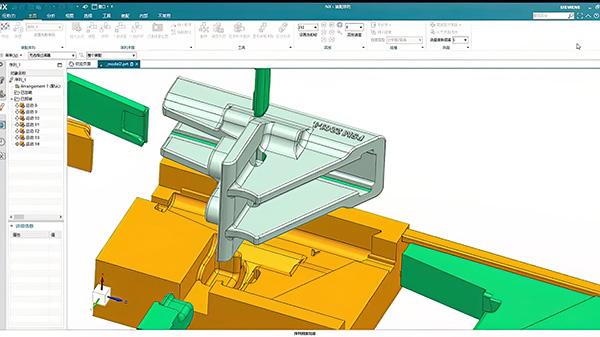
3D Drawing
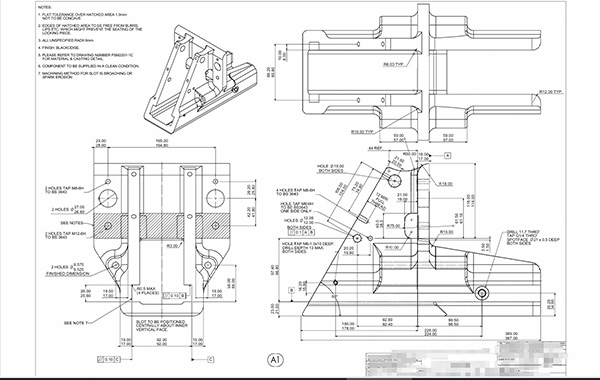
Processing Drawing

Sample
1. Provide Design Documents or Samples
2. Confirm Material, Process, and Performance
3. Make Production Molds and Samples
4. Comprehensive Sample Inspection
5. Mass Production
6. Post-Production Parts Multiple Quality Inspections
Custom Processing of Industrial Machinery Parts

Casting in Industrial Machinery
Casting processes make parts with complex shapes or large sizes in industrial machinery. This includes machine tool beds, engine blocks, and pump casings. Casting can quickly mass-produce complex structures. It also allows for flexible material choice to meet specific performance needs.

Forging in Industrial Machinery
Forging processes make highly stressed parts for industrial machines. This includes gears, shafts, and connecting rods. Forging ensures equipment is durable and reliable. This is vital when operating under heavy loads or extreme conditions. It keeps the machinery running efficiently and safely.
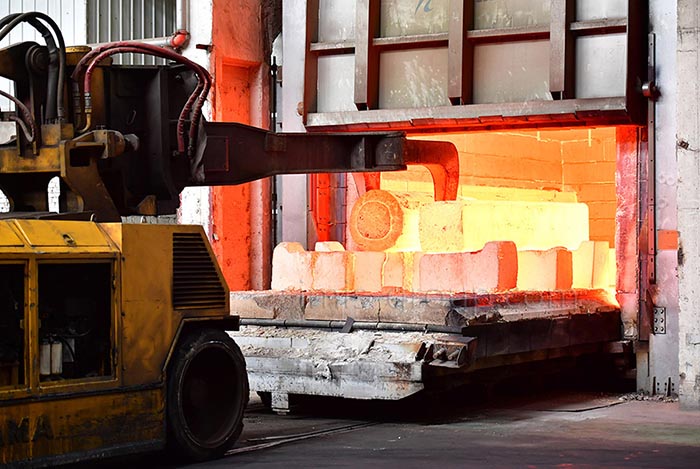

Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is used on parts like gears, shafts, and cutting tools in industrial machine making. It makes parts that face high stress or friction perform better and last longer. This ensures parts keep their operating efficiency and cuts down on maintenance needed for demanding applications.
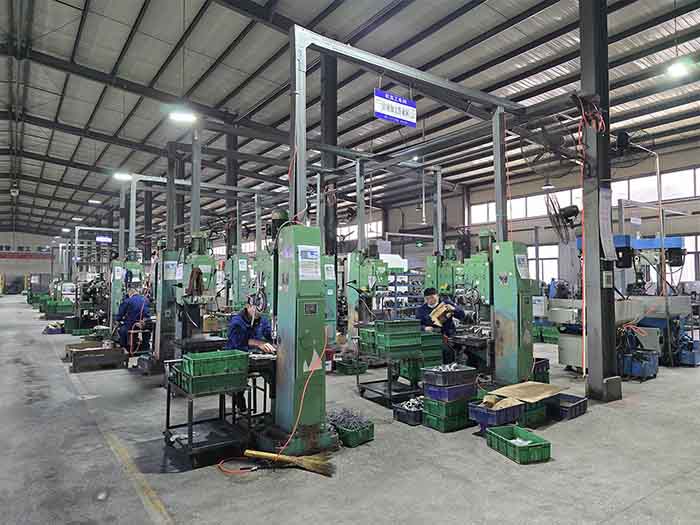

Machining in Industrial Machinery
Machining makes parts for industrial machines with tight tolerances. This includes turbine blades, molds, and precision gears. It achieves exact sizes and smooth surfaces. This ensures all parts fit together correctly. It makes the machinery run efficiently, reduces errors, and boosts operational reliability.

Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet metal fabrication makes lightweight but strong structural parts for industrial machines. This includes machine housings, frames, and brackets. These must handle pressure and harsh environments. This process makes complex shapes in a way that is cheap and flexible. It helps boost the machine's performance and structural integrity.

Surface Treatment
Surface treatment improves the outer layer of metal parts. This boosts the corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and durability of parts. Parts like gears, bearings, and hydraulic components are often treated. This protects them from environmental damage and makes them last longer. It ensures reliable performance and cuts down on maintenance time.