ISO Quality System Certification
China Simis Group operates under rigorous international quality standards. We hold the ISO 9001:2015 quality management system certification, complemented by globally recognized accreditations like CE, TÜV, and SGS.
This foundation allows us to implement strict production and quality control measures, ensuring every single casting and forging meets precise customer requirements. We further guarantee this commitment by providing comprehensive quality inspection reports. Simis products are, therefore, consistently high-quality and fully compliant worldwide.
Our rigorous quality management ensures the stability of all castings and forgings at every stage of production:
· Raw Materials: Initial inspection and verification.
· Process Monitoring: Continuous oversight of manufacturing operations.
· Final Product: Comprehensive performance verification.
This systematic approach guarantees that our products are safe and dependable across all designed operating environments.
Backed by international certifications and a comprehensive quality management system, Simis Group is dedicated to supplying high-standard, reliable castings and forgings to our global customers.

Quality Control Process
1.Raw material inspection
After determining the metal materials required for casting and forging, Simis will conduct chemical composition analysis, mechanical property testing, non-destructive testing, metallographic inspection, and physical property testing on the raw materials to be used for casting and forging to ensure that the metal materials used in the production process meet the design requirements, reduce production risks, and improve the overall quality of the product.
2.Appearance inspection
After the parts are produced, check the castings and forgings one by one to find out whether there are surface defects on the parts, such as cracks, pores, sand holes, sand marks, burrs, etc.
• Visual inspection: Check the surface of the castings and forgings for visible defects such as cracks, pores, and sand holes through manual visual inspection or using common magnifying tools such as magnifying glasses and microscopes.
• Surface finish: Check whether the surface of the castings and forgings meets the design requirements for finish, and avoid excess burrs or impurities on the surface.


3.Surface quality inspection
• Surface roughness inspection: Use a roughness meter to measure the surface of the castings and forgings to ensure that the surface roughness meets the design requirements of the parts.
• Coating and anti-corrosion layer inspection: For parts with special surface treatment (such as coating, electroplating, etc.), coating thickness, adhesion and other aspects need to be tested to ensure that the parts meet the technical requirements.
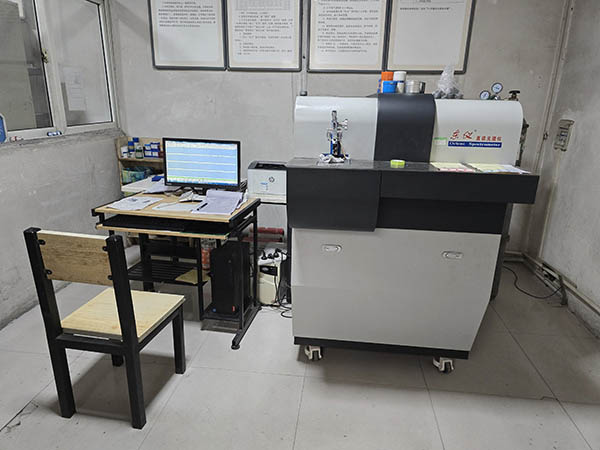
4.Chemical composition detection
• Spectral analysis: Use a spectrometer to analyze the chemical composition of the castings, measure the content of elements, and ensure that the parts meet the material requirements.
• Chemical analysis: Use chemical reagents and chemical analysis methods to determine the content of each element in the castings, such as silicon, manganese, copper, magnesium, etc.


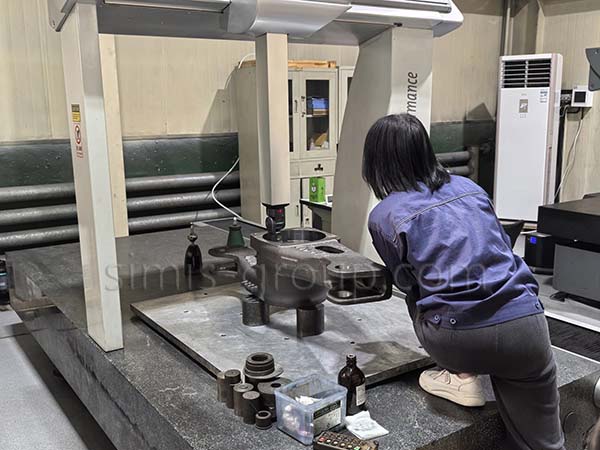
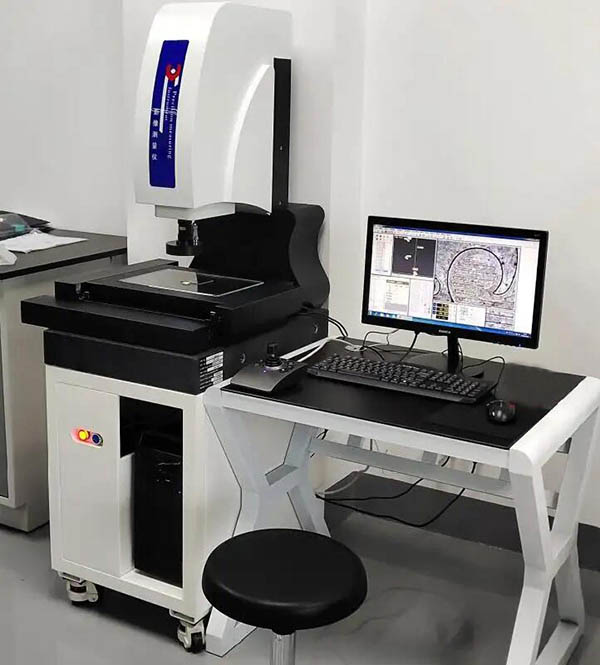
5.Size, shape and weight inspection
Use calipers, vernier calipers, micrometers, inner and outer diameter gauges and other measuring tools to sample and measure the various dimensions of castings to ensure that the castings and forgings meet the design tolerance requirements.
For high-precision castings, use a three-coordinate measuring machine to accurately measure the size, shape and position of castings and forgings in an all-round manner to ensure that the parts meet the requirements of the design drawings.
Check the geometric shape of the parts, including straightness, flatness, verticality, roundness, etc., to ensure that the parts meet the tolerance standards.
Use electronic balances, automated weight detection systems, weighing sensors and other weighing methods to determine whether the castings and forgings meet the part weight requirements by batch sampling and weighing.



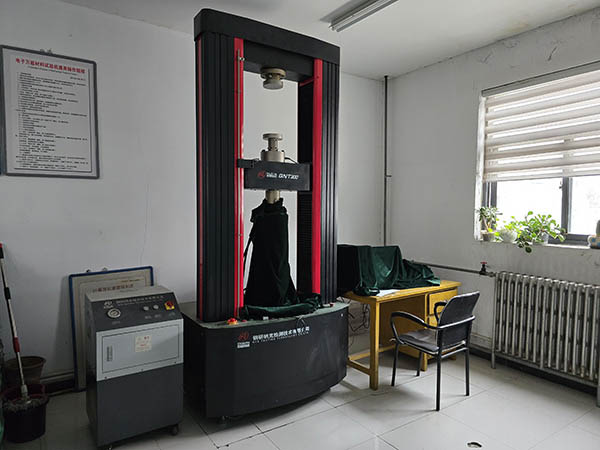
6.Mechanical properties testing
Use Rockwell hardness tester (Rockwell), Vickers hardness tester (Vickers), Brinell hardness tester (Brinell), etc. to measure the hardness of the parts to ensure that the hardness of the parts meets the design requirements.
Perform tensile test on casting and forging samples to measure their tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, etc., to verify whether the strength of the parts meets the design requirements.
Use an impact tester (such as Charpy impact tester) to measure the impact toughness of the parts and check their impact resistance, especially low-temperature impact performance.
Perform bending test on parts to measure their strength of fracture or yield during bending and evaluate their bending resistance.
Use a specific compression tester to determine the performance of parts under gradually increasing compression until they undergo plastic deformation or rupture.
Use a metallographic microscope to observe the metal structure of the casting to ensure that its structure meets the design requirements and avoid changes in the structure caused by excessive annealing or quenching.


7.Internal defect detection
Detect invisible defects such as pores, inclusions, cracks, etc. inside the parts. Suitable for castings with thick walls or complex structures.

Apply magnetic powder to the surface of the part and apply a magnetic field to find cracks and defects on the surface and near the surface of the part (applicable to ferromagnetic materials).
Detects defects inside parts by emitting high-frequency sound waves. It is used to detect internal defects such as pores and cracks. It is particularly suitable for parts with thicker or complex shapes.
Used to find tiny cracks or other defects on the surface of parts (commonly used for non-ferromagnetic materials such as aluminum alloys and copper alloys).
Detects defects inside castings through changes in the time and vibration of sound wave propagation. It is suitable for detecting defects such as cracks and voids.
8.Other special performance tests
• Sealing test: Use air tightness test, water tightness test, vacuum test and other sealing tests to detect whether the parts can effectively prevent the leakage of gas, liquid or other media during operation.
• Oxidation resistance test: Evaluate the oxidation resistance of parts in high temperature, humidity or exposure to air.
• Corrosion resistance test: evaluate the corrosion resistance of parts in chemical media (such as acid, alkali, salt water, etc.) or extreme environmental conditions.
• Environmental adaptability test: evaluate whether parts can maintain their structure and function in extreme environments (such as high temperature, low temperature, damp heat, ultraviolet radiation, etc.).
