The Importance of Forged Aluminum Process in Electric/Hybrid Vehicles and Auto Modification Fields
The global new energy vehicle industry’s rapid growth and the rising popularity of auto modification have elevated material selection to a make-or-break factor for vehicle performance, safety, and sustainability. Forged aluminum, a time-tested high-performance metal forming technology, has become irreplaceable in these fields due to its balanced advantages in lightweight, strength, and durability. As an forged aluminum parts manufacturer with years of experience in automotive material applications, I’ll break down forged aluminum’s importance, compare its performance with other metals, and explore its practical value—providing actionable insights for EV manufacturers and modification enthusiasts.
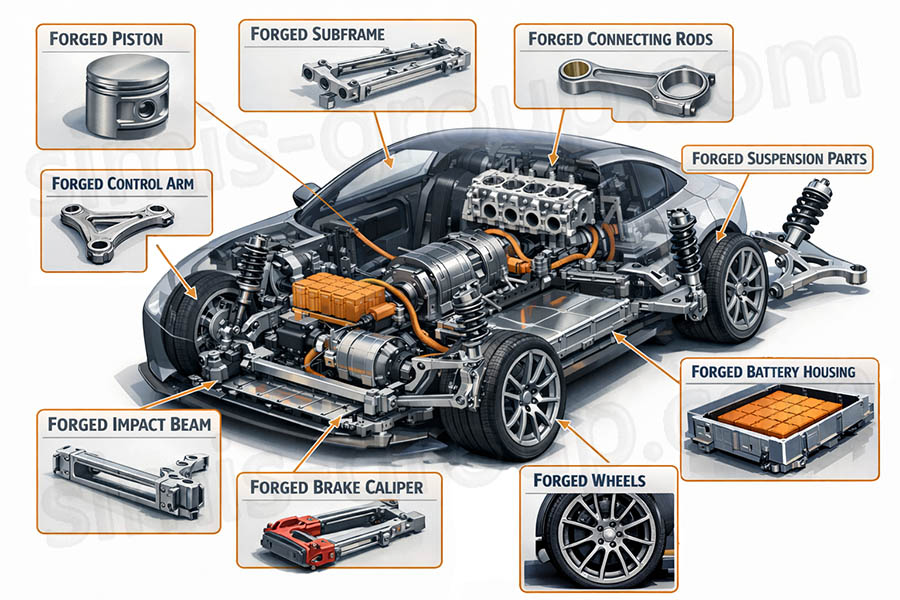
1. Why Is Forged Aluminum Indispensable for Hybrid Vehicles?
Forged aluminum is indispensable for hybrid vehicles primarily because it aligns with the three core demands of EV manufacturing: range extension, safety enhancement, and performance optimization. As the global EV market expands—with McKinsey projecting a sixfold growth from 6.5 million units in 2021 to 40 million by 2030—forged aluminum’s unique combination of lightweight, high strength, and excellent heat dissipation has made it a go-to material for key components, outperforming traditional metals in adapting to EV operational characteristics.
Aluminum’s density of 2.7 g/cm³—roughly one-third that of steel (7.85 g/cm³)—is the foundation of its lightweight advantage. For every 10% reduction in EV weight, we see a 5%-8% range boost in real-world applications. Tesla’s use of forged aluminum for battery cases and suspension components is a prime example: these parts cut over 120 kg from the vehicle’s curb weight compared to traditional steel, directly translating to longer per-charge range without compromising structural integrity.
·Forged aluminum materials enable lightweight designs and improve the driving range of hybrid vehicles
The weight of hybrid vehicles directly affects energy consumption and cruising range. Aluminum has a density of only 2.7 g/cm³, which is about 1/3 of steel (7.85 g/cm³). Forged aluminum components can significantly reduce the overall weight of the vehicle without sacrificing strength. Data shows that for every 10% reduction in the weight of an hybrid vehicle, its cruising range can be increased by 5%-8%. Taking Tesla as an example, the forged aluminum battery case and suspension components used in its models reduce the vehicle weight by more than 120 kg compared with traditional steel structures, effectively improving the range per charge.
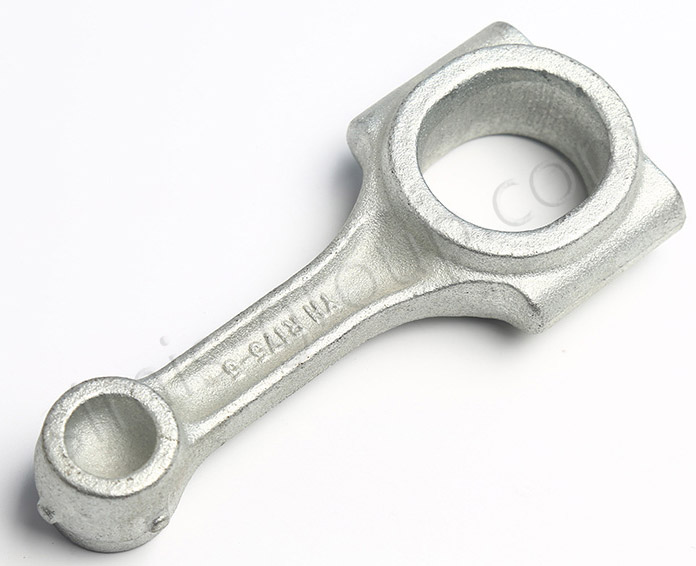

·Forged aluminum has good thermal conductivity and can be used in heat dissipation parts for core components of hybrid vehicles
Hybrid vehicle motors and battery packs generate a lot of heat during operation, and efficient heat dissipation is crucial to ensuring operational stability and extending component life. The thermal conductivity of forged aluminum is about 200 W/(m·K), which is 3-4 times that of steel. Forged aluminum cooling systems and motor housings can quickly transfer heat, maintaining the optimal working temperature of the battery pack at 25°C-40°C and reducing the risk of thermal runaway. Statistics show that hybrid vehicles using forged aluminum heat dissipation components have a 15%-20% longer battery cycle life than those using traditional materials.
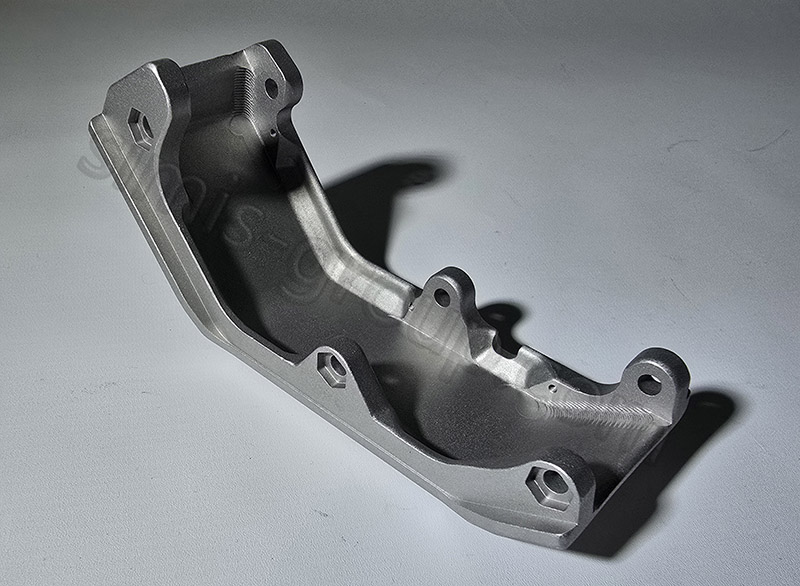

·Forged aluminum alloys possess high strength and durability, ensuring the safety of hybrid vehicles
The forging process compresses metal internally, eliminating pores and defects, and forming a regular grain structure that follows the component shape, which significantly enhances the material's strength and impact resistance. The yield strength of high-performance forged aluminum alloys (such as 7075 series) can reach 500-540 MPa, which is comparable to that of ordinary carbon steel, while the weight is only 1/3. This makes forged aluminum ideal for key safety components such as hybrid vehicle wheel rims, suspension control arms, and drive shafts, which can withstand high torque and impact loads during driving.
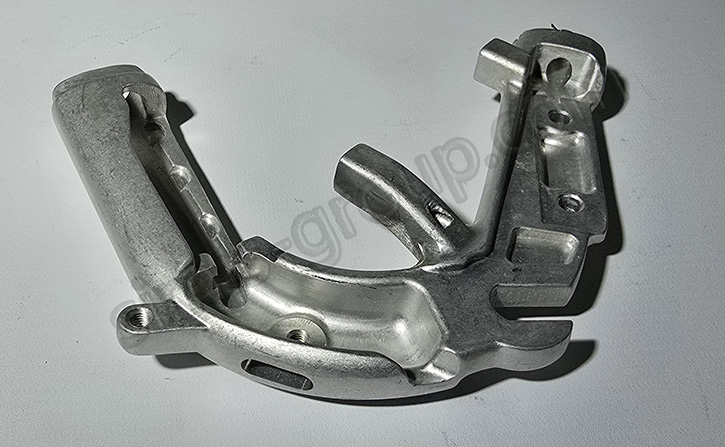

2. What Is the Application Value of Forged Aluminum in Auto Modification?
In auto modification, forged aluminum delivers significant value by meeting enthusiasts’ pursuit of extreme performance and personalized styling. Its superior strength-to-weight ratio, impact resistance, and formability make it ideal for upgrading core components—especially in suspension, wheel rims, and engine systems—where performance gains and durability are non-negotiable, and it has become a staple in high-end modification projects for both combustion and hybrid vehicles.
Its most common applications fall into three key areas, where performance and durability are paramount for both street and off-road modified vehicles.
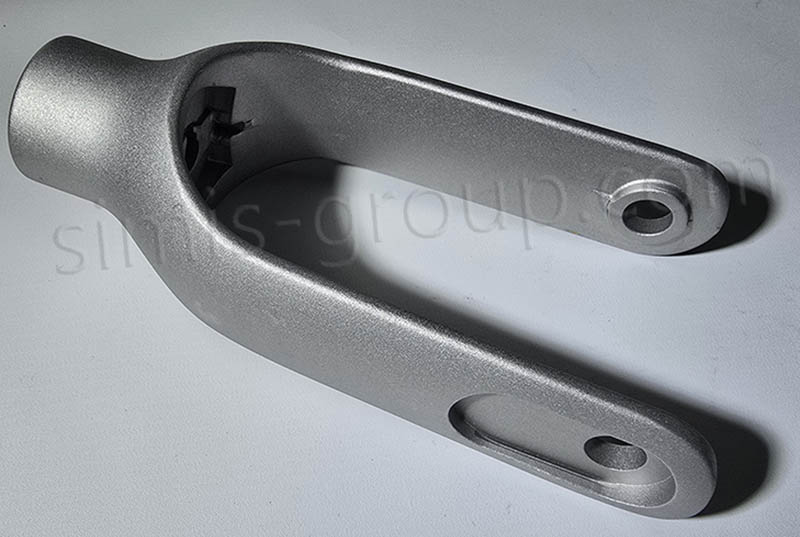
·Forged aluminum can be used to manufacture suspension components for modified vehicles
Suspension components are critical to vehicle handling and stability. In the modification of off-road vehicles such as the Tank 300, forged aluminum upper control arms have become a popular choice. Compared with the original steel control arms, forged aluminum products have a 40%-50% weight reduction, reducing unsprung mass, improving suspension response speed, and solving problems such as tire wear and deviation caused by suspension lifting. The 7075 forged aluminum upper control arm has a tensile strength of up to 570 MPa, which is far higher than that of ordinary steel, and can withstand the impact of extreme off-road conditions.

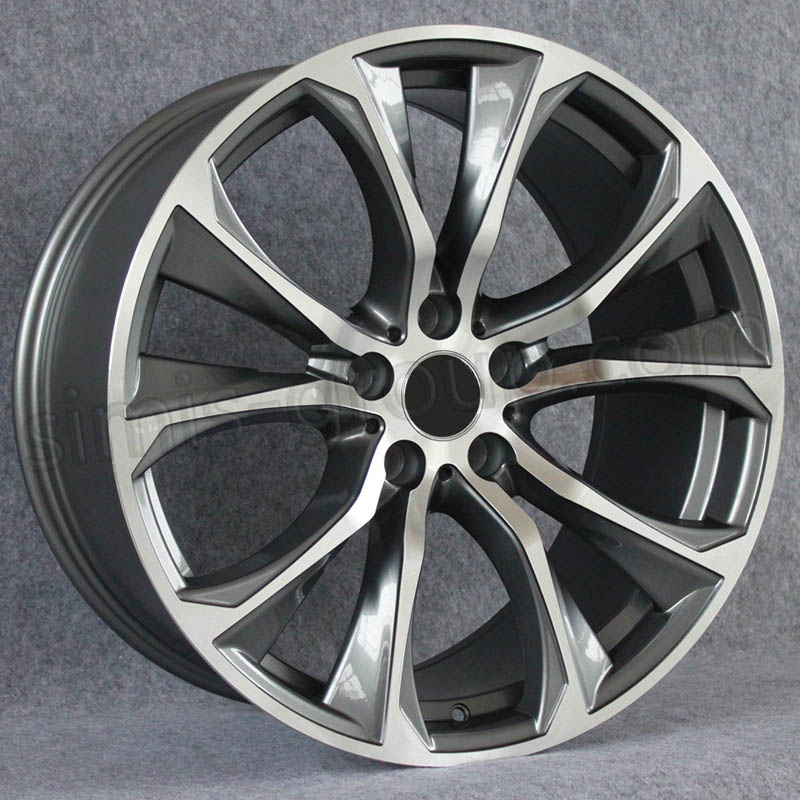
·Forged aluminum alloys can be used to manufacture high-end aftermarket wheels
Wheel rims are one of the most common modified components, and forged aluminum rims have become the first choice for high-end modifications. Compared with cast aluminum rims, forged aluminum rims have a 20%-30% weight reduction, and their impact resistance is increased by more than 50%. For example, a 20-inch forged aluminum rim weighs about 8-10 kg, while a cast aluminum rim of the same size weighs 12-15 kg. The lighter weight reduces rotational inertia, improving the vehicle's acceleration, braking performance, and fuel economy. In addition, the dense structure of forged aluminum makes the rim more resistant to deformation and corrosion, adapting to harsh driving environments.

·Forged aluminum can be used to manufacture modified engine parts and gearbox components
In performance modification, forged aluminum engine components (such as cylinder heads and connecting rods) can reduce inertial resistance, improve engine response speed, and enhance power output. The thermal conductivity of forged aluminum helps to dissipate heat from the engine cylinder head, reducing the risk of overheating during high-load operation. For modified hybrid vehicles, forged aluminum transmission housings can withstand higher torque while reducing weight, matching the performance of upgraded motors.

3. How Does Forged Aluminum Compare to Forged Steel, Cast Steel, and Cast Aluminum in Performance?
Forged aluminum outperforms forged steel, cast steel, and cast aluminum in key performance metrics critical to EVs and auto modification, particularly in strength-to-weight ratio and heat dissipation. Below is a detailed comparison of core physical and mechanical properties, which clarifies why forged aluminum is preferred for specific scenarios while highlighting the niche advantages of other materials.
We’ve compiled core physical and mechanical properties below, with data aligned to industry testing standards (ASTM B209 for aluminum alloys, GB/T 700 for Q235 steel), to illustrate how each material performs in EV and modification scenarios.
Performance Indicato | Forged Aluminum (7075 Series) | Forged Steel (Q235 | Cast Steel (ZG230-450) | Cast Aluminum (A356) |
Density (g/cm³) | 2.8 | 7.85 | 7.82 | 2.7 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 500-540 | 235 | 230 | ≥175 |
Tensile Strength (MPa) | 570-600 | 375-500 | 450 | ≥290 |
Thermal Conductivity (W/(m·K)) | 180-200 | 45-50 | 40-45 | 150-170 |
Elongation (% | 8-10 | 21-2 | 16-20 | 5-8 |
Cost (Relative Value) | 1.8-2.2 | 1.0 | 1.1-1.3 | 1.2-1.5 |
What are the differences between forged aluminum and forged steel, cast steel, and cast aluminum in hybrid vehicles and vehicle modification applications?
·Forged Aluminum vs. Forged Steel:
Forged steel offers excellent toughness and low cost but is 2.8 times denser than forged aluminum, adding unnecessary weight to EVs and blunting modification performance gains. We limit forged steel to heavy-duty components like drive shafts; forged aluminum is the clear choice for suspension, wheel rims, and battery cases, where lightweighting directly improves efficiency and handling.
·Forged Aluminum vs. Cast Steel:
Cast steel excels at complex shapes but has internal pores and lower precision, with tensile strength 30%-40% below forged aluminum. It’s rarely specified for EVs or high-end modifications—forged aluminum’s consistent density and strength make it the go-to for safety-critical parts.
·Forged Aluminum vs. Cast Aluminum:
Cast aluminum is more cost-effective for mass-produced complex parts but has irregular grain structure, poor impact resistance, and half the tensile strength of forged aluminum. We use cast aluminum for non-critical decorative components; forged aluminum is reserved for suspension, wheel rims, and other performance-focused parts in EVs and modifications.
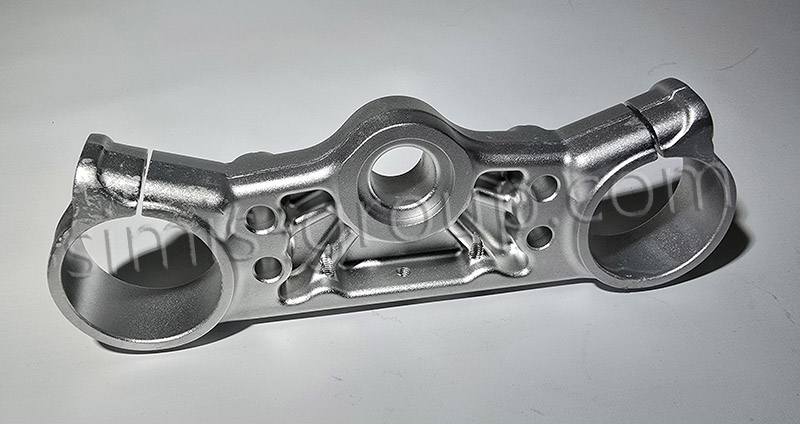

4. Which Forged Aluminum Manufacturer Is Reliable for EV and Modification Needs?
For EV and auto modification projects requiring high-quality forged aluminum components, SIMIS Group stands out as a reliable partner. With years of hands-on experience in casting and forging, the group has refined its forged aluminum capabilities to meet the strict performance and consistency requirements of these fields, backed by standardized production processes and quality control systems.
SIMIS Group’s subsidiary, Shanxi KSN Precision Forging Technology Development Co., Ltd., specializes in forged aluminum processes tailored to EV and modification needs, covering open die forging, closed die forging, and ring rolling. Equipped with high-capacity presses and complete inspection equipment, we process 6061, 7075, and other core alloys, handling both small-batch custom orders and large-volume production. Adhering to ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 standards, we control every step from raw material selection to delivery—validating material composition, monitoring forging parameters, and conducting non-destructive testing—to ensure parts meet load-bearing, heat dissipation, and durability requirements. Our track record in supplying automotive and new energy sectors reflects our ability to balance quality, cost, and on-time delivery for both standard and custom projects.
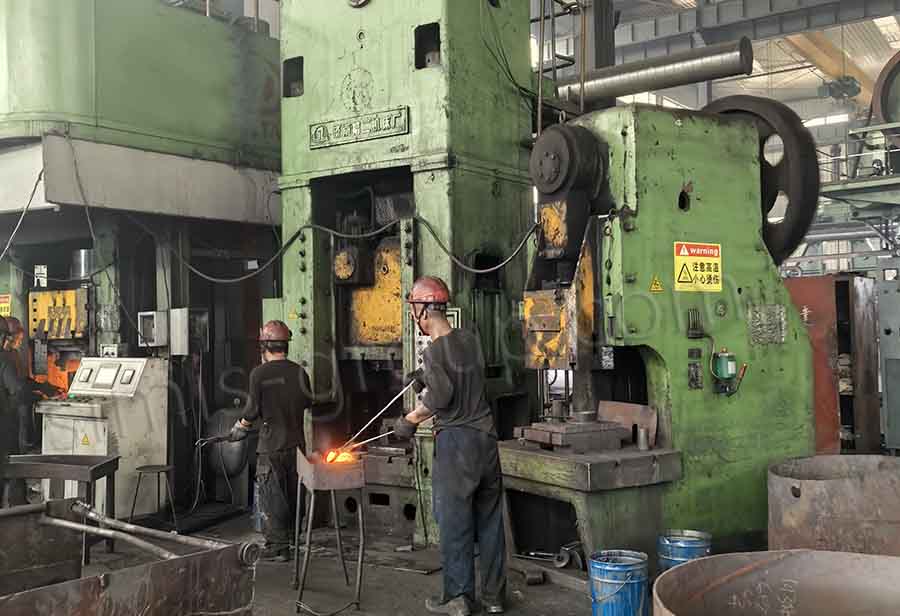

5. What Are the Key Process Steps of Forged Aluminum?
The forged aluminum process consists of six standardized, precision-controlled steps designed to eliminate material defects, refine grain structure, and ensure consistent mechanical properties. Each step is critical to maintaining the material’s performance advantages, and strict parameter control is required to avoid compromising strength or dimensional accuracy.
(1). Raw Material Preparation:
Select high-quality aluminum alloy billets (6061, 7075 series are most common for EV and modification parts) and cut them into cylindrical blanks of precise weight and size. We inspect blanks for impurities and uniform chemical composition—critical for avoiding forging defects later in the process.
(2). Heating Treatment:
Heat blanks to 400°C-500°C, a range that softens the aluminum without degrading its molecular structure. Overheating loosens grain structure, while underheating increases deformation resistance, so we monitor temperature with precision thermocouples throughout.
(3). Multi-Stage Forging:
Use 3000-9000 ton presses (scaled to component size) for step-by-step forming. Typically, we use three stages: first forming the blank into a cake shape, then refining details like spokes or flanges with dedicated dies. This gradual approach ensures uniform metal flow and prevents tearing.
(4). Shaping and Trimming:
For annular parts like wheel rims, cold rolling (near room temperature) finalizes the shape while preserving grain density. We then trim excess flash from forging to meet initial dimensional tolerances.
(5). Heat Treatment:
Anneal components to eliminate residual internal stress from forging and trimming—this prevents post-installation deformation and improves toughness. The result is a part with consistent, long-lasting mechanical properties.
(6). Precision Machining and Inspection:
Finish parts with CNC machining to hit tight tolerances, then conduct multi-stage inspections: visual checks, dimensional measurement, and ultrasonic testing to detect internal defects. Only parts meeting industry standards (ISO 9001, IATF 16949) move to delivery.
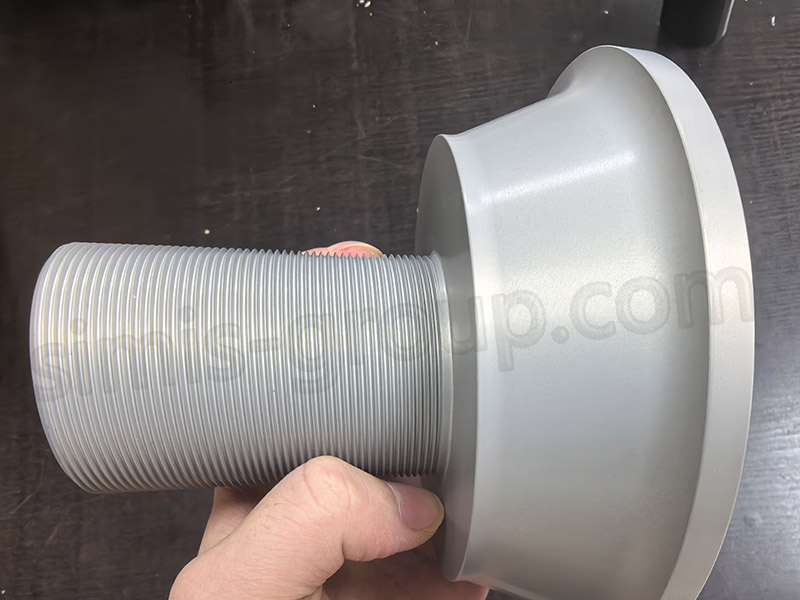

6. What Is the Process for Custom Forged Aluminum Components?
The custom forged aluminum component process follows a streamlined, engineer-led workflow to translate customer requirements into high-precision parts, with rigorous validation at each stage to ensure alignment with application needs. This process balances efficiency and accuracy, making it suitable for both EV and modification projects with unique specifications.
(1). Needs Communication:
Our technical team collaborates directly with customers to define core requirements: component use case (EV, off-road modification, etc.), performance targets (strength, weight limits), dimensional tolerances, and batch size. We also advise on alloy suitability—for example, 7075 for high-strength suspension parts, 6061 for balanced heat dissipation and formability.
(2). Design and Scheme Formulation:
Using customer 2D/3D drawings, we design forging dies and process plans, leveraging metal flow simulation to optimize die geometry and avoid forming defects. The final scheme includes alloy recommendations, process parameters, and a clear delivery timeline.
(3). Prototype Production and Testing:
We produce small-batch prototypes using the finalized process, conducting tensile, yield, and dimensional tests to validate performance. We adjust process parameters iteratively until the prototype meets all specifications—this step is non-negotiable for custom parts.
(4). Mass Production:
Post-prototype approval, we launch mass production, monitoring heating temperature, forging pressure, and heat treatment in real time. Full-process inspection ensures consistency across every unit, with no deviations from the validated prototype.
(5). Finished Product Delivery and After-Sales Service:
After precision machining and final inspection, parts are delivered on schedule. We provide on-site installation guidance and technical support to resolve any application issues, ensuring long-term reliability in real-world use.
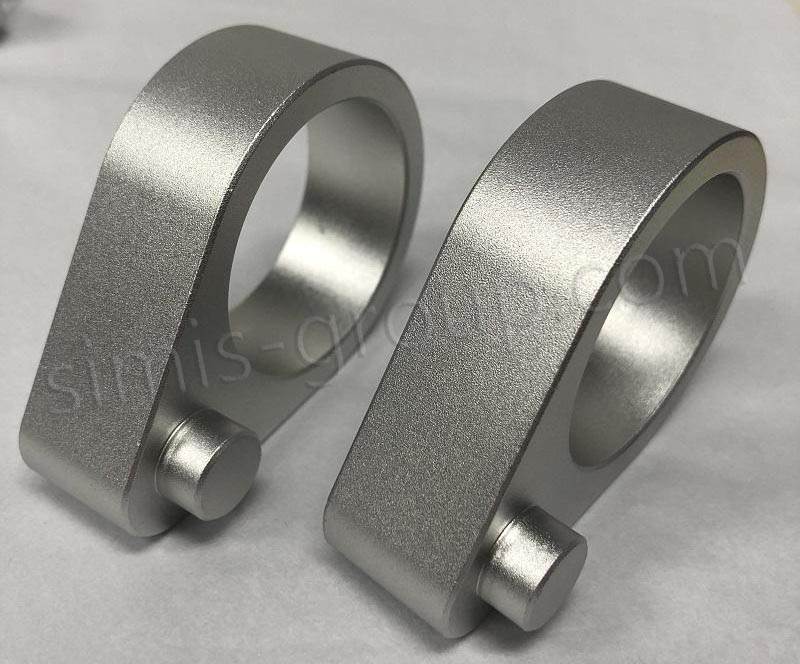

7. How to Obtain a Quotation for Custom Forged Aluminum Components?
Obtaining an accurate quotation for custom forged aluminum components requires clear, detailed information about the part and its application, as this allows our team to assess process complexity, material costs, and production cycles. The quotation process is transparent and collaborative, designed to align with engineering project timelines.
(1). Prepare Detailed Information:
Share 2D/3D drawings (with dimensional tolerances), specified aluminum alloy (or performance targets if unsure), batch size (custom small-batch or mass production), and use scenario (e.g., EV battery case, modified suspension arm). The more detailed the specs, the more accurate our quotation—vague requirements can lead to costly revisions later.
(2). Contact Forged Aluminum Parts Manufacturer (China SIMIS Group):
Reach out via our official website, email, or sales hotline, clearly stating your custom forged aluminum needs and submitting the prepared documentation. Our team prioritizes technical clarity in initial communications.
(3). Technical Evaluation:
Our engineers assess process difficulty, die development costs, material consumption, and production lead times. This evaluation is data-driven, based on our experience with similar EV and modification parts.
(4). Quotation Confirmation and Negotiation:
We issue a formal quotation with unit price, total cost, delivery cycle, and payment terms. We’re flexible on batch discounts and timeline adjustments to align with your project schedule, finalizing terms once all details are agreed upon.
(5). Sample Confirmation (Optional):
If quality verification is required before mass production, we include sample production costs and lead times in the quotation. Final cooperation is confirmed only after you approve the sample’s performance and dimensions.
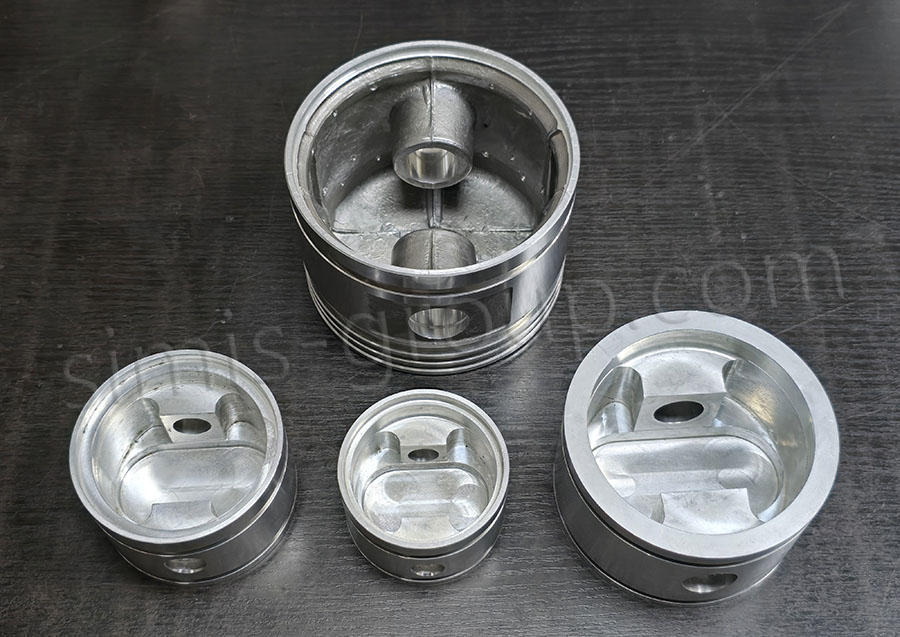

8. Future Development of Forged Aluminum Technology
The forged aluminum process is evolving to meet the growing demands of EV and modification industries, with advancements focusing on higher strength, lower production costs, and more complex forming capabilities. These trends are driven by material innovation and process optimization, expanding the material’s application scope.
Material innovation is breaking traditional trade-offs: Tesla’s new forged aluminum alloy achieves 90-150 MPa yield strength and 40%-60% IACS conductivity, resolving the historic conflict between strength and hybridal conductivity—a game-changer for EV motor and battery components. In modifications, one-piece integrated forged aluminum parts (like single-piece suspension arms) are gaining adoption, as they simplify assembly and boost structural rigidity compared to multi-part steel alternatives. Additionally, aluminum’s recyclability enhances its environmental value: recycling aluminum consumes only 5% of the energy required for primary production, aligning with the EV industry’s sustainability goals. As forging technology matures and economies of scale kick in, forged aluminum costs will continue to decline, opening up broader applications in mid-range EVs and modification projects.
As the EV market expands and modification standards become more rigorous, forged aluminum’s role will only grow. Its ability to adapt to new alloy developments and process optimizations—while maintaining sustainability through high recyclability—positions it as a long-term core technology for the automotive industry’s shift to efficiency and performance.
As the new energy vehicle market grows and auto modification culture matures, forged aluminum will play an even more pivotal role. Its ongoing evolution—toward higher performance, lower costs, and greener production—will further solidify its position, driving the automotive industry’s transition to more efficient, safe, and sustainable solutions.