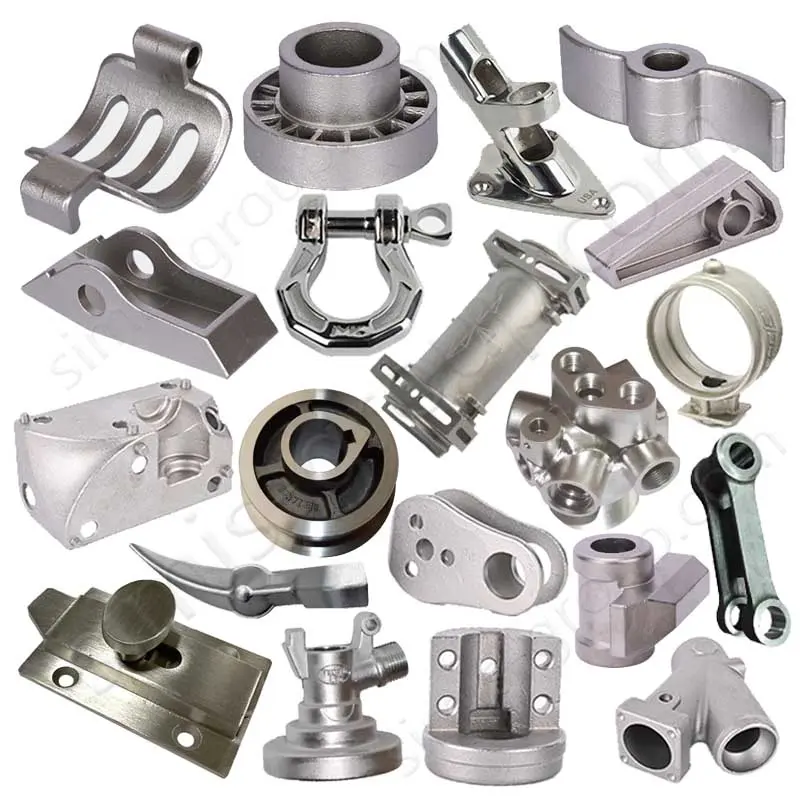
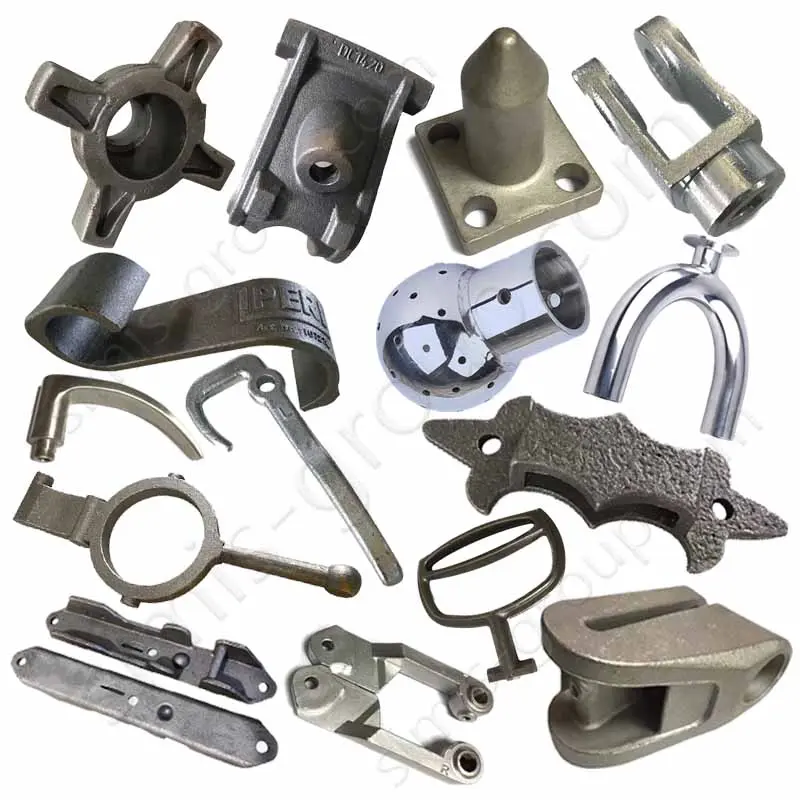
Investment Casting VS Lost Foam Casting
Investment casting and lost foam casting are two common precision casting technologies. Both belong to the category of precision casting and use disappearing mold materials to form the cavity of the casting, but they have significant differences in process, scope of application and cost. Below, Simis casting engineers will conduct a detailed comparative analysis of investment casting and lost foam casting.
1. Differences in process production principles
Investment casting:
also known as precision casting or lost wax casting, using fusible materials (such as wax) to make the shape of the casting, coating the surface of the wax mold with multiple layers of refractory ceramic shells to form a shell layer, and then high-temperature roasting to melt the wax mold to form a cavity, and then pouring metal.
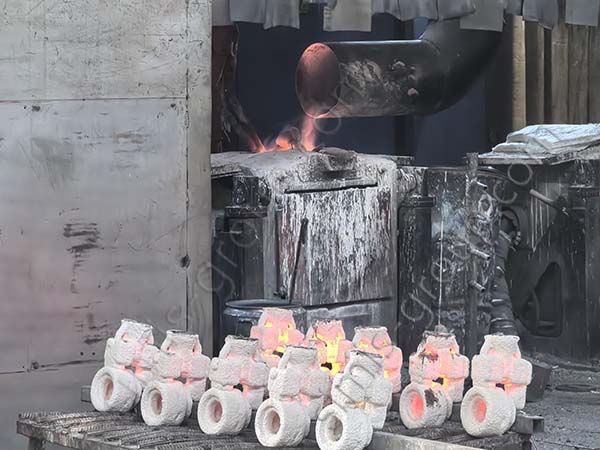

Lost foam casting (LFC):
Use expandable polystyrene (EPS) or other degradable materials (STMMA) to make casting molds, coat the outside of the mold with refractory materials to form a shell, and directly bury the foam mold in the sand mold. When pouring, the foam is heated and vaporized and disappears, and the metal fills the cavity.

2. Comparison of various aspects of investment casting and lost foam casting
| Process | Investment casting | Lost foam casting |
| Model materials | Wax or similar materials (such as resin wax) | Foam plastic (EPS or STMMA) |
| Casting precision and surface quality | High surface finish (Ra 3.2-6.3 μm) | Low surface finish (Ra 12.5-25 μm) |
| Applicable materials | Suitable for high melting point and high value-added materials such as stainless steel, alloy steel, high temperature alloy, titanium alloy. | Suitable for cast iron, cast steel, aluminum alloy and other materials. |
| Production efficiency | The production cycle is long, and the processes such as shell making, dewaxing and roasting are time-consuming. | The production cycle is short, and no shell making and dewaxing are required. |
| Cost comparison | High mold cost and high material cost (wax, ceramic slurry). | Low mold cost and low material cost (foam plastic). |
| Scope of application | Suitable for small parts with high precision, high added value and complex shapes in small batches. | Suitable for mass production of medium to large castings with low cost and medium shape complexity. |
| Advantages and disadvantages | Advantages: high precision, good surface quality, suitable for complex shapes. Disadvantages: high cost, long production cycle, complex process. | Advantages: low cost, short production cycle, suitable for mass production. Disadvantages: low precision, poor surface quality, not suitable for high melting point materials. |
3. Conclusion
Investment casting and lost foam casting have their own advantages and disadvantages, and are suitable for different application scenarios. Investment casting is suitable for the production of high-precision, small and complex parts. Although the cost is high, it can ensure good surface quality and dimensional accuracy. Lost foam casting is more suitable for large-sized and complex castings, with low production costs and suitable for mass production. When choosing a casting process, customers should comprehensively consider factors such as casting requirements, production costs, and manufacturing cycles to select the best casting solution.